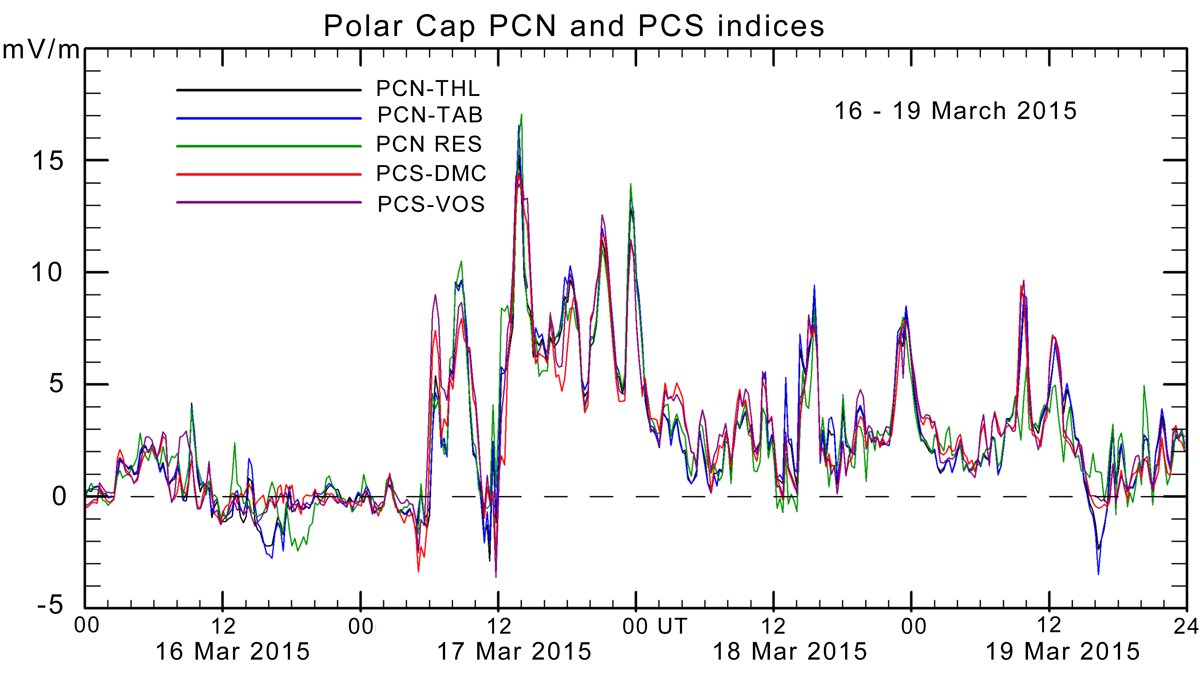
Updated procedures enable consistent use of a wide network of polar magnetometers to monitor energy flow into the tail of Earth’s magnetosphere during the growth phase of substorms.
Michael A. Hapgood
Editor, Space Weather
Can Aurora Enhance Radar Monitoring of Arctic Aviation?
Enhanced E-region ionization produced by the aurora can be used to reflect signals from over-the-horizon radars and thus enable those radars to better monitor aviation in Arctic regions.
Looking Down to See Upwards
Hydrological observations of cosmic ray neutrons scattered by water in soil can also provide information on space weather events such as Forbush decreases and ground level enhancements.
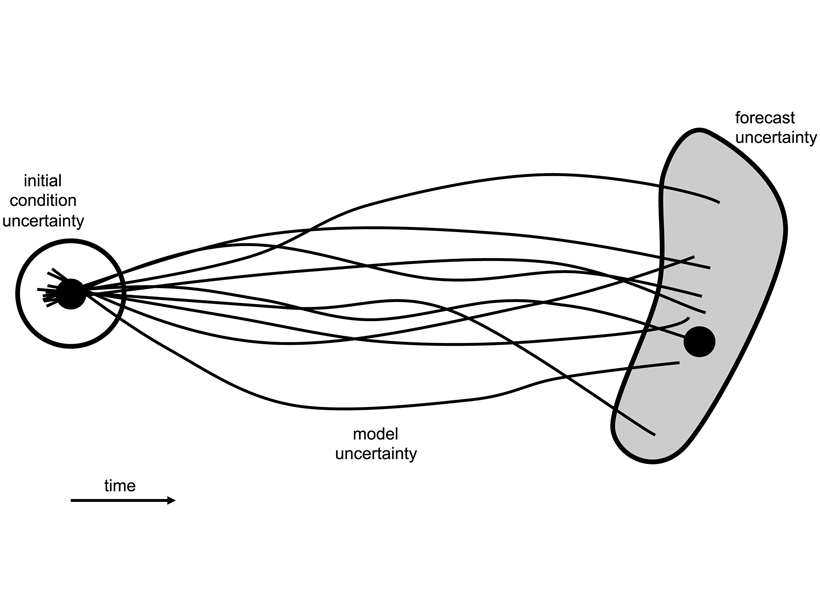
How to Assess the Quality of Space Weather Forecasts?
The assessment of space weather event forecasts would benefit from more nuanced approaches that take account of event intensities peaking near the thresholds used to identify such events.
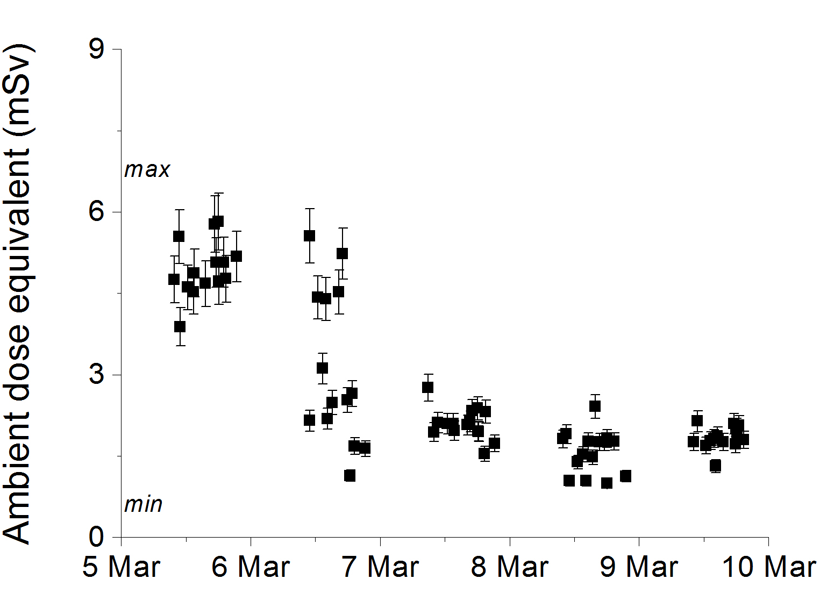
Severe Radiation Storms Pose Health Risk to Air Travel
Simulations of radiation storm fluxes on real flight paths highlight how severe space weather could expose aircrew and passengers on busy transatlantic routes to significant radiation doses.
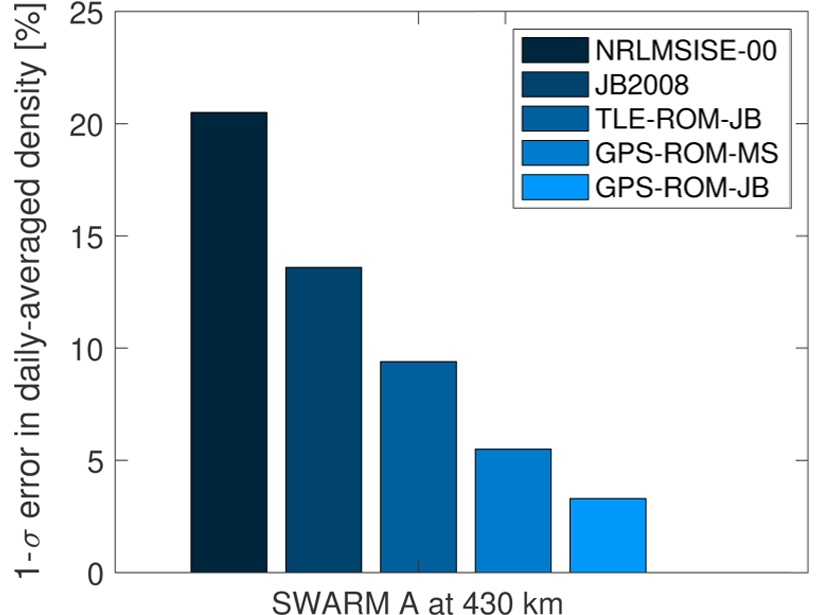
Better Thermospheric Monitoring is Vital to Space Safety
Better real-time estimates of thermospheric density are vital to the safe management of satellite traffic in Low Earth orbit, ensuring those satellites continue to deliver critical services.
Observing the Sun via Soil Moisture Measurements
Solar radio bursts are background noise for satellite-based radio observations that monitor soil moisture, so, with appropriate processing, those observations can provide data on radio bursts.
The Importance of Solar Lyman-alpha Emissions for Space Weather
Lyman-alpha emissions convey a major part of the solar-flare photon energy reaching Earth and play a significant role in flare-driven enhancements of ionospheric conductivity.
Is Space Weather Worse by the Sea?
A new simulation of space-weather driven geoelectric fields at the land/sea conductivity boundary shows how these fields are magnified by both coastal effects and inhomogeneous land conductivity.
Advancing Ensemble Methods in Space Weather Forecasting
A short, must-read, report for anyone developing new space weather forecasts.