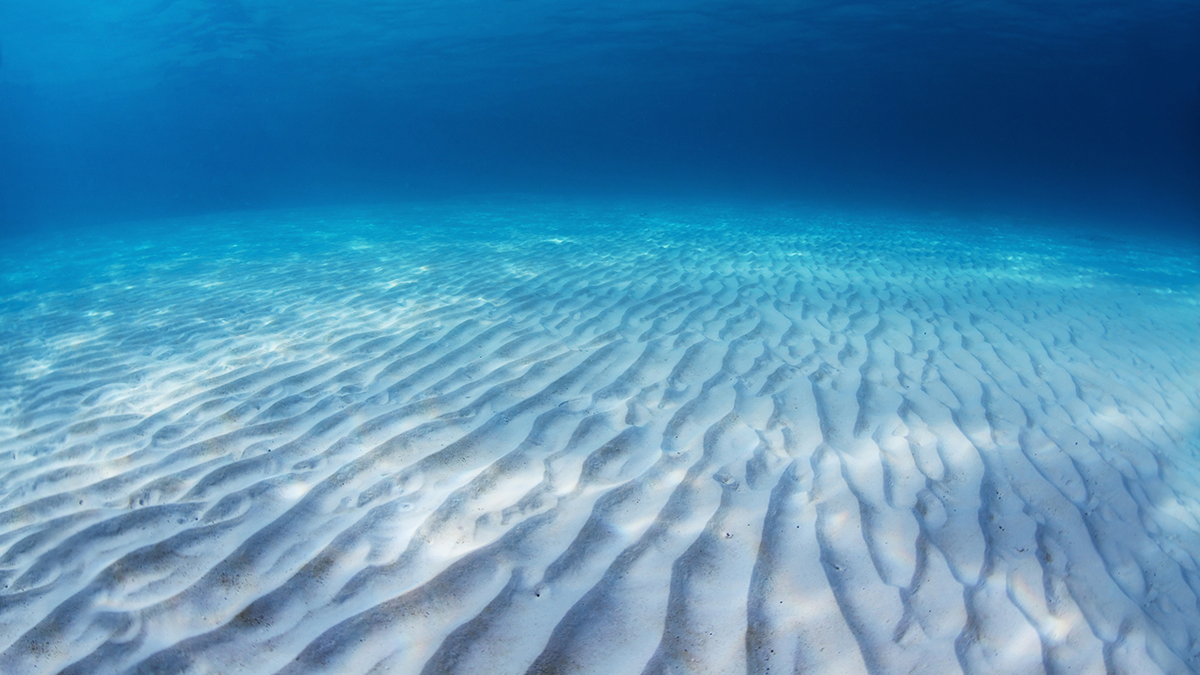
A detailed numerical model shows how sediment particles experience wave-driven shear stress inside and above a sea bed with sand ripples.
Editors’ Highlights
Smallholder Farmers Face Risks in China’s Push for Modern Agriculture
A study of a circular agriculture project in China shows both the promise and the political challenges for smallholder farmers’ autonomy and fair representation.
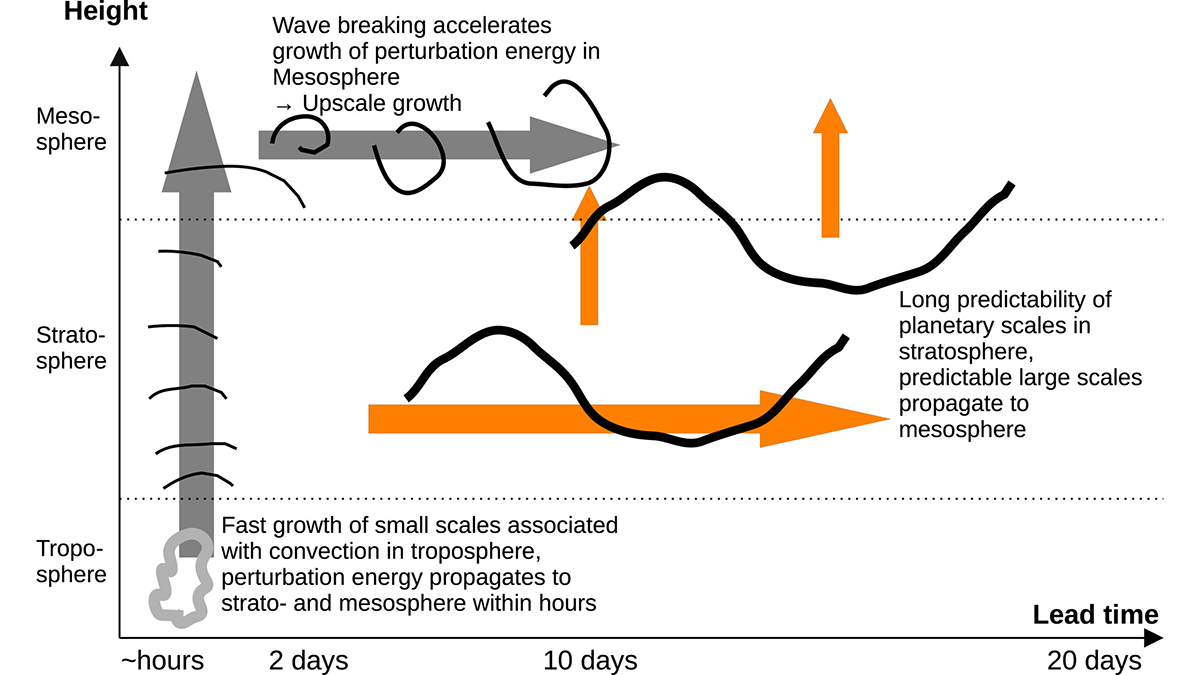
Quantifying Predictability of the Middle Atmosphere
A new high-resolution global model is used to study predictability of atmospheric circulation from the surface to 120 kilometers.
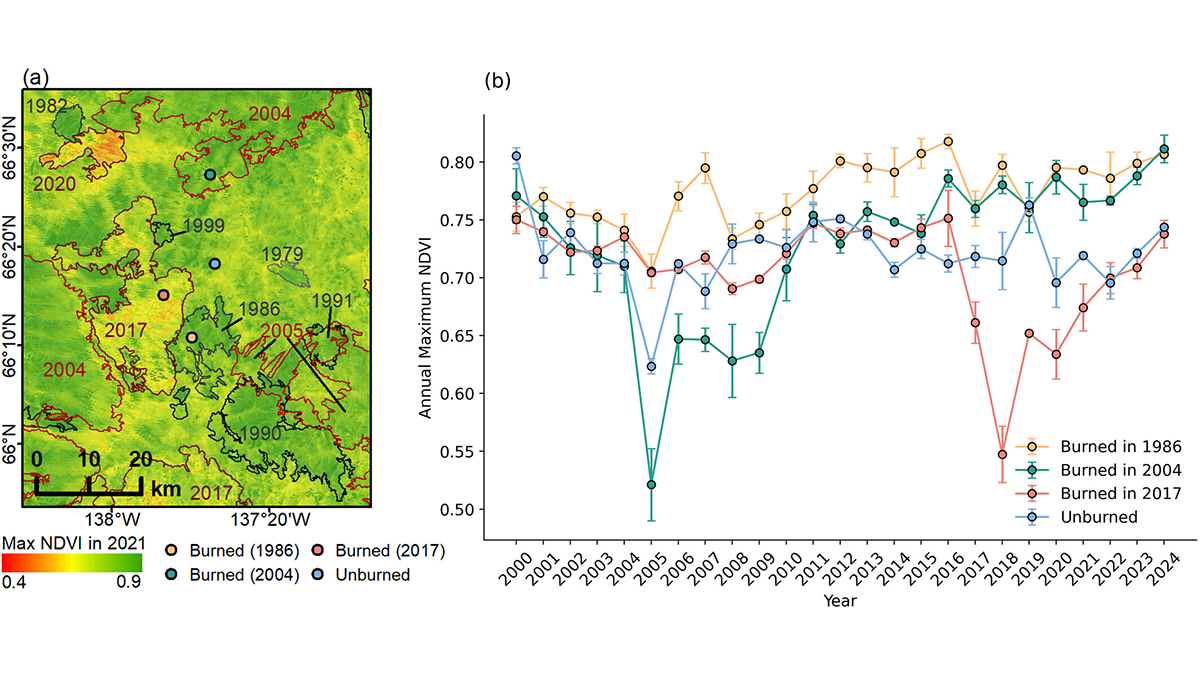
Radar Surveys Reveal Permafrost Recovery After Wildfires
Boreal-permafrost systems are still resilient against wildfires, but continuous and long-term monitoring is needed to control the impact of climate change.
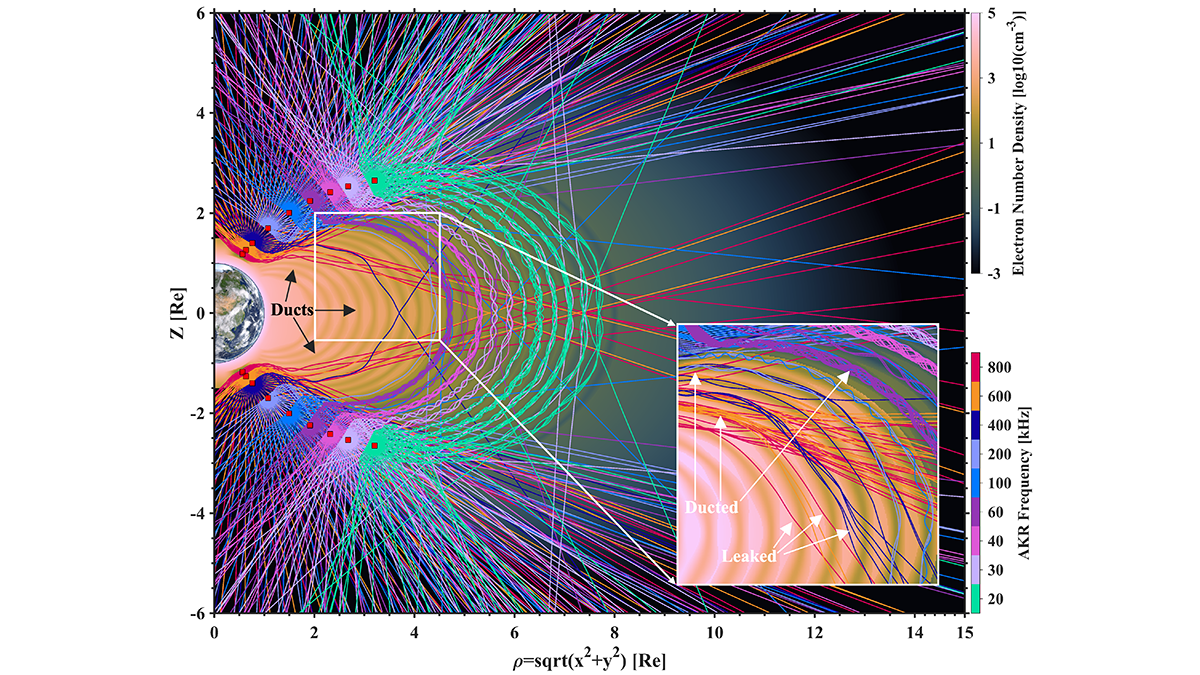
Spacecraft Surveys Shed New Light on Auroral Kilometric Radiation
Observations show low-density space channels guide Auroral Kilometric Radiation, like wind through mountain tunnels, offering new insights into its occurrence and directionality.
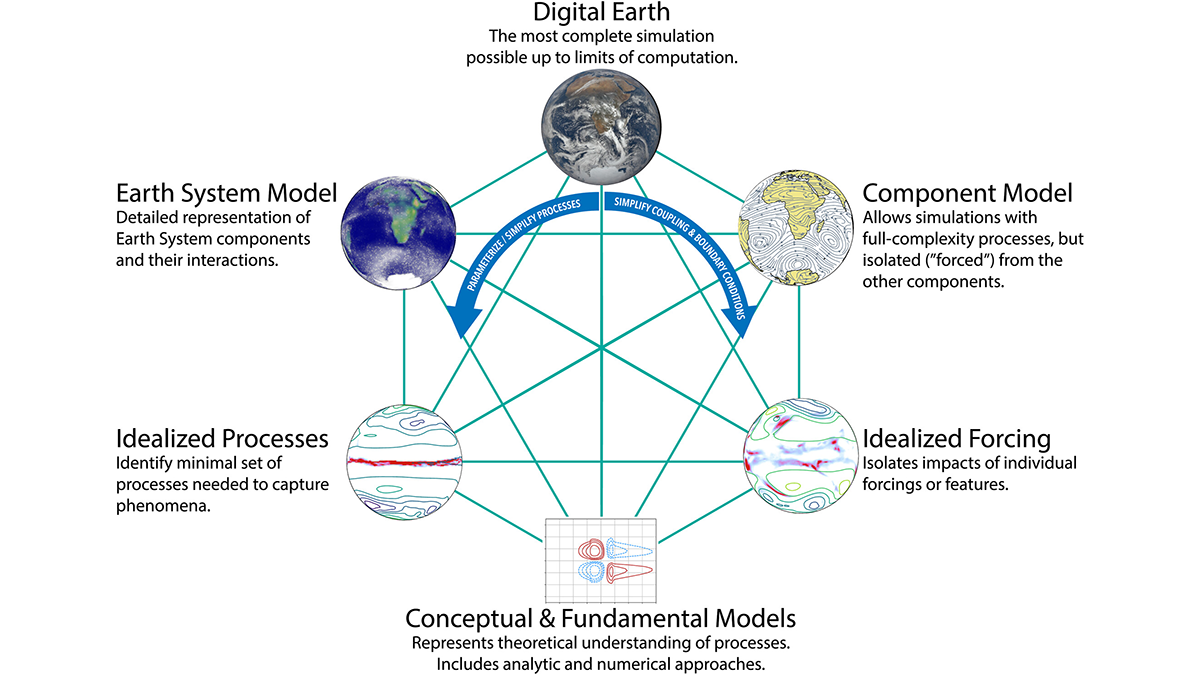
As Simple as Possible: The Importance of Idealized Climate Models
As models that simulate Earth’s climate system become increasingly complex, the use of simpler and more flexible idealized models remains important for science and education.
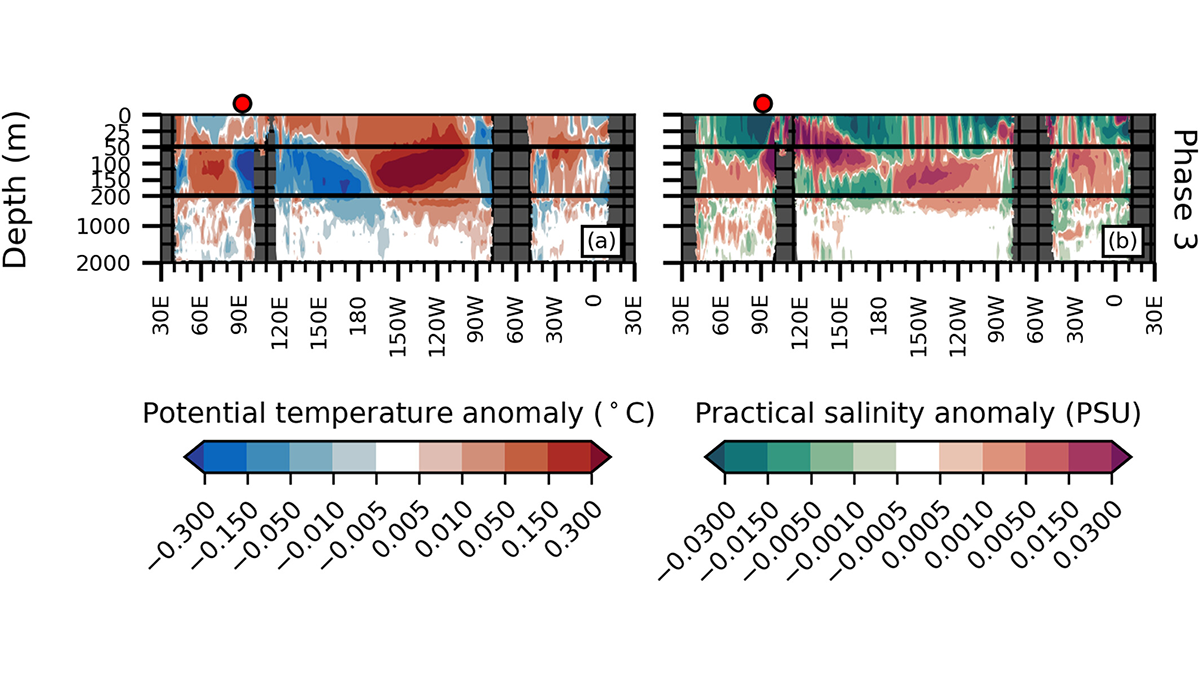
Equatorial Deep Ocean Response to the Madden-Julian Oscillation
The changes in Madden-Julian Oscillation wind can trigger a response in the deep equatorial Pacific and Indian Ocean.
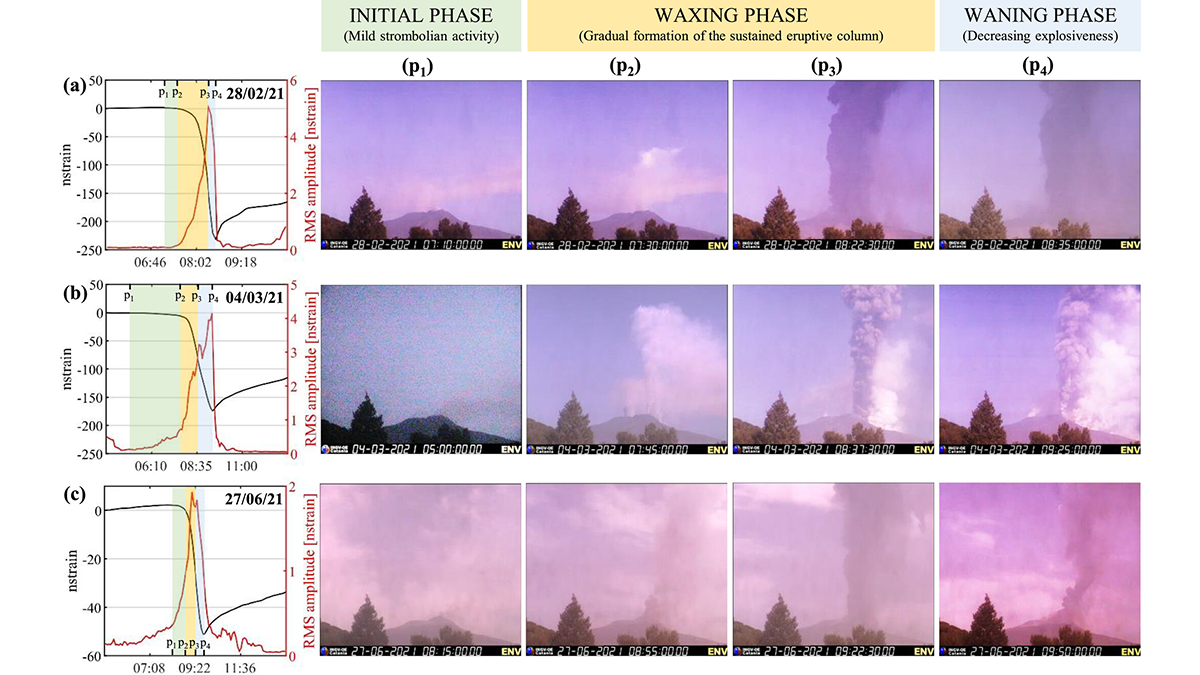
Long-Term Strain Record of Mount Etna Captures 84 Fountaining Eruptions
Scientists use over a decade of high-resolution data to demonstrate that strain signals provide a better match to eruptive style than seismic tremors.
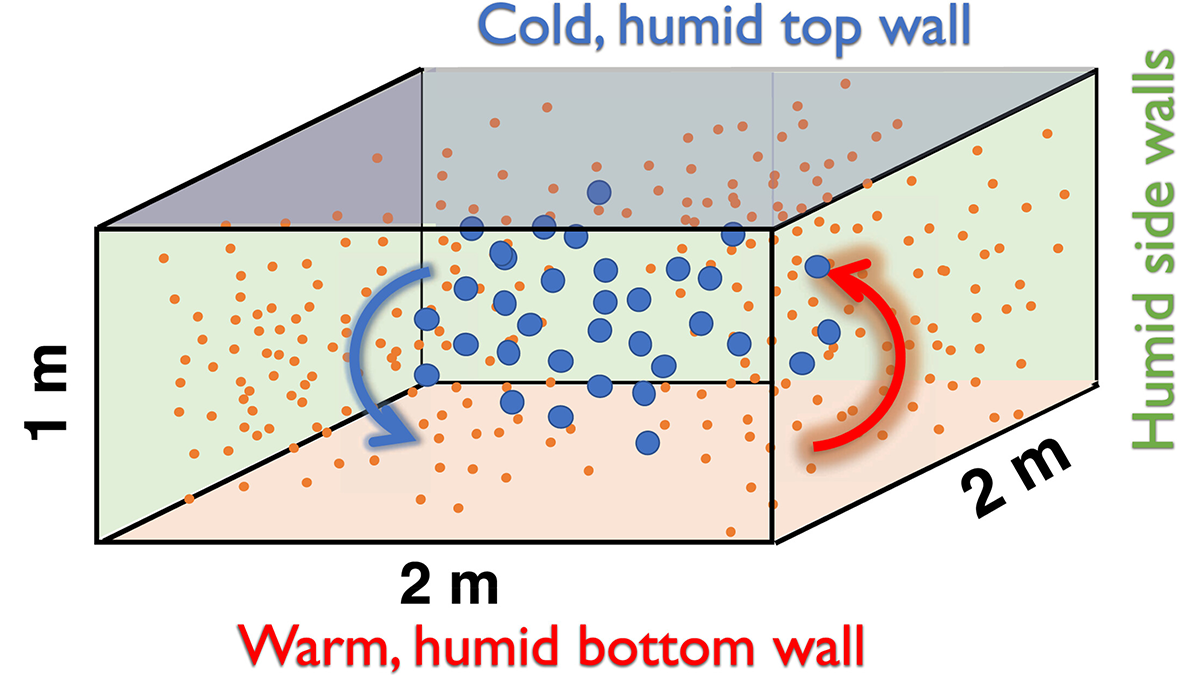
From Aerosols to Clouds: Testing Models with a Convection Cloud Chamber
Researchers benchmark seven cloud models against cloud chamber measurements to reveal how well models capture aerosol-cloud-turbulence interactions and where models still diverge.
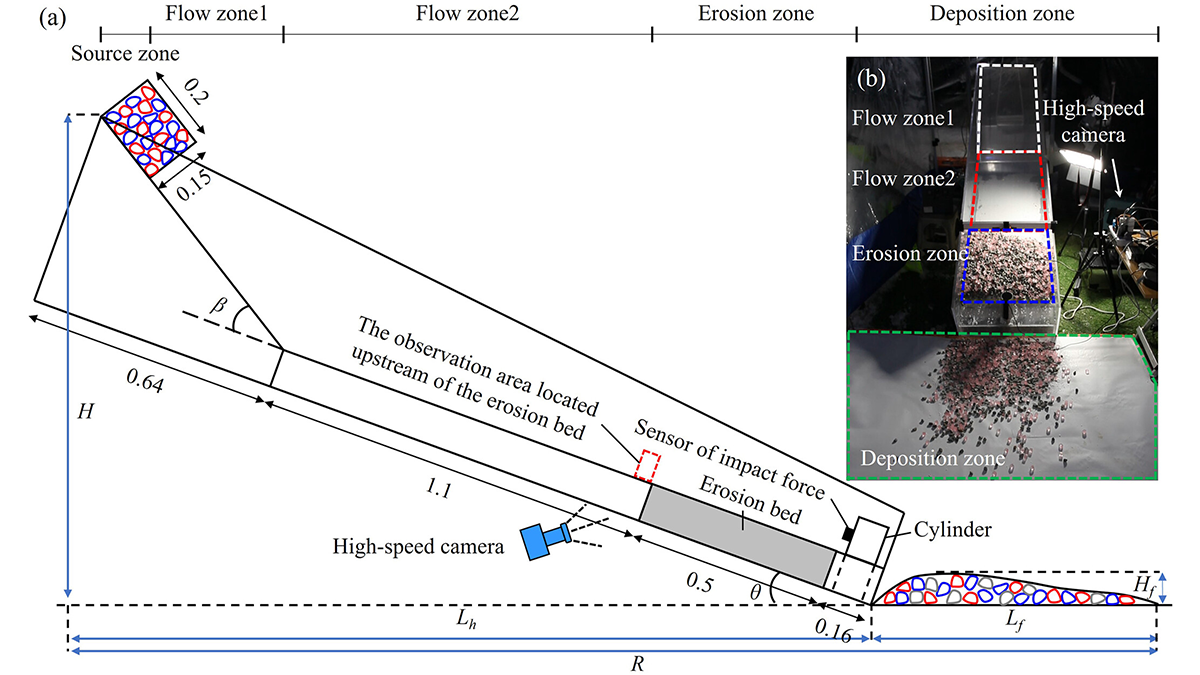
Rock-Ice Avalanche Dynamics: What it Erodes Can Affect How Far it Goes
Using small-scale physical experiments, the mobility of rock-ice avalanches is linked to variability in the earth materials that are encountered along the flow runout path.