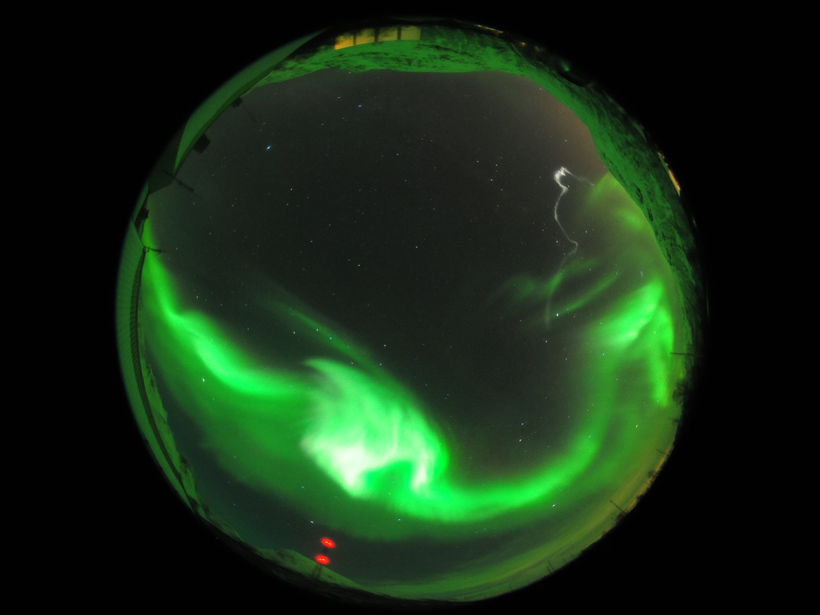
High-speed particles cause indentations in the magnetopause to form “throat auroras.”
aurorae
An Aurora of a Different Color
Meet STEVE, a purple and green, low-latitude, aurora-like phenomenon whose inner workings were uncovered with the help of citizen scientists.
Modeling Geospace: Quantifying the Known-Unknowns
Imperfect knowledge of high-latitude forcing of the coupled ionosphere-theremosphere system translates into uncertainty in the low-latitude and midlatitude response to a geomagnetic storm.
Sounding Rockets Probe the Northern Lights Above Norway
Scientists measure how the aurora affects winds in the upper atmosphere.
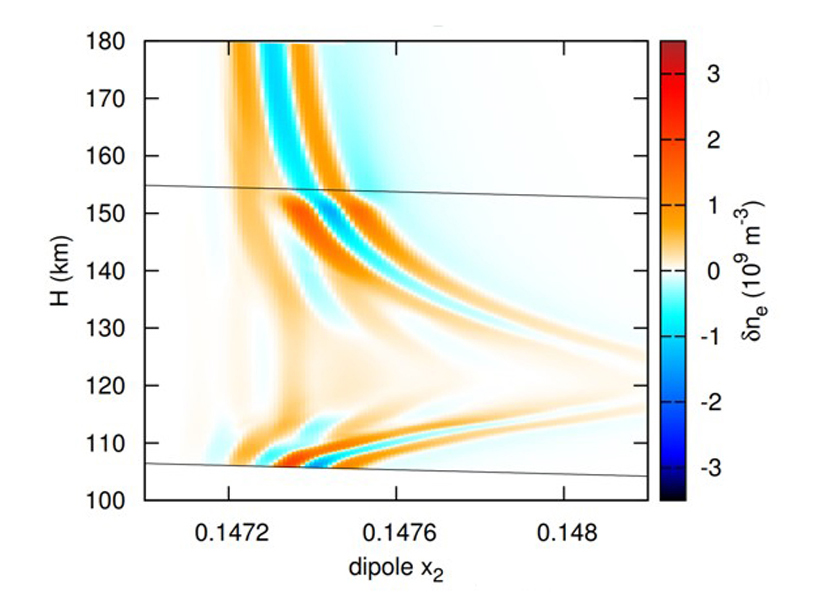
New Insight into Ionospheric Feedback Instability
A new modeling effort could change our understanding of auroral arc formation.
Can Large Electric Fields Power Jupiter’s X-ray Auroras?
Electric fields with megavolt potentials in Jupiter’s polar region accelerate particles to 100 times more energy than Earth’s typical auroral particles, a new study finds.
Juno Gets Spectacular View of Jupiter’s Aurora
The NASA spacecraft has taken images of Jupiter’s powerful aurora dancing around its poles, revealing never-before-seen details in their structure.
Simulations Give New View of Global Auroral Storms
New computer models capture the movement of the strongest auroral storms as they sweep across Earth at night, challenging scientists’ views of what drives them.
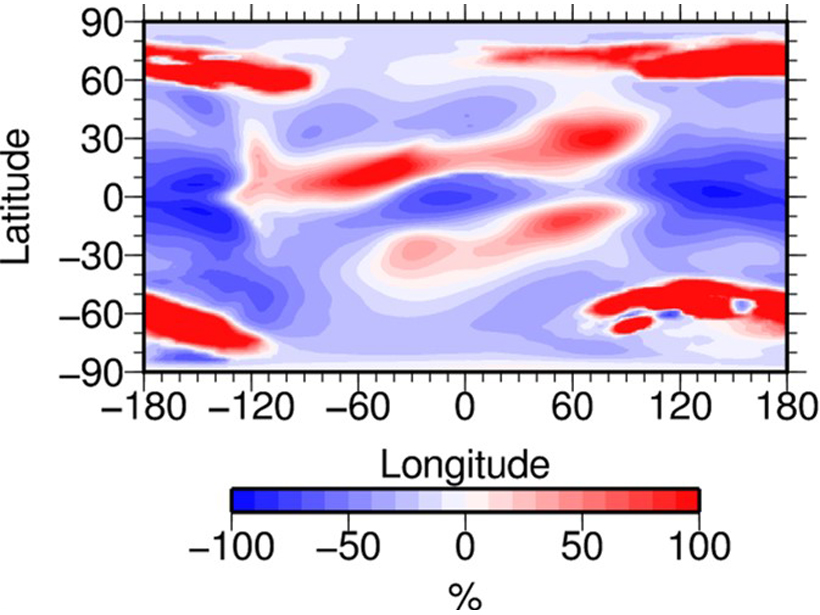
Auroras May Explain an Anomaly in Earth’s Ionosphere
A new study finds that the ionospheric anomaly over the Weddell Sea is likely influenced by proximity to auroral energy input, rather than by tilting magnetic fields.
Hubble Reveals Less Studied Regions of Jupiter’s Auroras
With a dose of fiery plasma, the secondary arcs of Jupiter’s aurora shine bright.