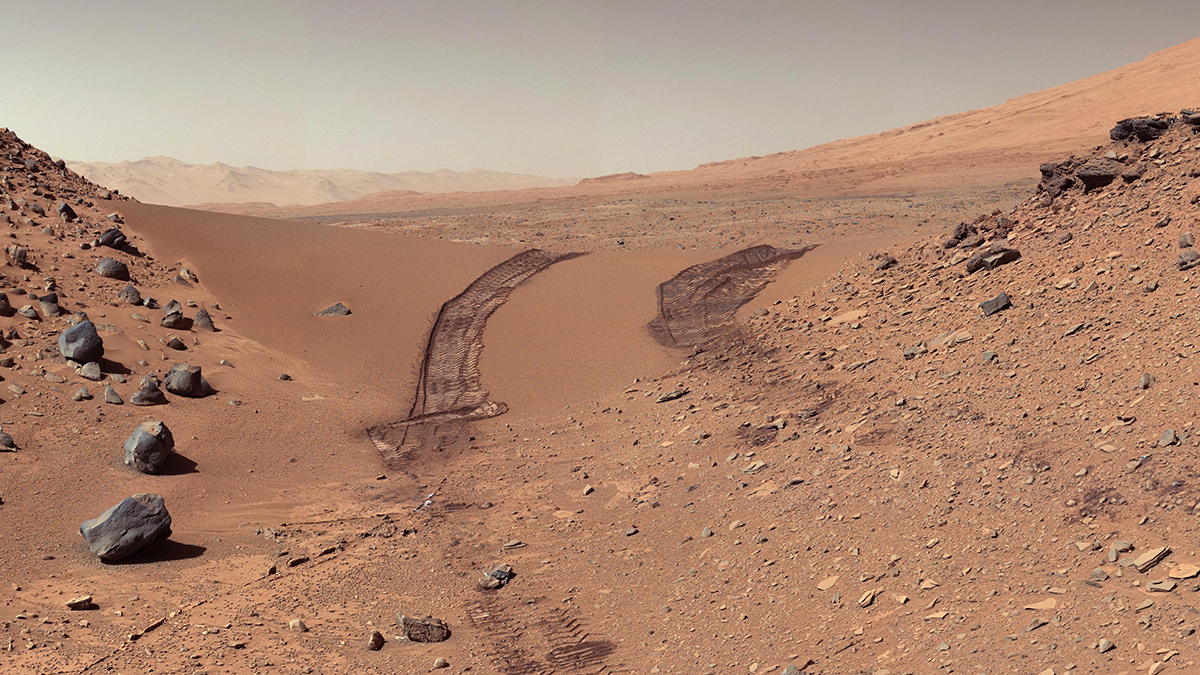
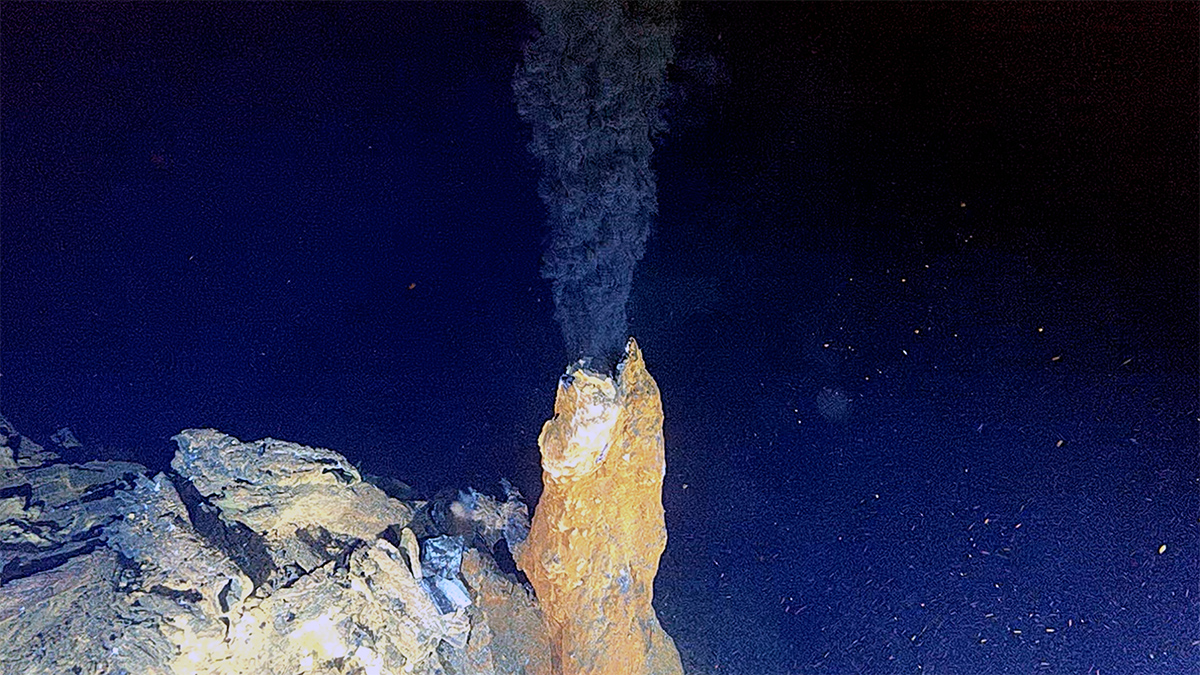
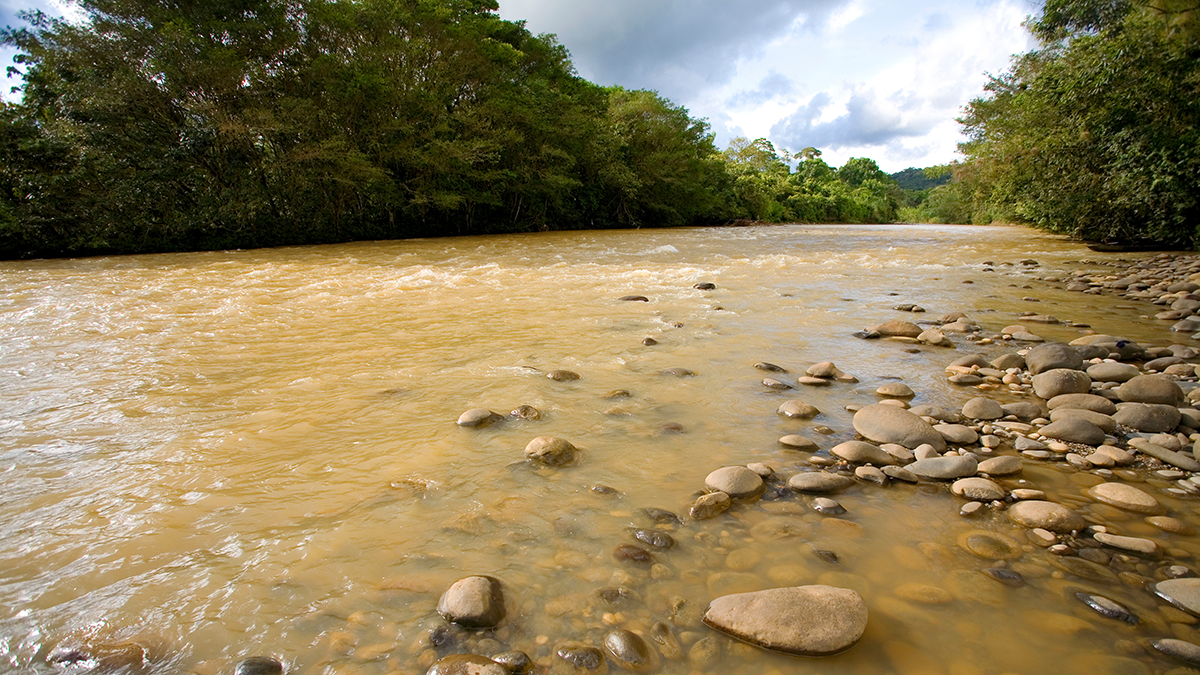
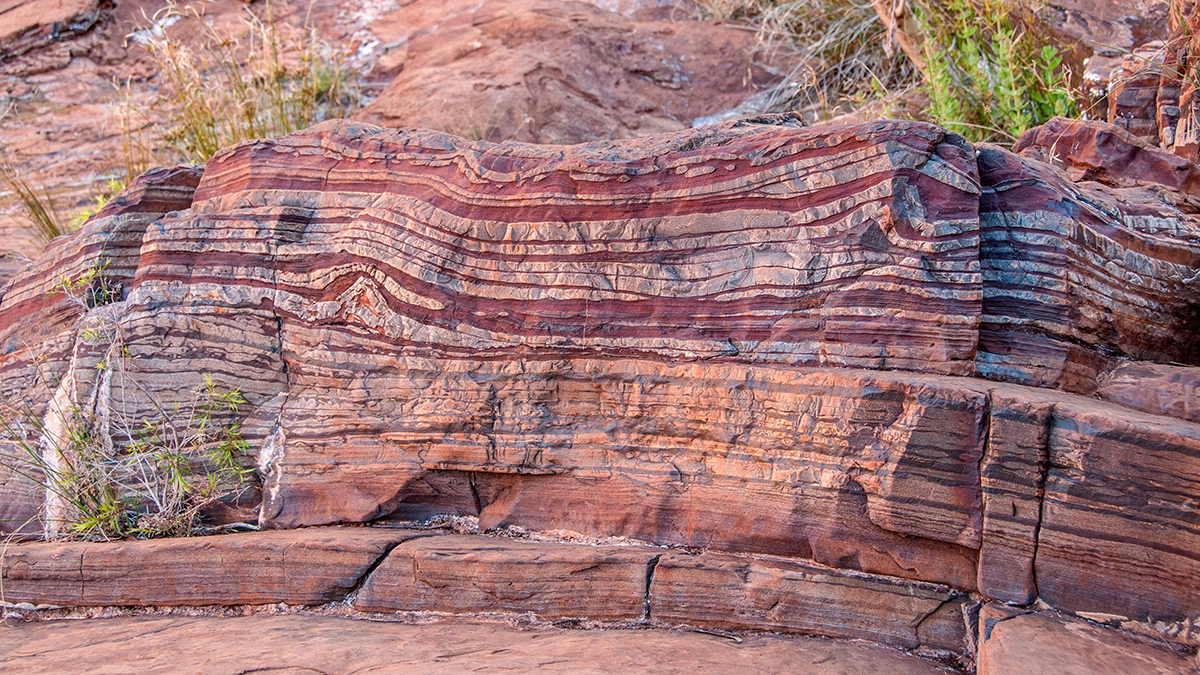
Fluid-rock interactions on ancient Mars may have produced abundant magnetic minerals that preserved unusually intense records of the planet’s now-extinct magnetic field.
bacteria & microbes
Extreme Heat and Rain Turned These Arctic Lakes Brown
Scientists are stunned by the changes in multiple Arctic lakes, all transforming in the same way.
Rice Paddies, Like Cows, Spew Methane. A New Variety Makes Them a Lot Less Gassy.
Rice plants are a big source of methane, an extremely potent greenhouse gas. Scientists just developed a strain that cuts those emissions by 70 percent.
Arctic Hydrothermal Vents May Resemble Those on Enceladus
By studying hydrogen-rich vent sites on Earth, scientists could learn more about the hidden ocean of Saturn’s icy moon—one of our solar system’s likeliest candidates for harboring life beyond Earth.
Climate Change Is Driving Dangerous Bacteria Farther North
Satellite data could help address rising rates of vibriosis infections, often the result of eating undercooked seafood, along the East Coast of the United States.
Mid-Ocean Ridges Could Be Dispersing Thermophilic Bacteria
Scientists suggest that two strains of endospores located more than 4,000 kilometers away from one another originated in the same place: along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge.
Physics and Biology as Likely Stream Bedfellows
Streambeds are key sites for removal of nutrients and other contaminants through microbial processes, but are limited by diffusion, which can now be modeled from streambed physical properties.
The Arctic’s Uncertain Future
Over the next century, the Arctic will change and look much different than it does today. Just how different is still unknown.
Bacteria Battled for Iron in Earth’s Early Oceans
Billions of years ago, iron-oxidizing microbes may have competed for dissolved iron in the ocean, with some strains producing toxic gases that smothered their rivals.
Machine Learning Enhances Image Analysis in Biogeosciences
Machine learning can enhance our ability to identify communities of microorganisms and how they change in response to climate change over time.