Movement of carbon from land to ocean and atmosphere plays an important, but understudied, role in the global carbon cycle.
carbon dioxide
Grow-Fast-Die-Young Strategy Increases Swiss Forest Biomass
Climate change and CO2 fertilization can increase both growth and mortality of trees. The net effect on forest biomass depends on that trade-off, which long-term studies in Switzerland reveal.
Marine Sediments Reveal Past Climate Responses to CO2 Changes
Climate records stored in marine sediments reveal different ice sheet and ocean responses to falling atmospheric CO2 concentrations from the warm Pliocene to the ice ages of the Pleistocene.
Our Evolving Understanding of Biological Carbon Export
The array of processes and organisms that make up the biological carbon pump has immense influence on Earth’s carbon cycle and climate. But there’s still much to learn about how the pump works.
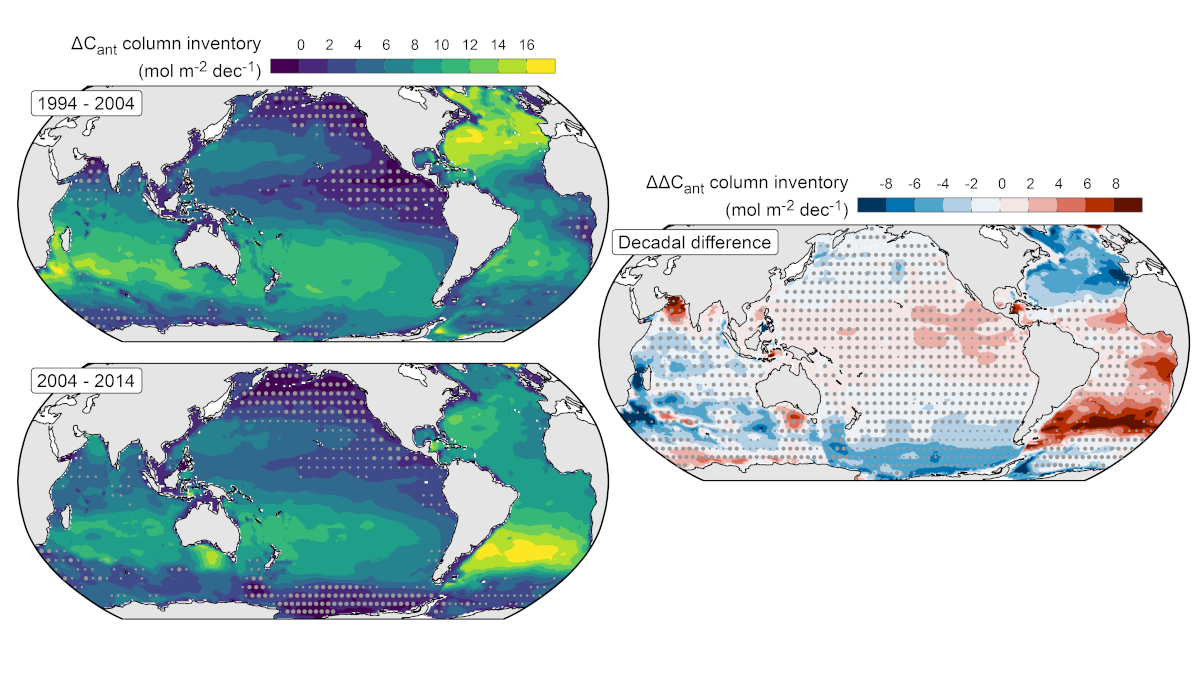
A Multidecadal View of Oceanic Storage of Anthropogenic Carbon
A decline in the ratio of ocean carbon accumulation to atmospheric carbon dioxide growth between 1994-2004 and 2004-2014 suggests a reduction in the sensitivity of the ocean carbon sink.
Thin Skin Helps Regulate Ocean Carbon Uptake
Cooler and saltier than even the water just below it, the ocean skin plays a critical role in ocean-atmosphere gas exchange.
An Open and Inexpensive ‘Fluxbot’ for Measuring Soil Respiration
An inexpensive system of automated gas sensors and open-source software, tested in a Kenyan savanna, will help democratize and expand science research on soil respiration.
Ambidextrous Microbes May Pump Out CO2 as Temperatures Rise
Certain microbes that engage in both photosynthesis and predation are more likely to do the latter as the planet warms, resulting in a net release of carbon dioxide.
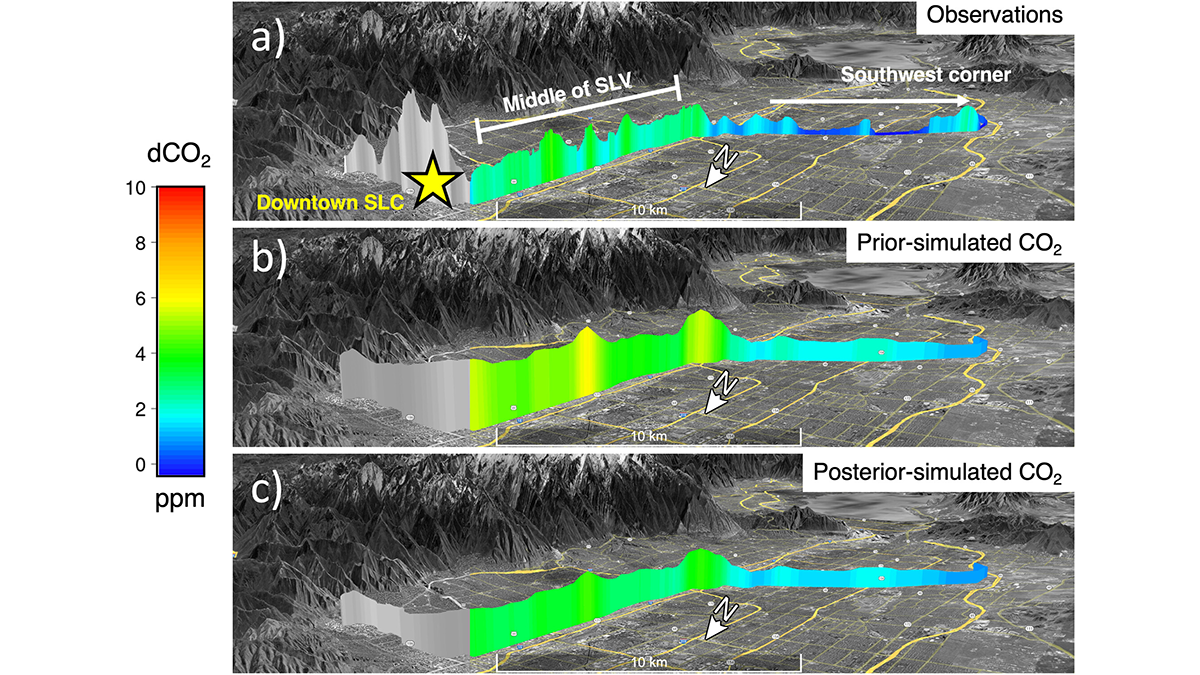
Tracking Human CO2 Emissions from Medium-Sized Cities
Atmospheric inverse models, combined with observations, successfully tracked modest CO2 emission reductions in Salt Lake City during the first COVID-19 lockdown in 2020.
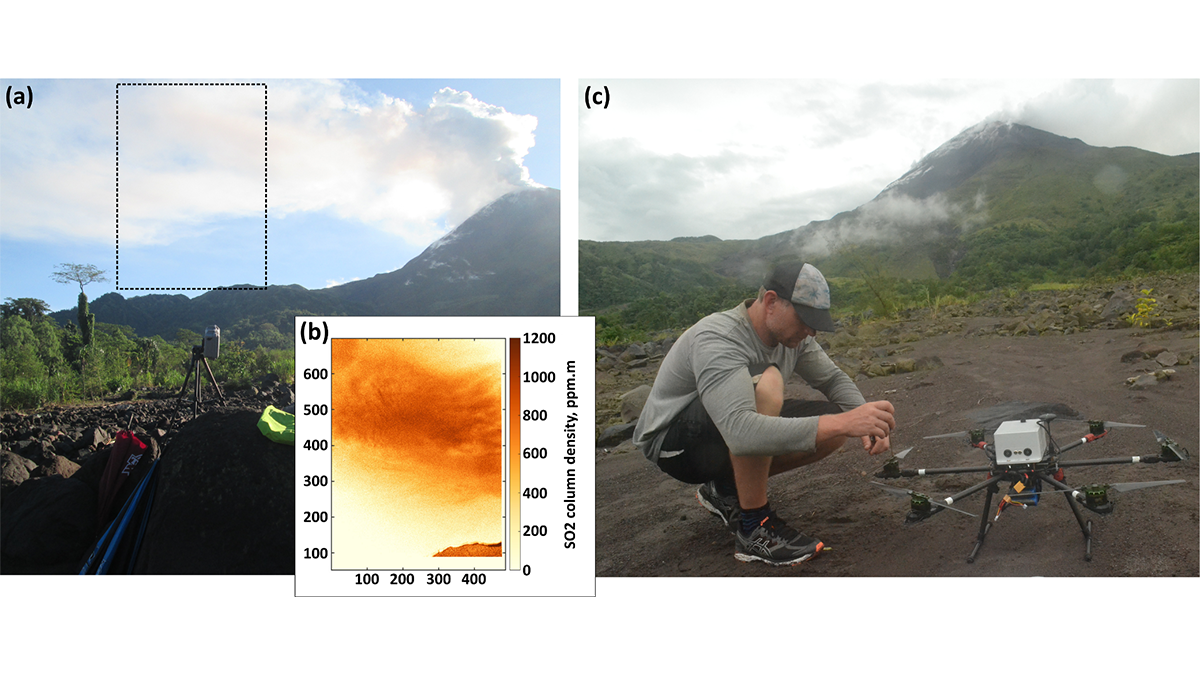
Send in the Drones: Safely Monitoring Volcanic Gas Emissions
New drone technology was combined with satellite and ground-based data to improve volcanic gas flux monitoring at the remote Bagana Volcano in Papua New Guinea.