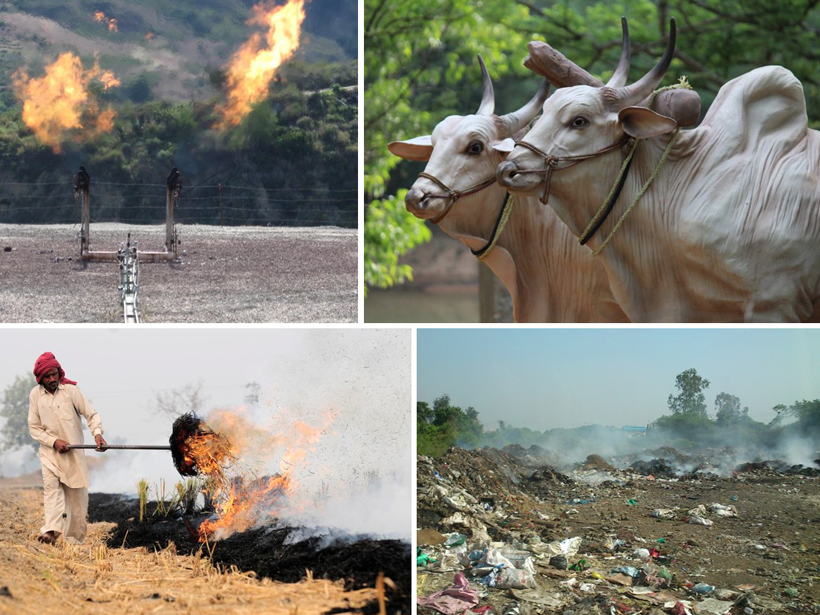
Reducing methane emissions is critical for addressing climate warming, but which are the easiest and most cost-effective ways to do this?
carbon emissions
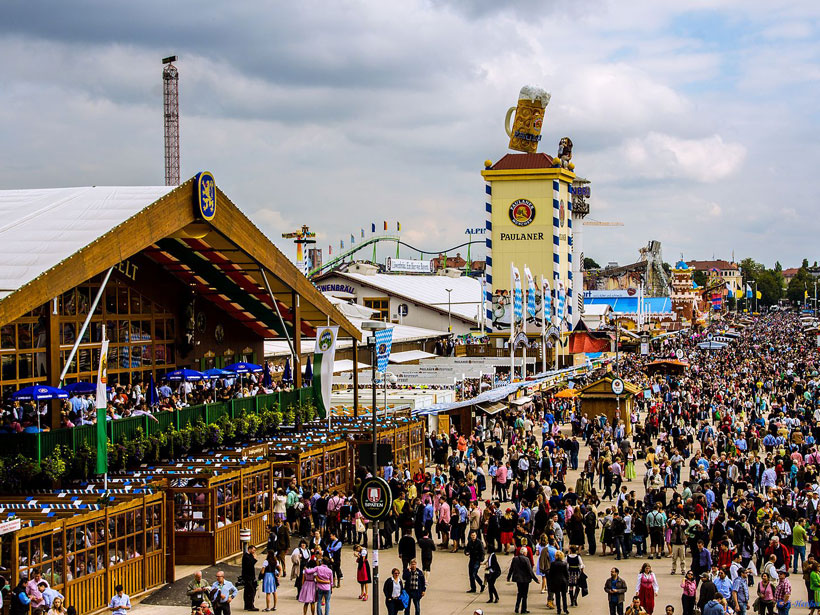
Oktoberfest’s Methane Rise Is the Wurst
Incomplete combustion and biogenic emissions—exhalations and flatulence—make Oktoberfest a significant, albeit temporary, source of the potent greenhouse gas.
How Modern Emissions Compare to Ancient, Extinction-Level Events
Researchers find that a pulse of volcanic activity spanning several hundred years released as much carbon dioxide into the atmosphere as anthropogenic emissions projections for the 21st century.
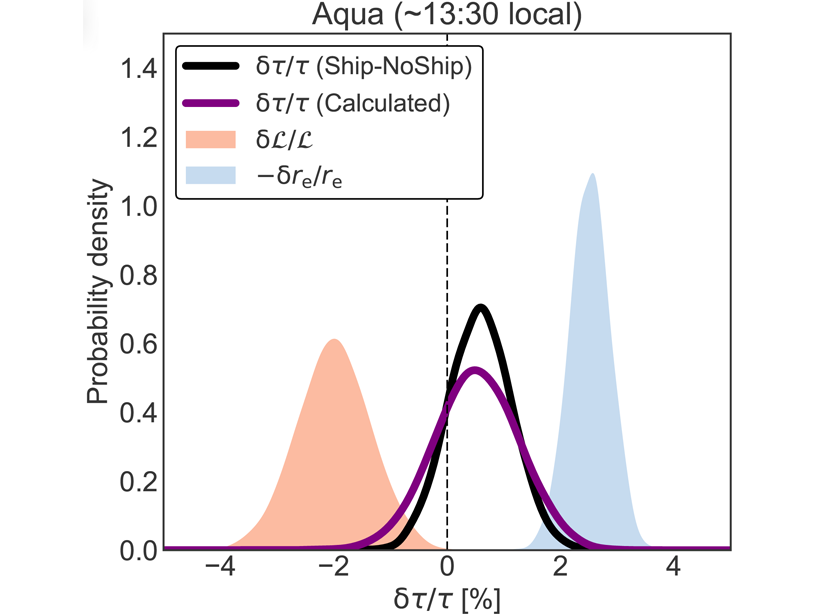
Quantifying Aerosol Effects on Climate Using Ship Track Clouds
A new methodology for measuring how human emissions influence cloud properties and radiative forcing developed by reconstructing cloud fields in maritime shipping lanes.
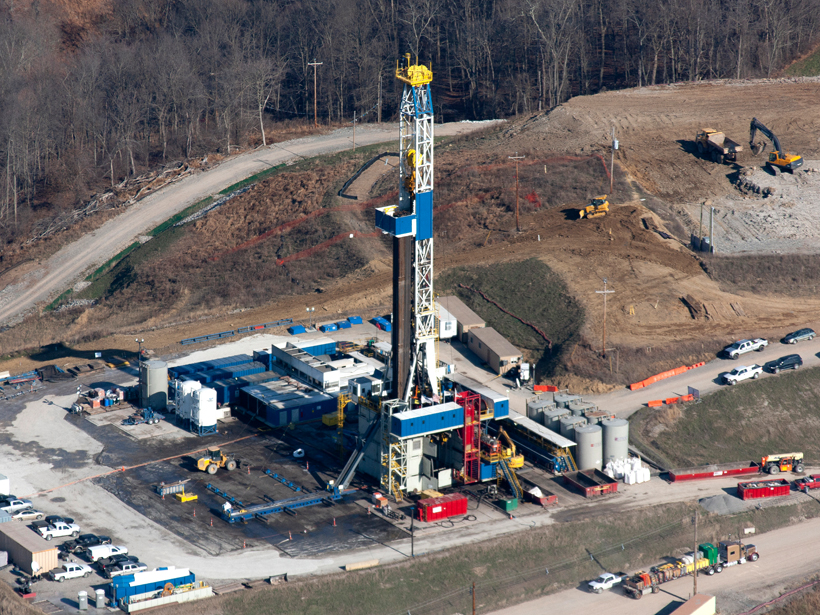
How Death and Disaster Followed the Shale Gas Boom in Appalachia
In the past decade, fracking has contributed to the deaths of more than a thousand people and the emission of more than a thousand tons of carbon dioxide in the Appalachian Basin.
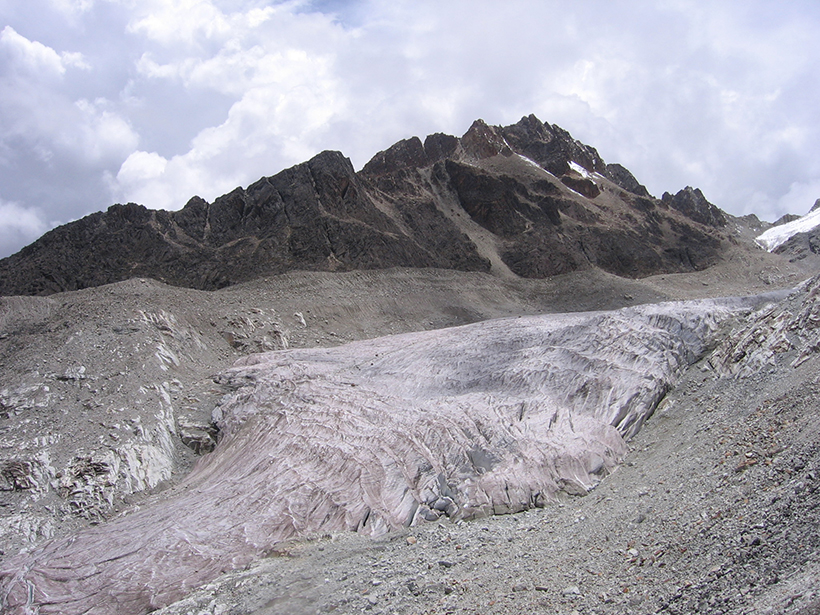
Los Incendios del Amazonas Contribuyen al Derretimiento de los Glaciares Andinos
Investigaciones recientes revelan que las emisiones de carbono negro producidas por los incendios en el Amazonas causan que los glaciares en los Andes absorban más radiación solar y se derritan más.
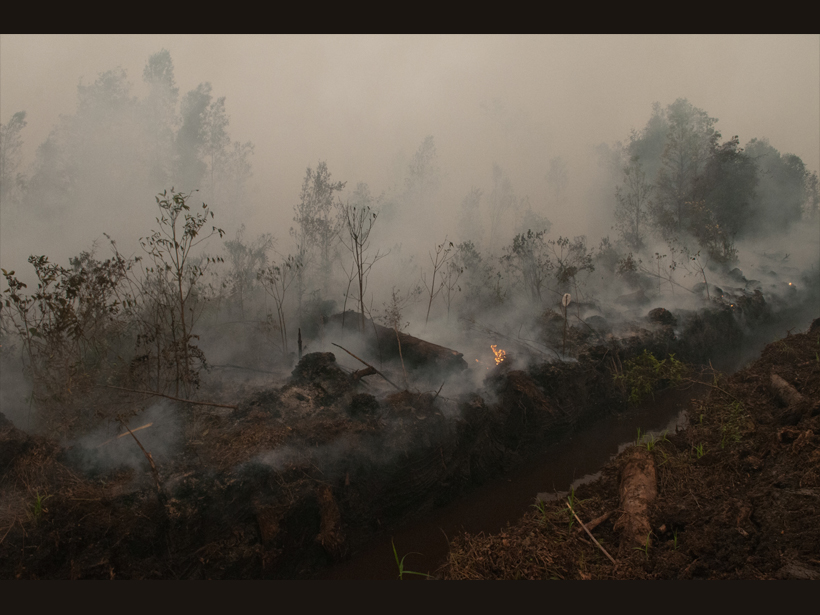
Starting (and Stopping) a Fire to Study It
Fire experiments on peatlands in Southeast Asia have identified previously unknown emissions patterns and could point to ways to detect these smoldering fires before they become too big to fight.
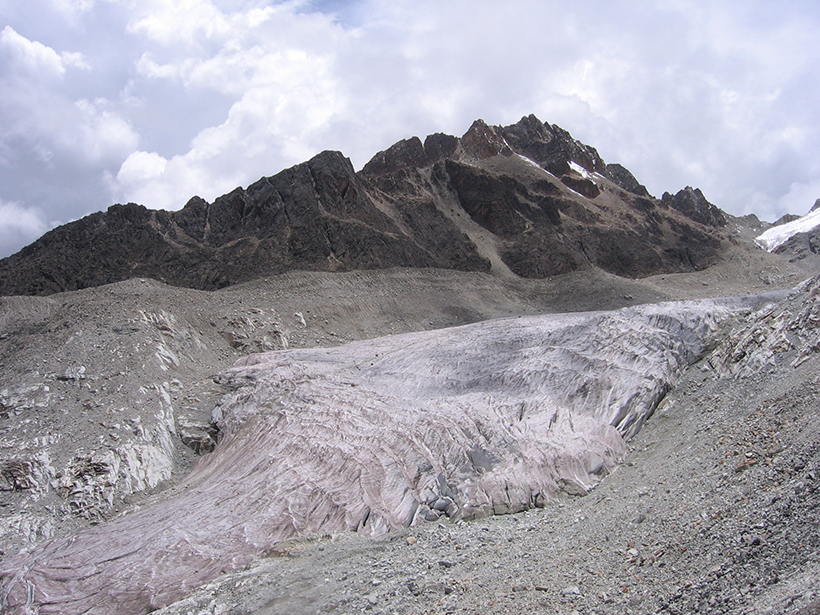
Amazon Fires Contribute to Andean Glacier Melting
New research finds that black carbon emissions produced by fires in the Amazon cause glaciers in the Andes to absorb more sunlight and melt more.
2020 Hindsight: A Website for All Paleo-CO2 Data
A new website will soon compile and display all ancient atmospheric CO2 data.
Fugitive Gas Abetted by Barometric Pressure
Barometric pressure, in addition to factors such as lithology and the depth of the water table, can influence patterns of natural gas that escapes to subsurface soils.