Editors’ Highlights are summaries of recent papers by AGU’s journal editors.
Source: AGU Advances
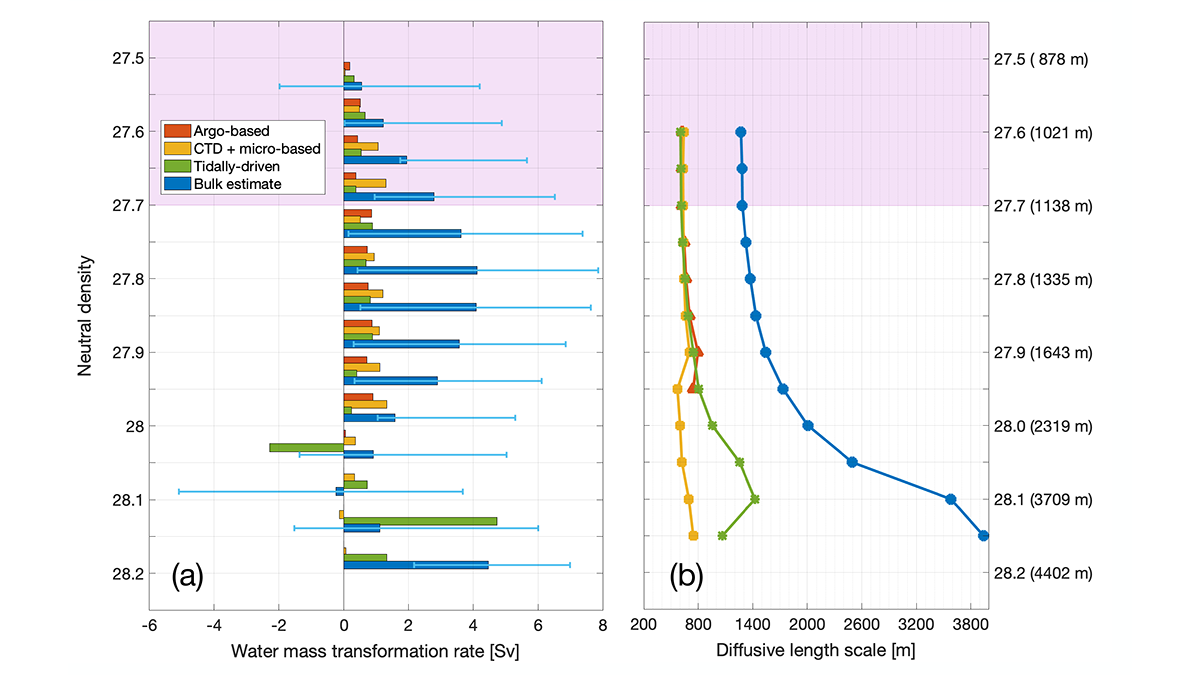
The mixing of fluid across density surfaces, diapycnal mixing, is critical to shaping the distribution of heat and tracers in the ocean. Cimoli et al. (2023) analyze observation-based estimates of turbulence to develop quantitative assessments of the contribution of diapycnal mixing to the Atlantic Meridional Overturing Circulation and its significance in moderating water mass transformations and tracer distributions. These estimates show that diapycnal mixing contributes to the AMOC, but its largest contribution is to Atlantic Ocean tracer budgets. These results have implications for the representation of mixing in ocean circulation and climate models.
Citation: Cimoli, L., Mashayek, A., Johnson, H. L., Marshall, D. P., Naveira Garabato, A. C., Whalen, C. B., et al. (2023). Significance of diapycnal mixing within the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation. AGU Advances, 4, e2022AV000800. https://doi.org/10.1029/2022AV000800
—Eileen Hofmann, Editor, AGU Advances