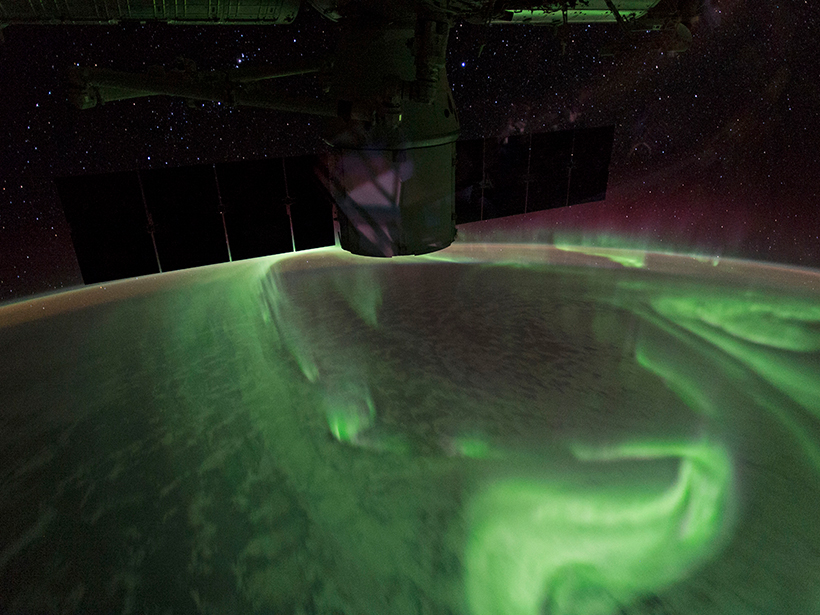
The first movie of Jupiter’s infrared aurora gives scientists a new look at the Jovian magnetic field.
aurorae
Bringing Clarity to What Drives Auroras
A new classification scheme helps researchers distinguish what accelerates the electrons that create auroras.
Atmospheric Gravity Wave Science in the Polar Regions
A joint special issue explores the potential of collaboration to help understand atmospheric gravity waves in the Polar Regions and their effect on global circulation.
What Drives Temperature Inversions in the Mesosphere?
A study of nightglow over India reveals that gravity waves are less important than previously thought.
Probing the Origin of a New Celestial Phenomenon
The first statistical study of STEVE events suggests that the appearance of these narrow ribbons of light is closely correlated with violent disturbances in Earth’s magnetosphere.
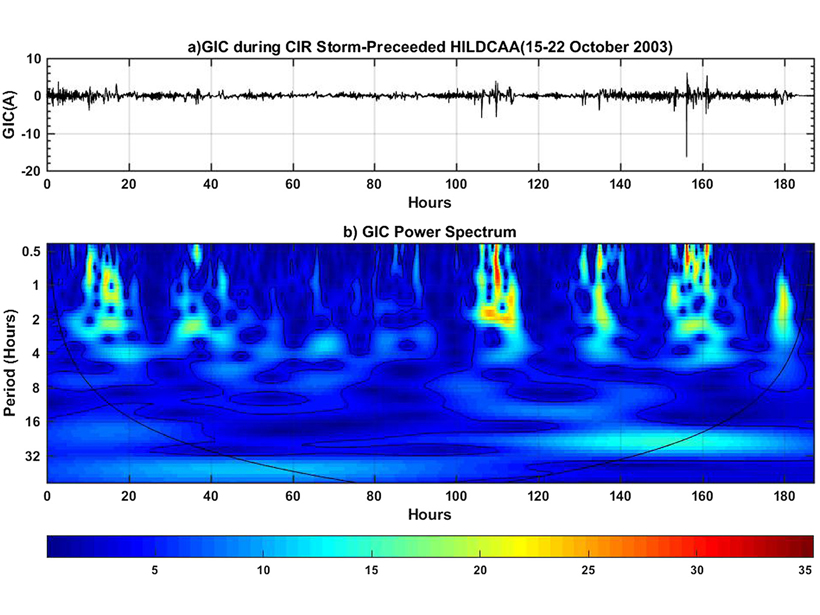
Can Moderate Space Weather Have Major Impacts?
Pipeline corrosion is an example of why we need better awareness of how long-term exposure to moderate space weather may have significant economic impact by slowly degrading vulnerable systems.
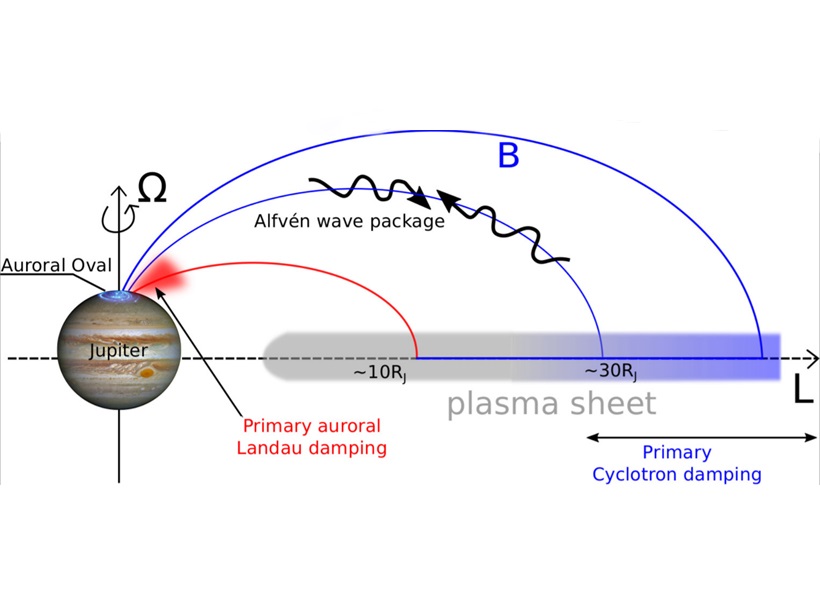
Jupiter’s Stressed Out Magnetosphere Causes Aurora and Heating
Force imbalance between Jupiter’s ionosphere and magnetosphere leads to wave generation to release this stress, but the waves also accelerate particles, causing aurora and heating.
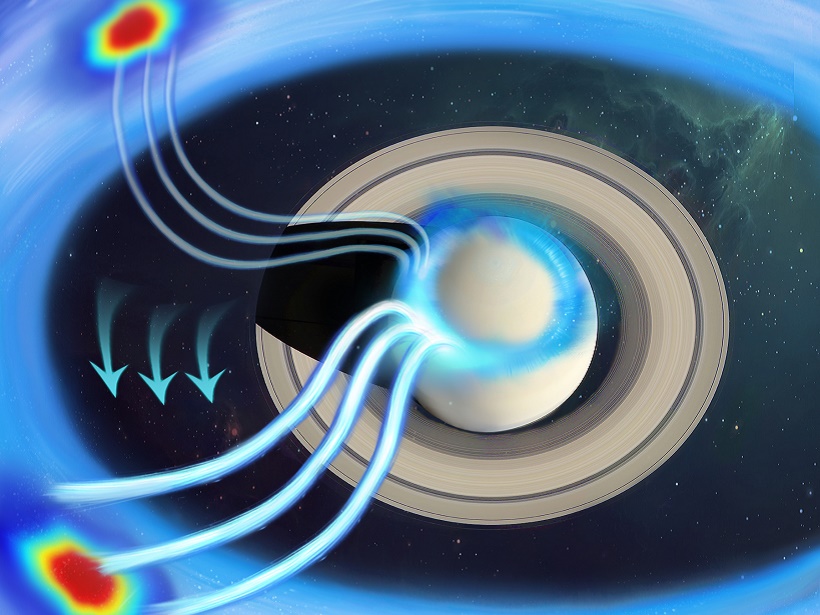
Cassini Reveals a Missing Link on Saturn’s Rotating Aurora
The bright aurorae dancing in the sky are produced by charged particles traveling along the magnetic field lines from tens of planetary radii. By why do aurorae rotate at Saturn but not at Earth?
Extreme Space Conditions at Mars: The 10 Largest Electron Events
A solar cycle of data was scoured for the biggest electron energy fluxes seen in the Mars space environment.
How Two Massive Space Storms Zapped Alaska
New study reveals how space weather causes rapid fluctuations in Earth’s surface geomagnetic field.