The first multidecadal, satellite-based study of Latin America’s most active volcanoes could help researchers better predict eruptions.
CC BY-NC-ND 2019
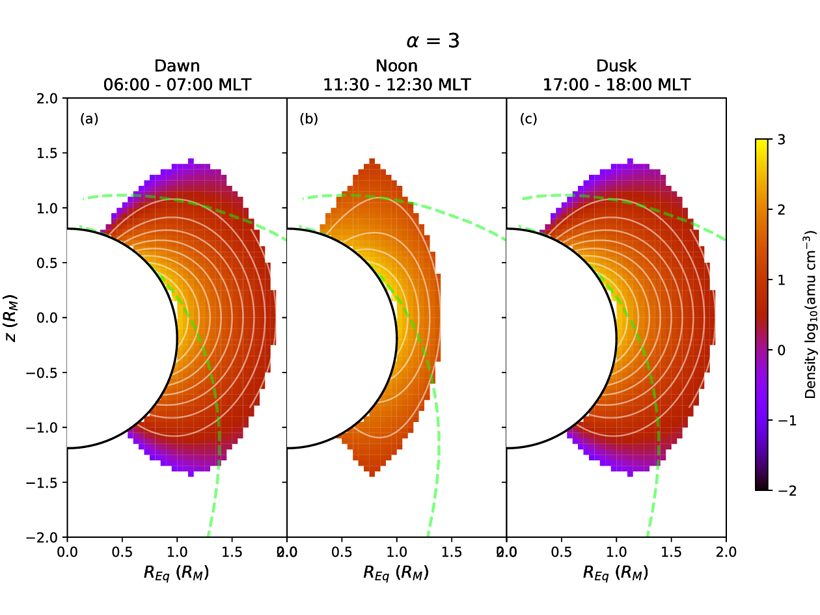
Plasma Density Distribution in Mercury’s Magnetosphere
A new measurement of plasma density distribution in Mercury’s magnetosphere obtained from observations of field line resonance events provides necessary constraint for many planetary science issues.
Three Decades of Atmospheric Optics Research in Camagüey, Cuba
Workshop for Thirtieth Anniversary of the Grupo de Óptica Atmosférica de Camagüey; Camagüey, Cuba, 23–26 October 2018
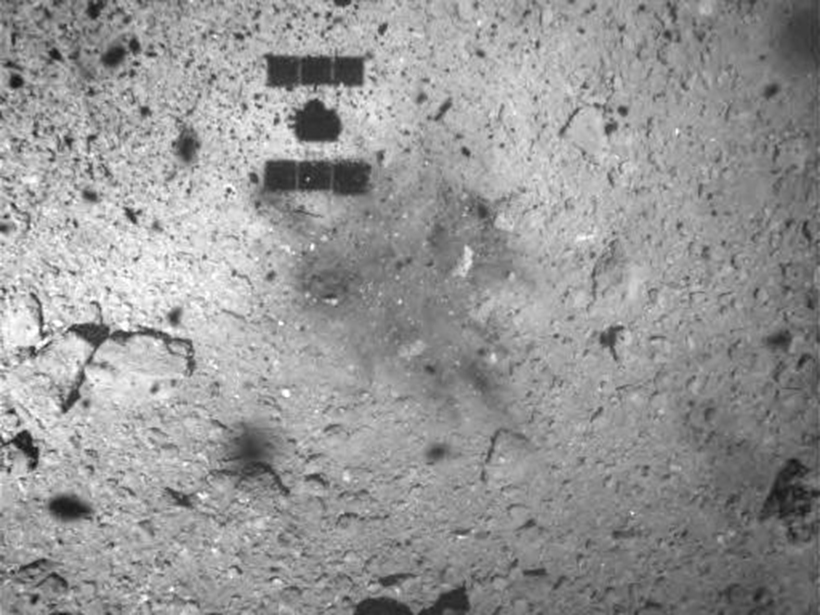
A Target Before Shooting Ryugu
The asteroid’s rough surface surprised Hayabusa2’s mission scientists. So they pulled out their spare gun and shot an “asteroid” at home first.
Varying Impact of Earthquake- and Monsoon-Induced Landslides
Using nearly 50 years of satellite data and records stretching back millennia, scientists determine the relative frequency—and the erosional power—of monsoon- and earthquake-induced landslides in Nepal.
Extending the Record of Surface Melt on the Larsen C Ice Shelf
The first use of Advanced Scatterometer radar data to determine melt duration on an Antarctic ice shelf shows the season has decreased by up to 2 days per year during the extended 21st century record.
Assessing the Benefits of Improved Space Weather Forecasting
A new framework assesses the economic impact of space weather on power distribution networks and the supply of electricity.
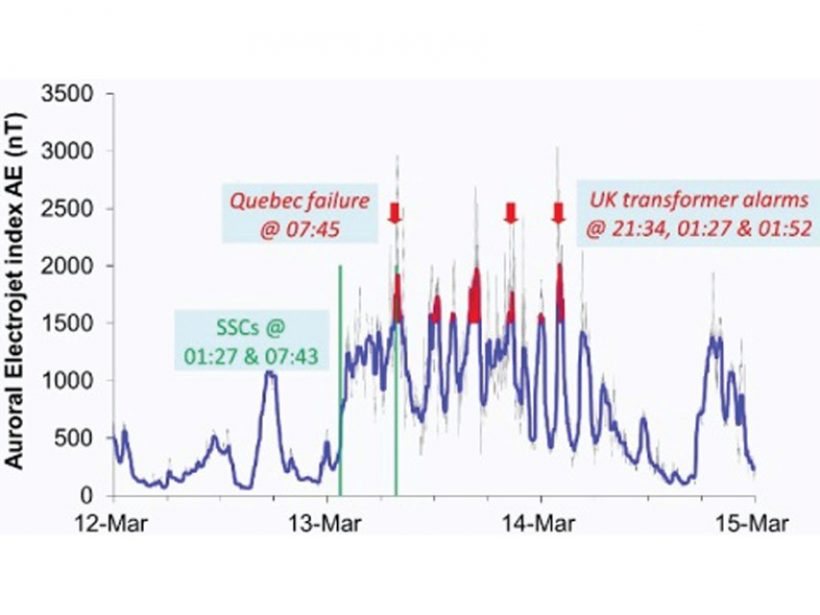
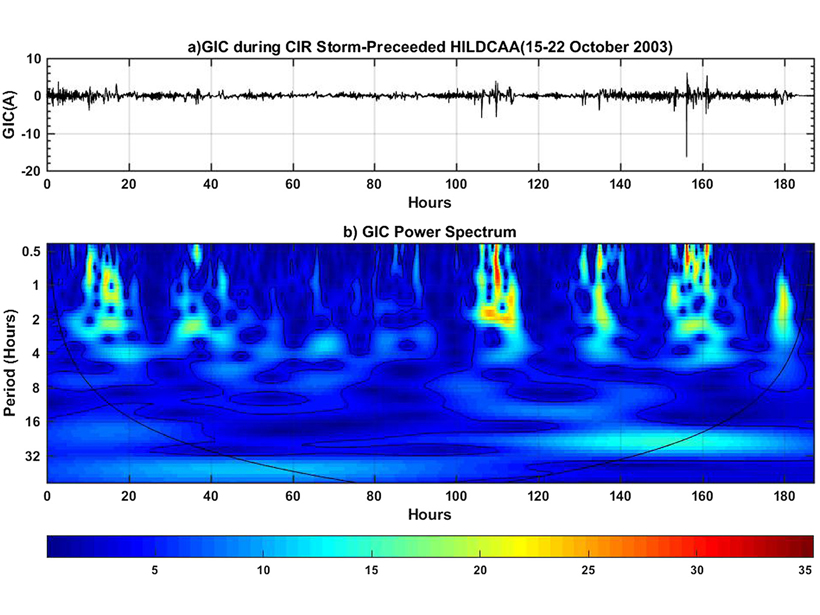
Can Moderate Space Weather Have Major Impacts?
Pipeline corrosion is an example of why we need better awareness of how long-term exposure to moderate space weather may have significant economic impact by slowly degrading vulnerable systems.
Humming Ice Shelf Changes Its Seismic Tune with the Weather
Seismic waves resonating within the upper layers of the Ross ice shelf could help scientists monitor the Antarctic melt season and understand factors that could lead to sudden ice shelf collapse.
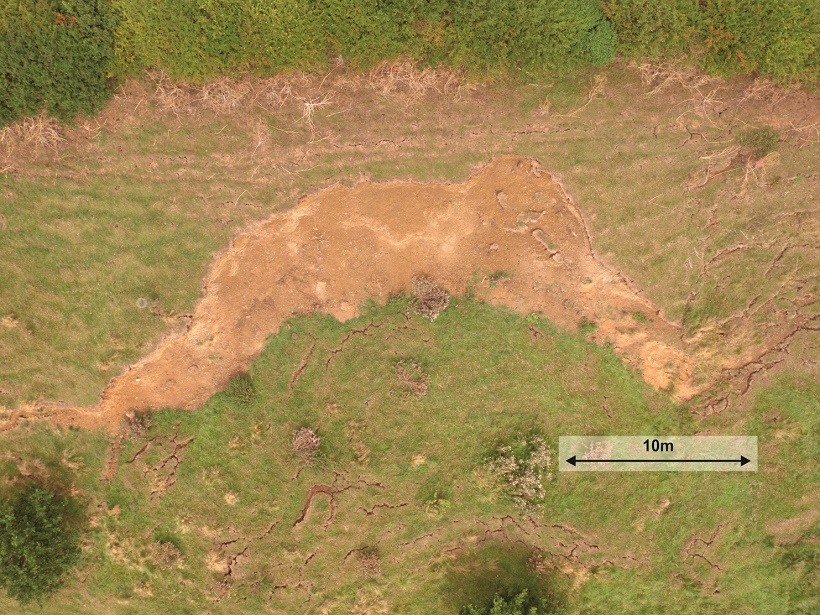
Downhill All The Way: Monitoring Landslides Using Geophysics
Developments in geophysical methods used to monitor surface and subsurface changes prior to landslides can lead to improved prediction and early warning.