Until recently, this type of zigzag shape—formed by energetic rearrangement of magnetic field lines—had been seen only near the Sun.
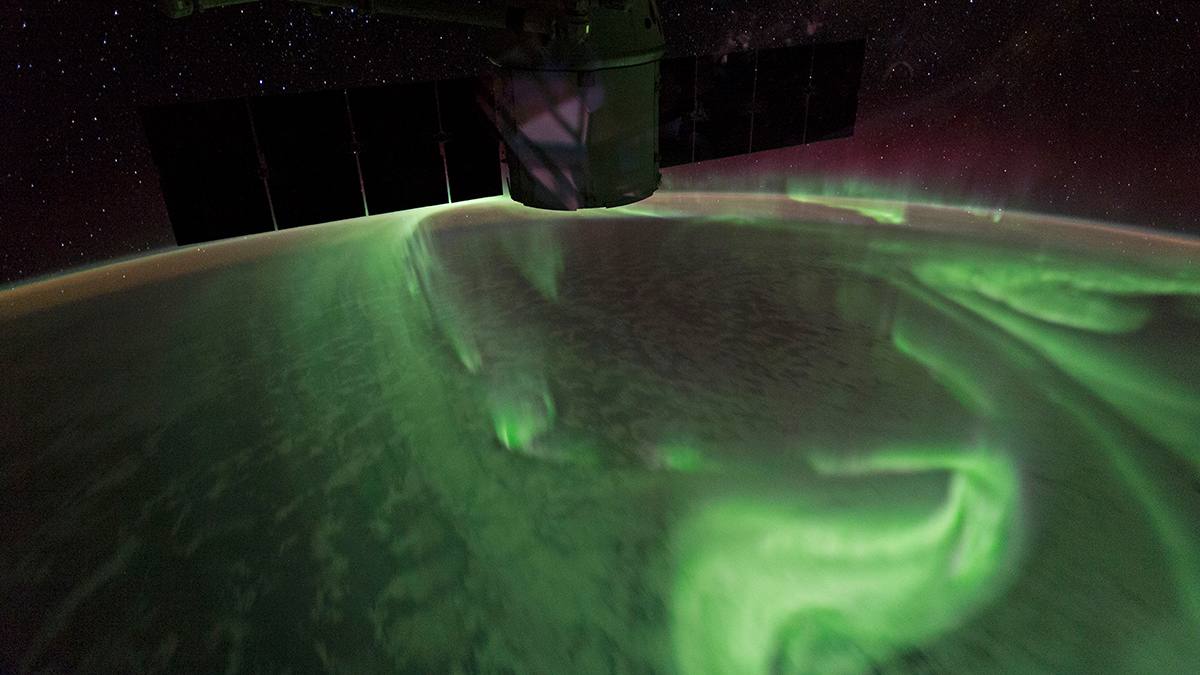
aurorae
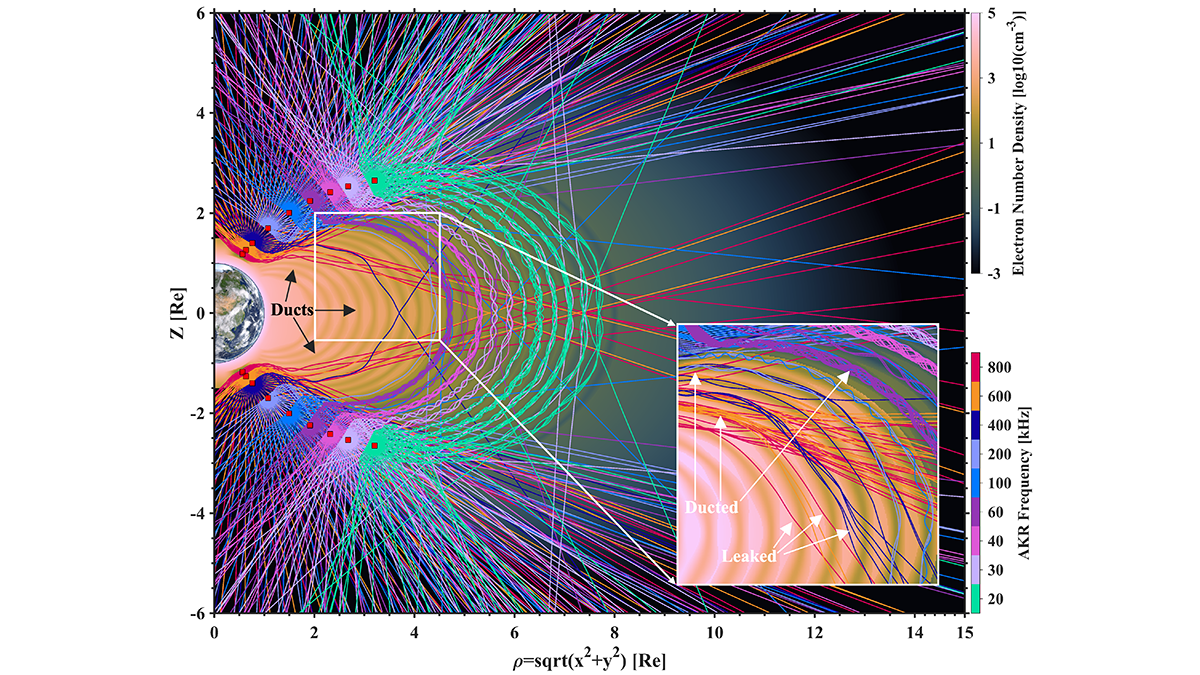
Spacecraft Surveys Shed New Light on Auroral Kilometric Radiation
Observations show low-density space channels guide Auroral Kilometric Radiation, like wind through mountain tunnels, offering new insights into its occurrence and directionality.
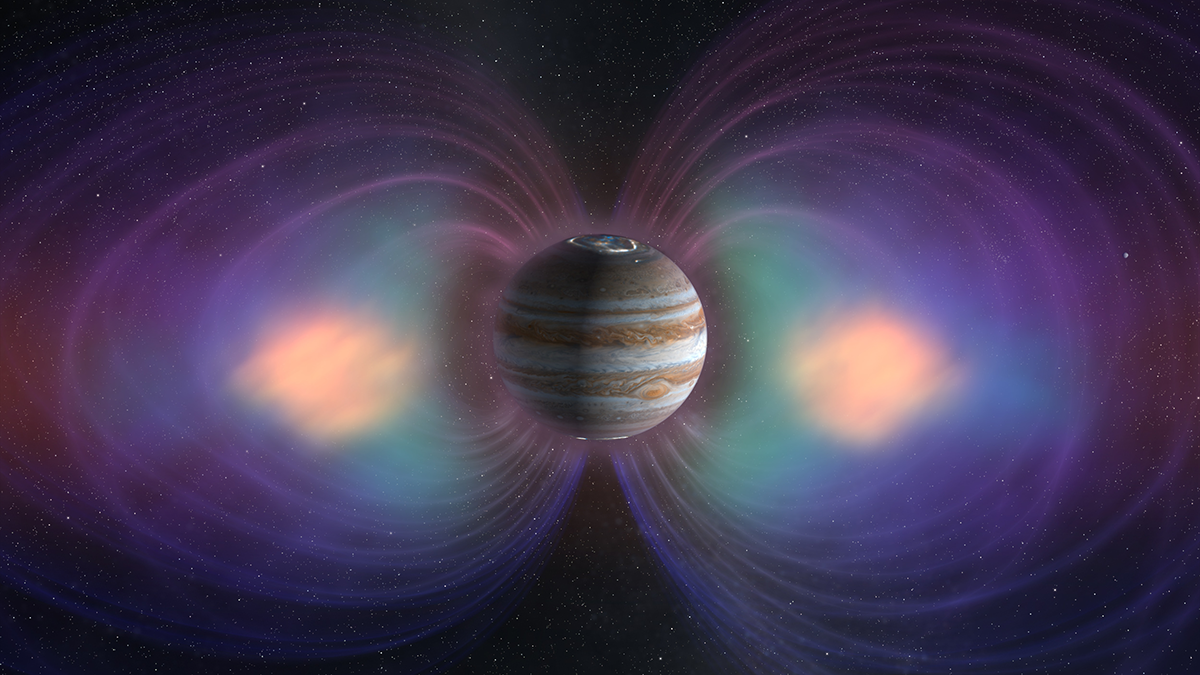
A Solar Wind Squeeze May Have Strengthened Jovian Aurorae
Juno spacecraft data suggest an extreme compression of the planet’s magnetosphere in December 2022, caused by the solar wind, briefly brightened the ultraviolet light displays.
After 30-Year Search, Scientists Finally Find an Aurora on Neptune
The planet’s elusive aurorae are much colder than expected, which is how they evaded detection for so long.
Watching a Solar Event from All Angles
A fleet of spacecraft captured unprecedented details of the major solar outbursts in May and June 2024.
Radar Reveals Electrical Activity in the Ionosphere
A new method could improve understanding of communication disruptions.
Unusual Occurrence of STEVE: An Aurora-Like Glow
STEVE is a mysterious purple-white arc near the aurora, typically seen after space disturbances called substorms. A new study reveals a rare STEVE event without a substorm, prompting questions about its origin.
Scientists Captured the First Glimpse of a Rare Polar Aurora
After a decade-long search, scientists captured a type of elusive aurora on camera.
Space Hurricanes Swirl in the Southern Hemisphere, Mostly in Summer
Previous studies of the recently discovered space weather feature focused on the Northern Hemisphere. Dozens hit the Southern Hemisphere each year, new research shows.