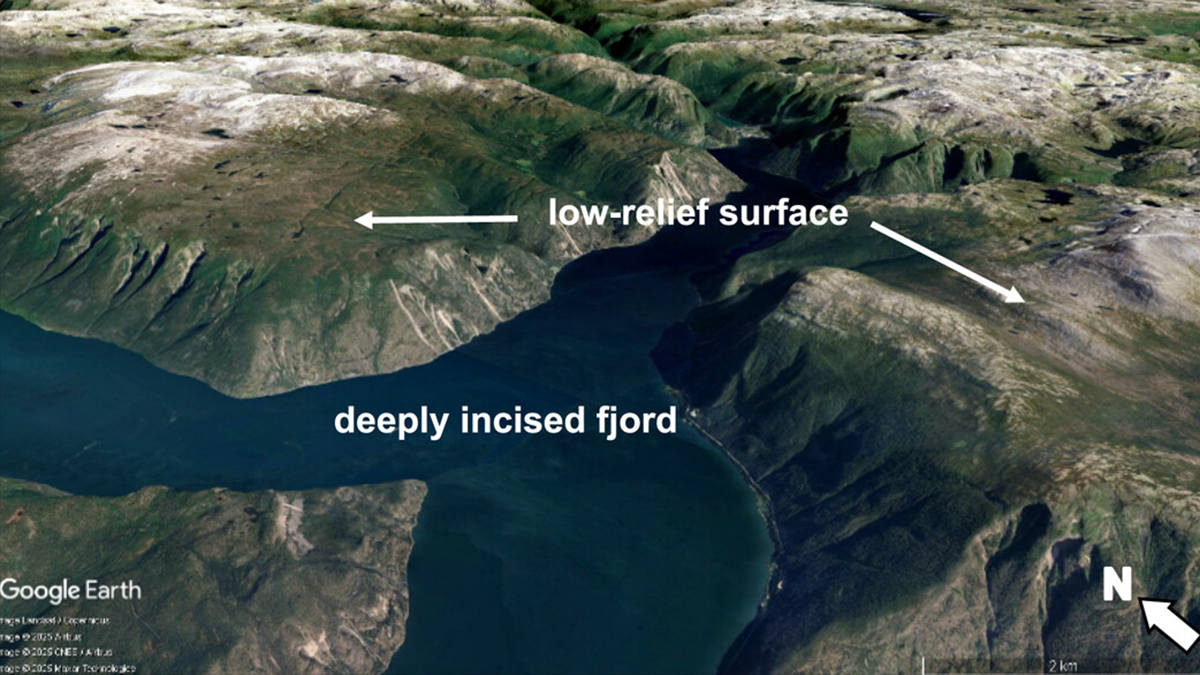
Contrary to conventional wisdom that glaciers just carve landscapes, they can also form low-relief surfaces by sheltering rock from erosion, enriching understanding of how mountain landscapes evolve.
Editors’ Highlights
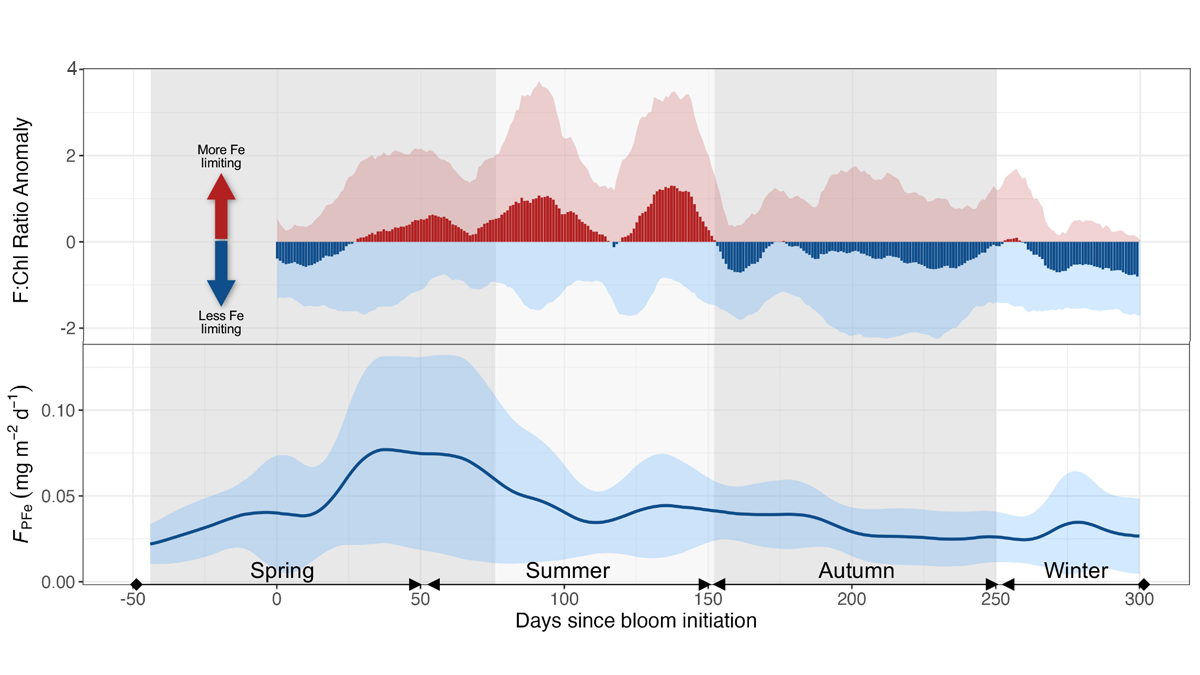
Seasonal Iron Cycle and Production in the Subantarctic Southern Ocean
Long-term monitoring at a site in the subantarctic region south of Australia combined with ship-based observations reveals three distinct phases between cycles of phytoplankton productivity and dissolved iron.
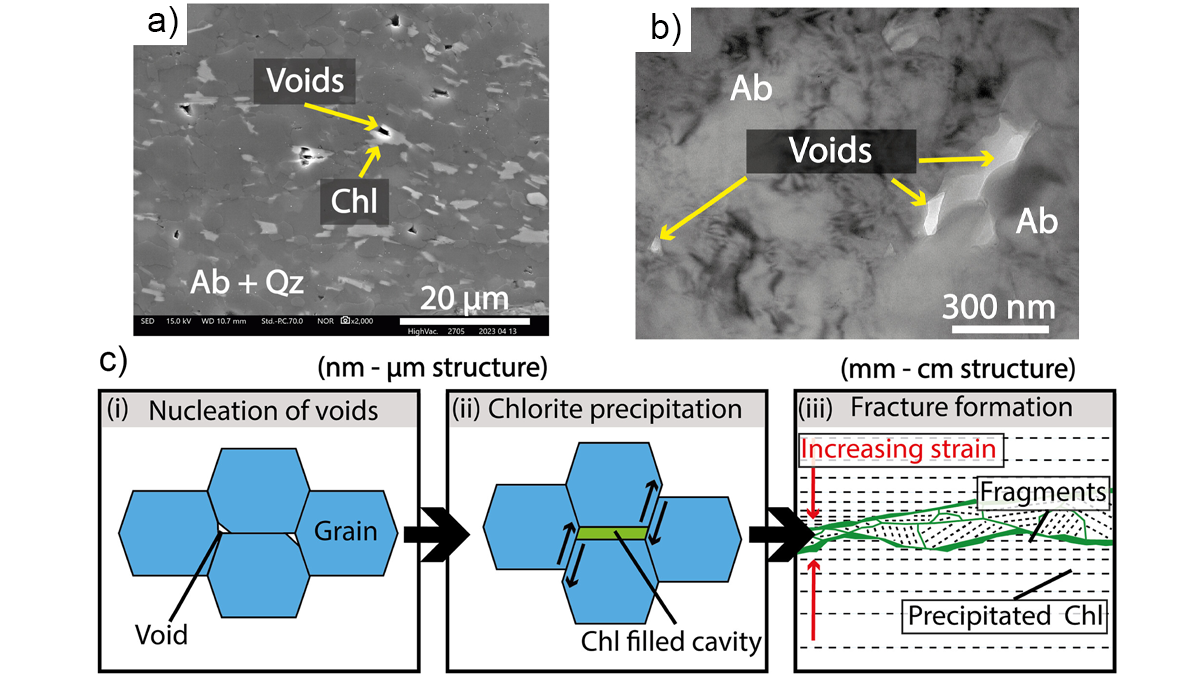
Creep Cavitation May Lead to Earthquake Nucleation
Ultramylonites, rocks of ultrafine grainsize, bring records of nanometer-scale cavities generated at the base of seismogenic crust along Japan’s largest on‐land fault.
Rock Solid Augmentation: AI-Driven Digital Rock Analysis
Boosting digital rock images with AI-powered augmentation and quality analysis could improve subsurface engineering decisions.
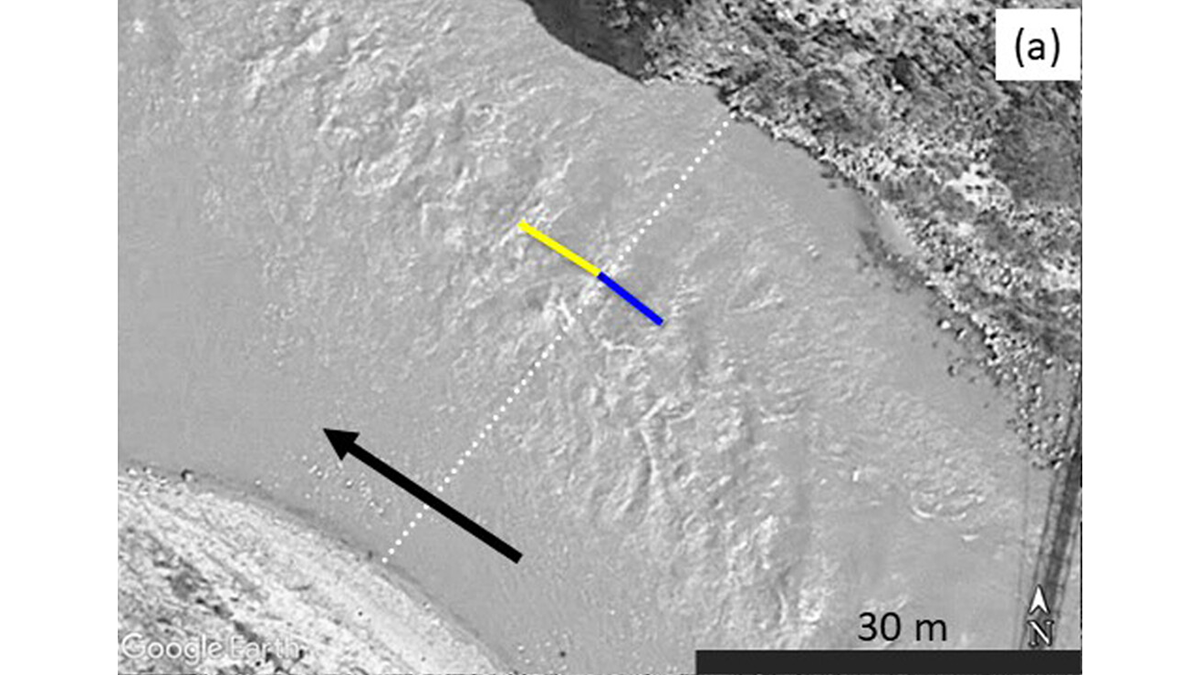
Inferring River Discharge from Google Earth Images
Critical flow theory can predict river discharge based on the spacing of standing waves captured by Google Earth images.
Bringing Storms into Focus
A new study evaluates the performance of kilometer-scale models in predicting large tropical storms, which are key drivers of extreme rainfall and severe weather.
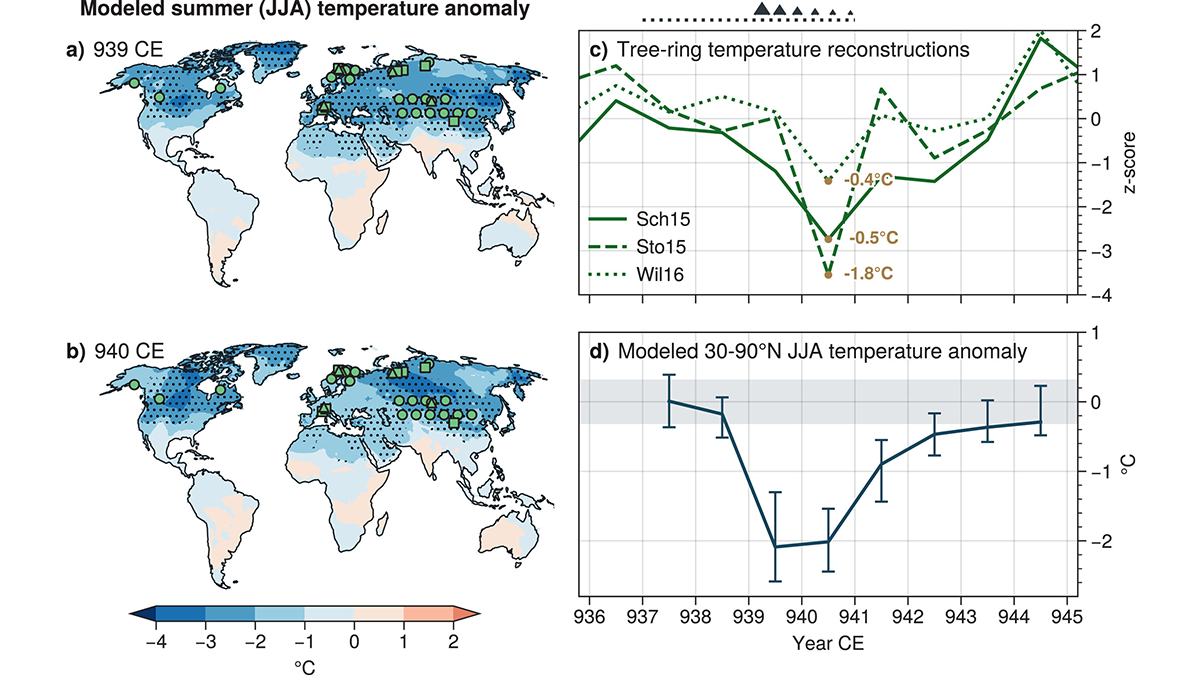
Revised Emissions Show Higher Cooling in 10th Century Eruption
The associated cooling from the Eldgjá eruption is larger than previously predicted and better matches tree-ring temperature reconstructions based on updated estimated emissions.
Old Forests in a New Climate
It’s usually cooler under a forest than outside the forest, but that natural temperature buffering didn’t make global warming any less strong during the last 45 years in an old-growth forest of Oregon.
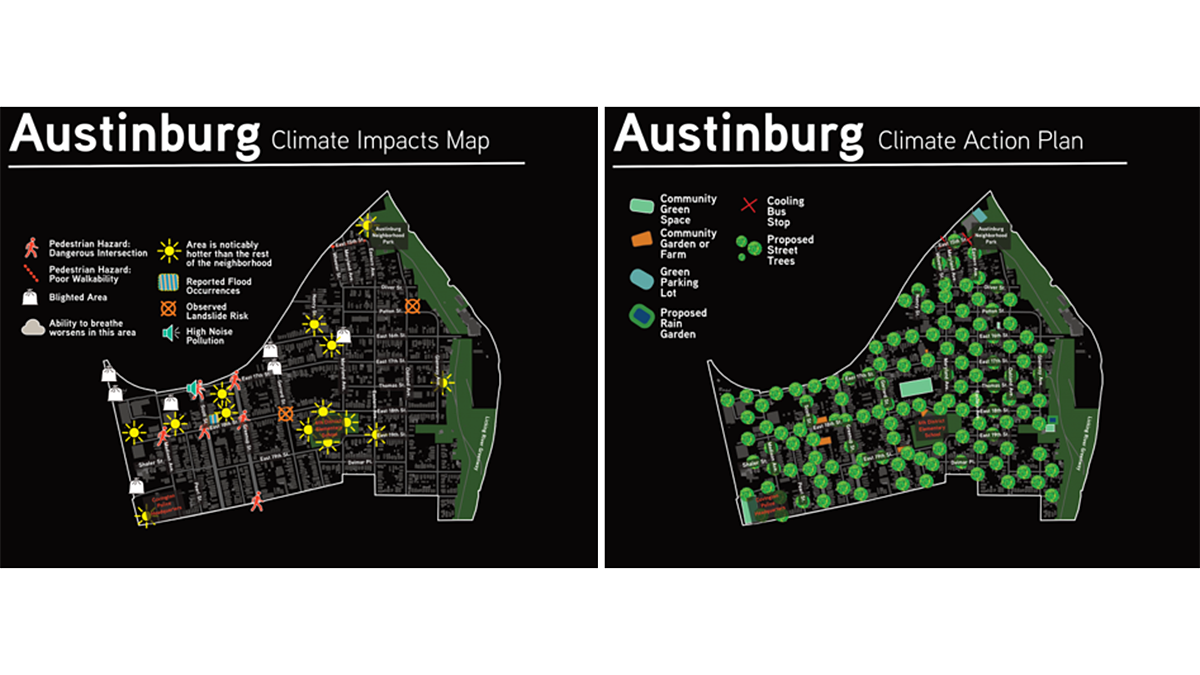
Resilient Solutions Involve Input and Data from the Community
Data dashboards assist in understanding a community’s vulnerability to climate impacts, but input from the communities themselves helps identify and support actionable solutions.
Beyond Up and Down: How Arctic Ponds Stir Sideways
Contrary to common assumptions, Arctic ponds mix in more than one direction. A new study finds that nighttime sideways flows, not vertical mixing, renew bottom waters.