Scientists have long suspected that high salinity levels in the deep ocean were responsible for keeping carbon dioxide locked away during the last ice age. New research finds the strongest evidence yet.
carbon capture & sequestration
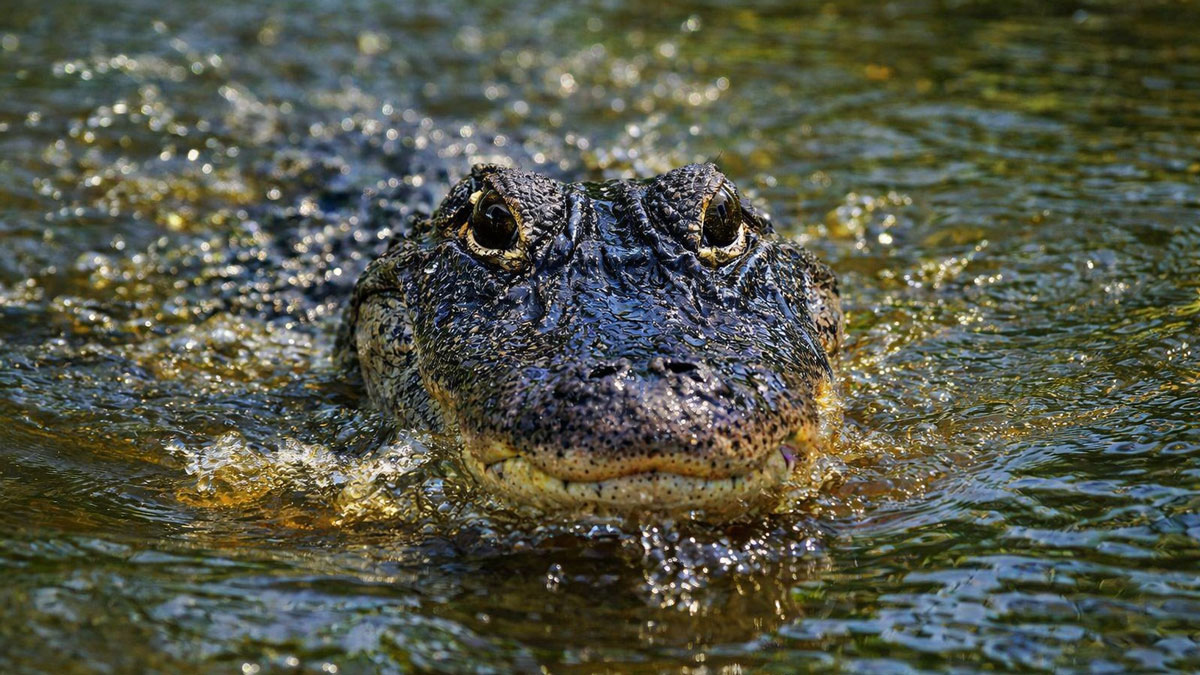
Alligators May Boost Carbon Storage in Coastal Wetlands
Research suggests that American alligators help coastal wetlands retain more carbon, linking predator recovery in the southeastern United States to ecosystem function and climate processes.
As Some Soils Warm, Microbes Stockpile Essential Nutrients
A study in Iceland found that microbes are hoarding more nitrogen for themselves, altering nutrient cycling and leaving less for plants.
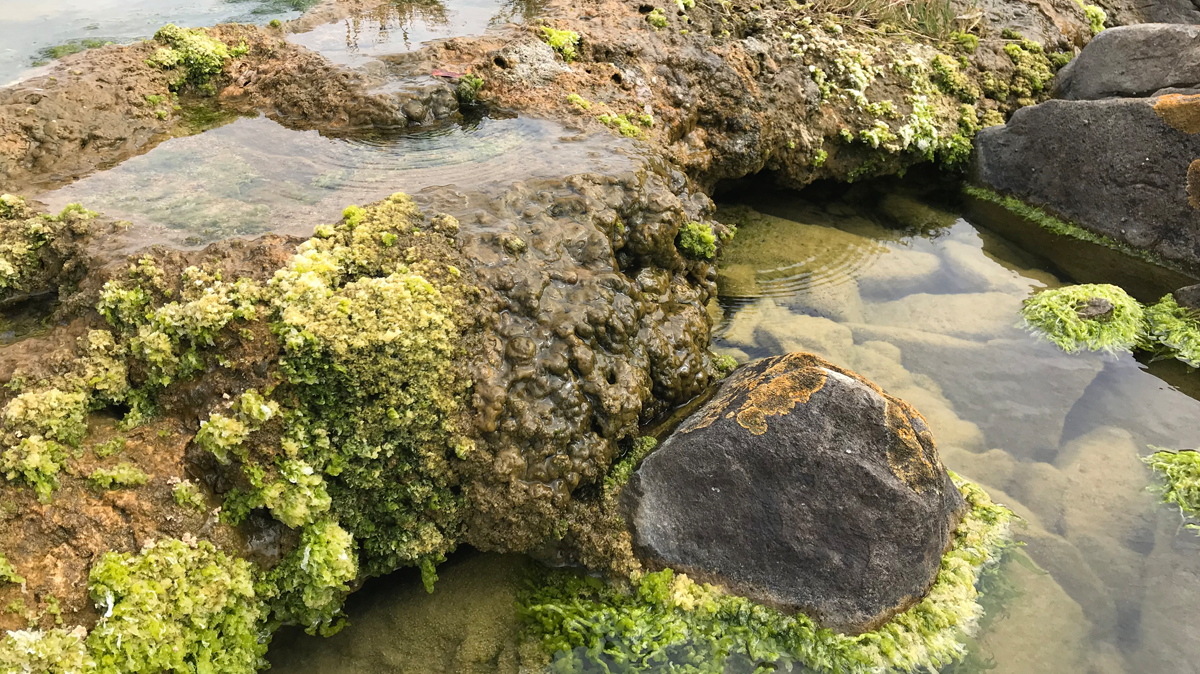
Rocks Formed by Microbes Absorb Carbon Day and Night
Microbialite ecosystems in South Africa stored an “astonishing” amount of carbon, according to new research.
Las olas de calor marinas lentifican el flujo de carbono de los océanos
Cuando el plancton se encuentra en agua caliente, la materia orgánica se estanca en la superficie e interrumpe el transporte de carbono hacia el fondo océanico.
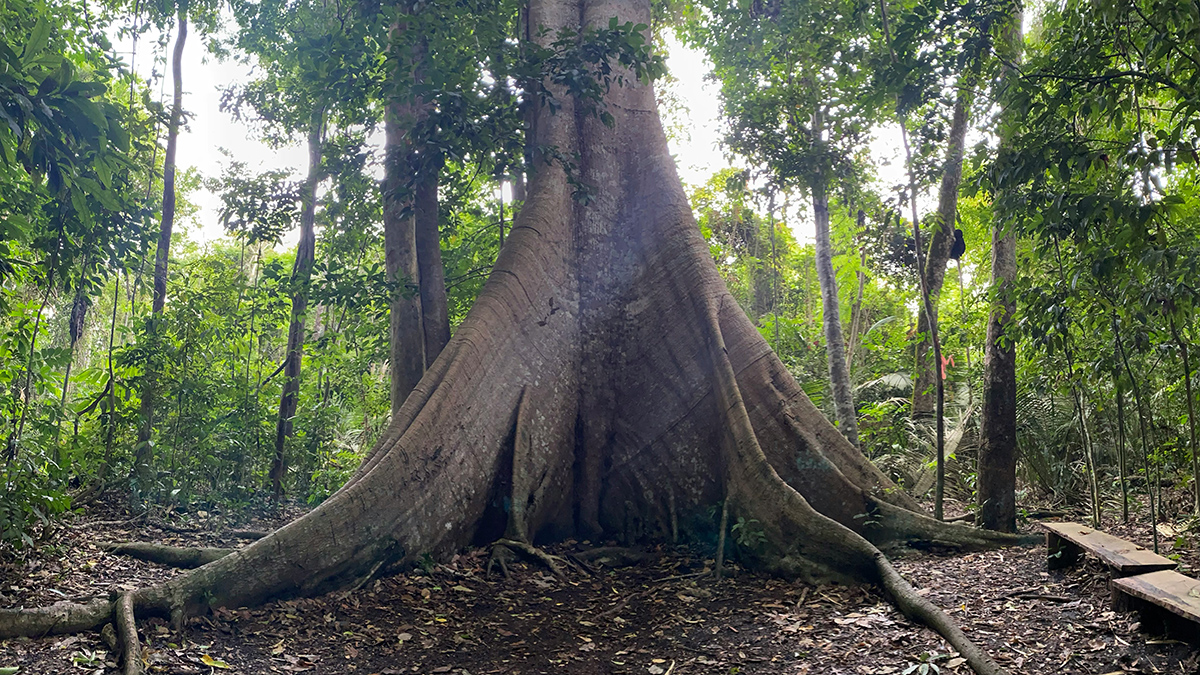
As CO2 Levels Rise, Old Amazon Trees Are Getting Bigger
New data show resilience among the rainforest’s giants, though scientists warn that nutrient limits and rising heat could end the trend.
Marine Heat Waves Slow the Ocean’s Carbon Flow
When plankton find themselves in hot water, organic matters stalls at the surface and disrupts transport of carbon to the deep ocean.
In Arctic Soils, Methane-Eating Microbes Just Might Win Out over Methane Makers
Methanotrophs, including those that capture methane from the air, seem to outcompete methanogens in dry environments, a new study shows.
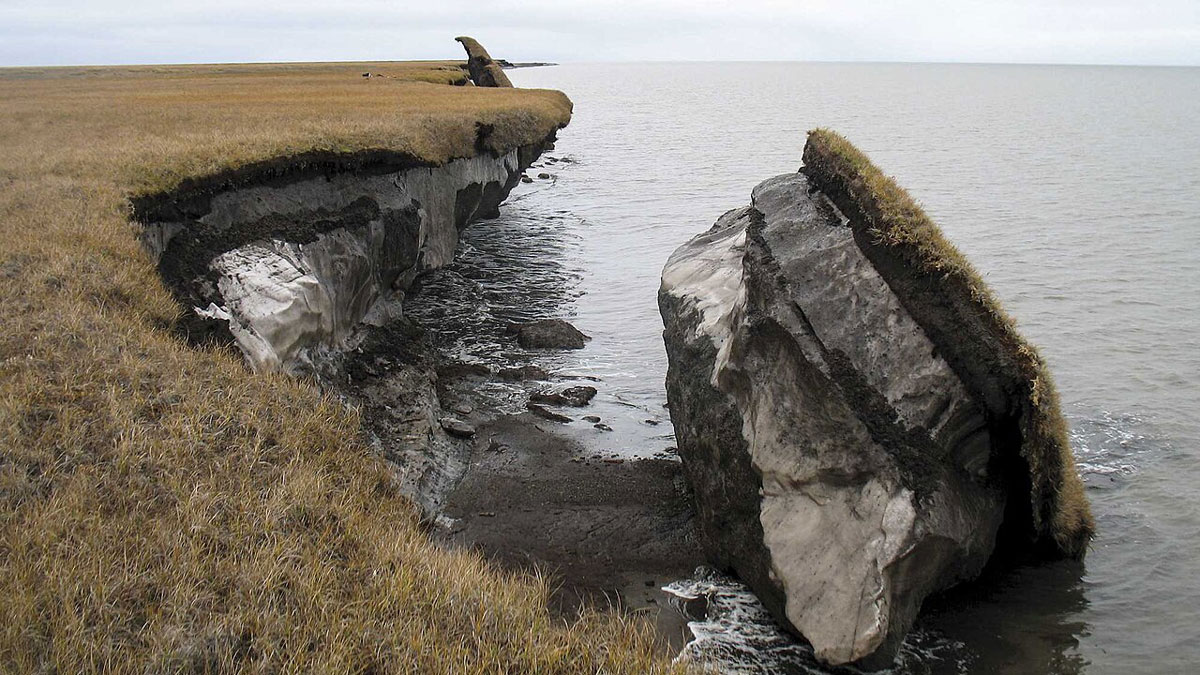
A medida que el Ártico se calienta, los suelos pierden nutrientes clave
El cambio climático calienta tanto el aire y el océano, como el suelo, donde los procesos clave que determinan la fertilidad y la captura de carbono operan en un delicado equilibrio.
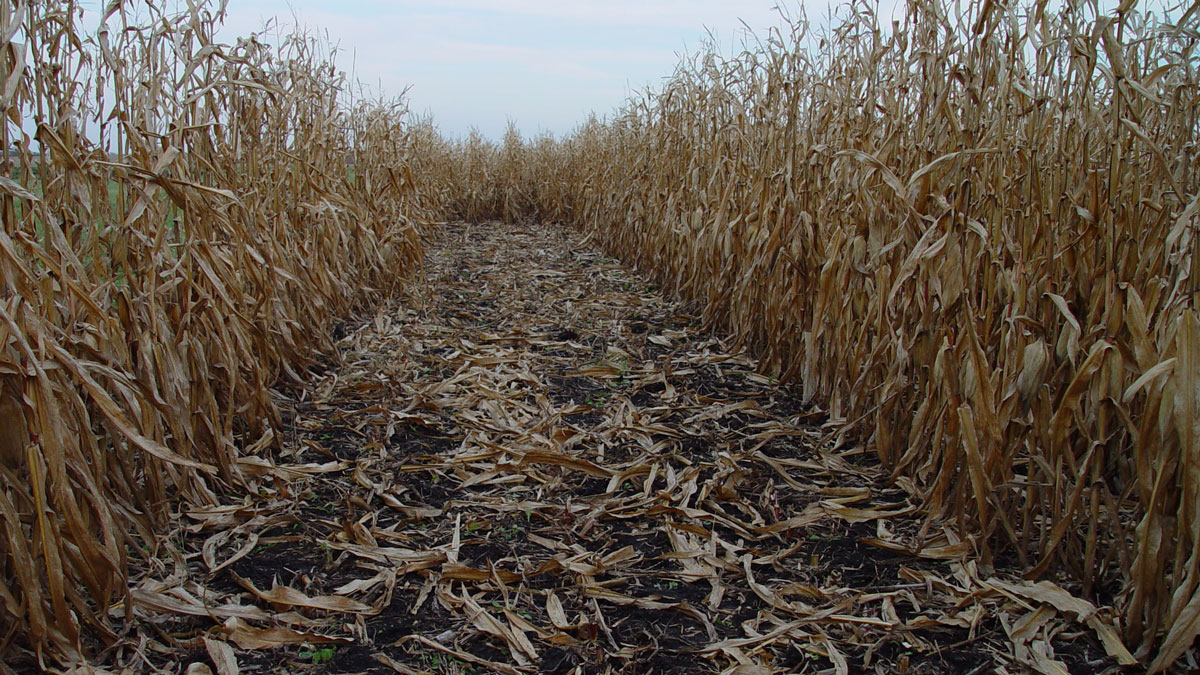
How Might Leftover Corn Stalks Halt Fugitive Carbon?
Bio-oil made from plant waste could help limit carbon emissions from orphaned oil and gas wells. But would it help or hinder farmers’ bottom line?