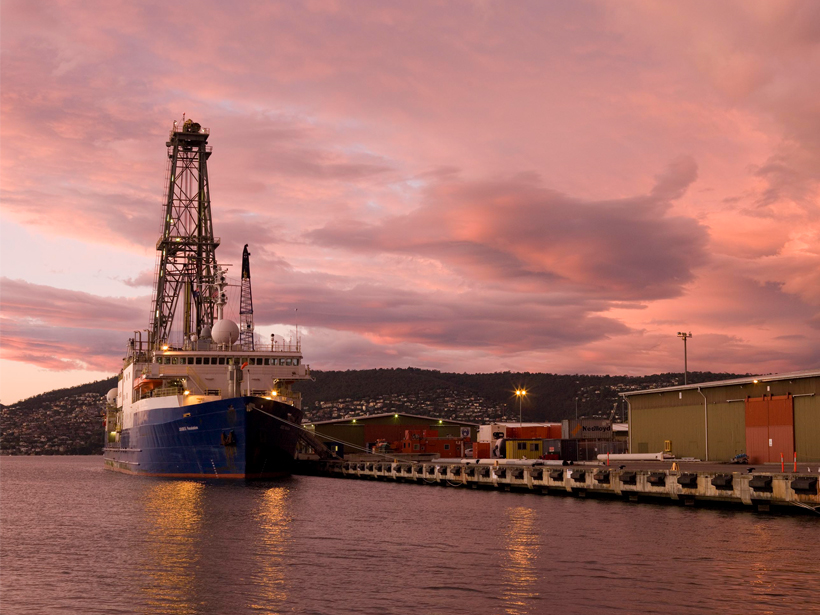
The first basin-wide compilation of seismic and geologic data shows that both margins experienced similar sedimentation patterns prior to the onset of Antarctic glaciation.
Research Spotlights
Research spotlights are plain-language summaries of recent articles published in AGU’s suite of 24 journals.
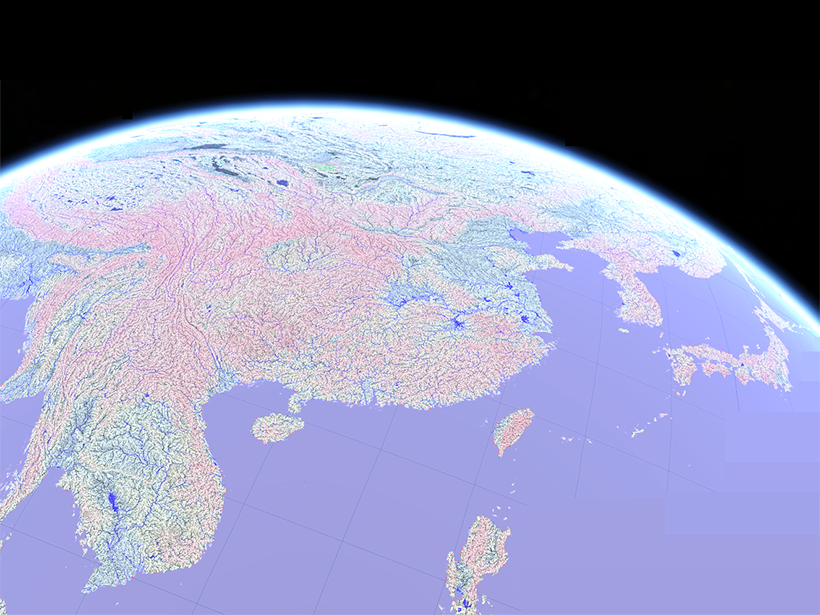
A More Accurate Global River Map
A new map of global river systems is based on crowdsourcing and the latest topography data sets.
Tracking Earth’s Shape Reveals Greater Polar Ice Loss
Researchers offer a solution to better track mass changes in ocean water and polar ice.
New Perspectives on 2,000 Years of North Atlantic Climate Change
A review of recent research advancements takes a deep dive into North Atlantic ocean circulation and its potential role in historical climate shifts.
Demystifying Sea Level Changes Along the New England Coast
No direct causal connection exists between coastal sea level changes and the strength of the North Atlantic’s overturning circulation, according to new, longer-term observational records.
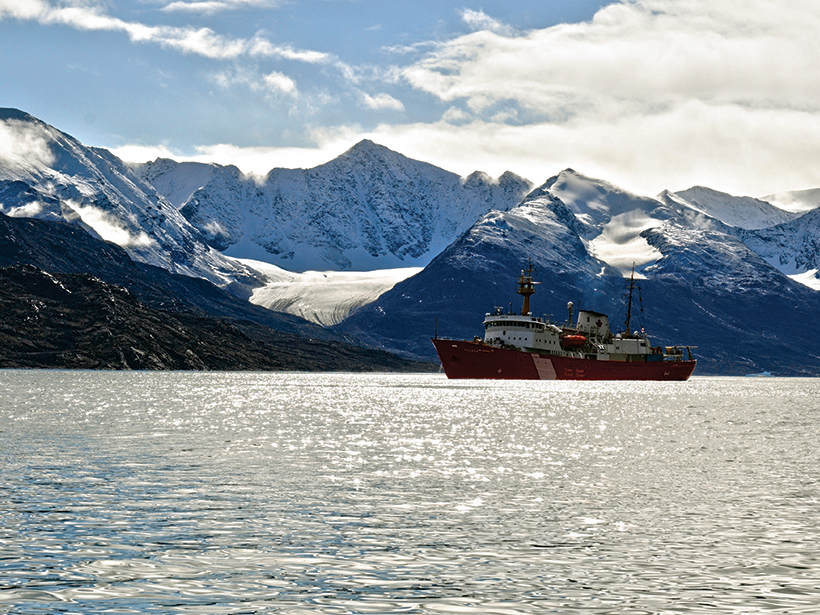
Arctic Glacial Retreat Alters Downstream Fjord Currents
High-resolution mapping efforts could improve predictions of coastal changes as glaciers shrink around the world.
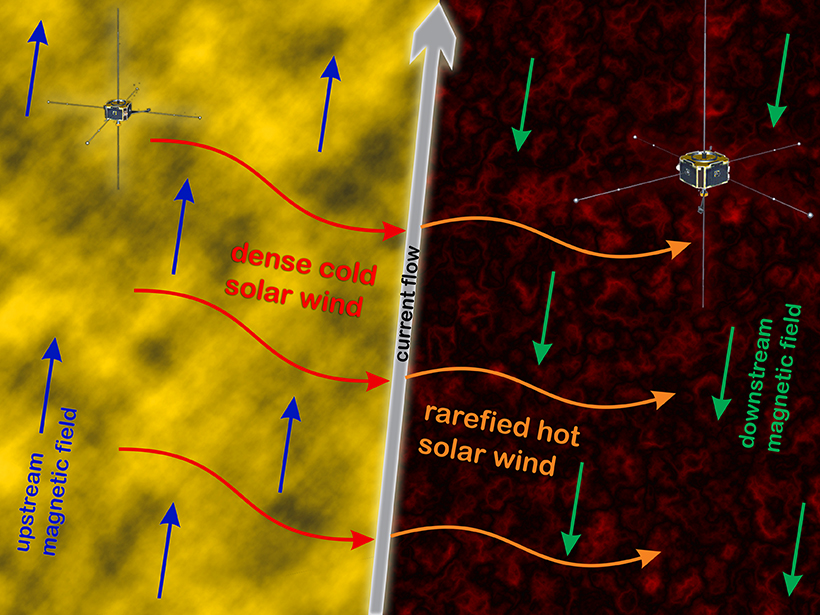
Understanding the Turbulent Nature of the Solar Wind
Sometimes the conditions in the solar wind can change dramatically over short distances. Satellite observations of these features show that they’re more complex than previously thought.
Fading Air Pollution Reduces Fog in Central Valley
The tule fog in California’s Central Valley is notorious for causing delays and accidents throughout the region; however, a decrease in air pollutants is reducing the fog’s frequency.
Extreme Precipitation Expected to Increase with Warming Planet
A new analysis indicates that the frequency and magnitude of extreme precipitation events are expected to increase as Earth continues to warm.
Ordinary Security Cameras Could Keep an Eye on Rainfall
A new opportunistic sensing strategy could use existing closed-circuit television networks to accurately capture rainfall intensity, despite low-cost equipment and visually complex scenes.