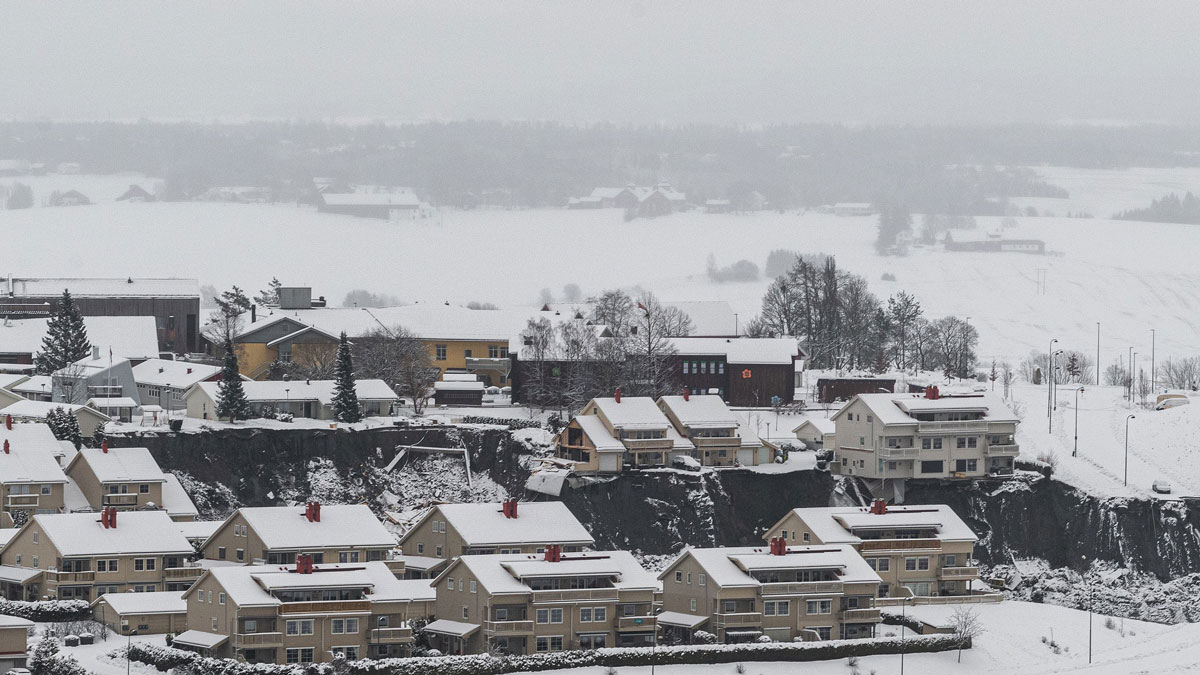
In a quick clay landslide, solid soil liquefies suddenly, sometimes washing over entire towns. New modeling examines what kinds of salts could help stabilize these clays.
clays
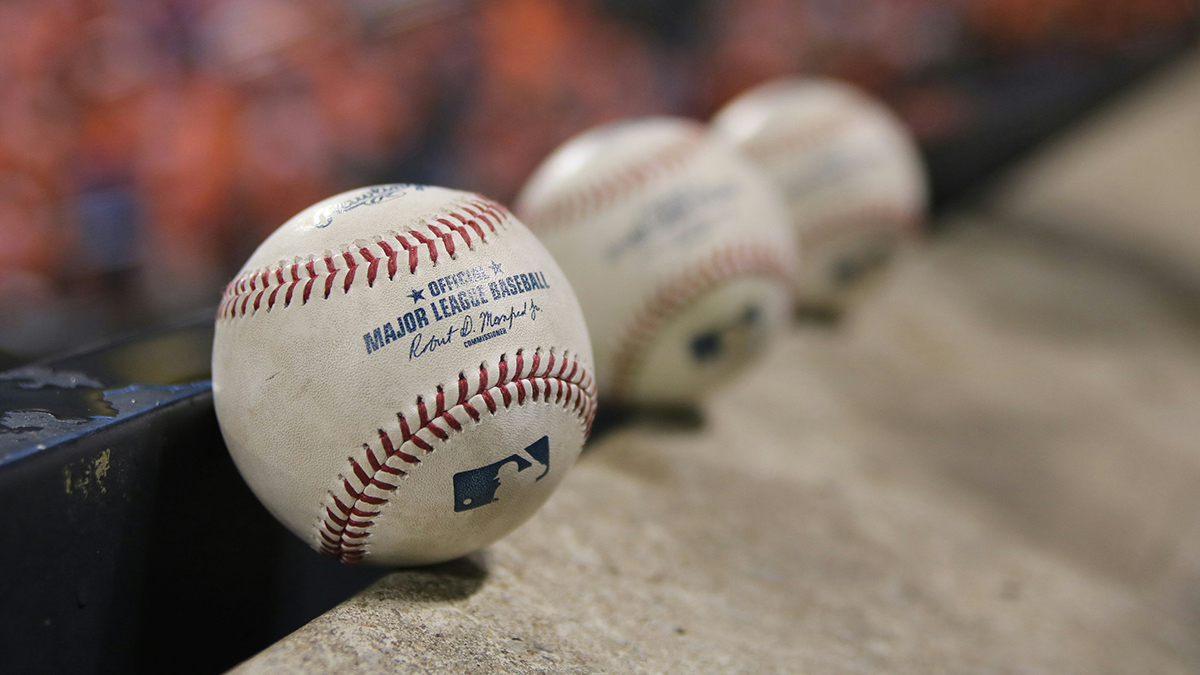
Geoscientists Demystify Baseball’s Magic Mud
Taking baseball’s mysterious Rubbing Mud into the lab revealed no magic ingredients—but plenty of useful natural properties from geomaterials.
Uma Ilha Tropical Há Muito Perdida Fica no Litoral do Brasil
Um platô vulcânico submerso no sudoeste do Atlântico foi uma ilha tropical há 45 milhões de anos.
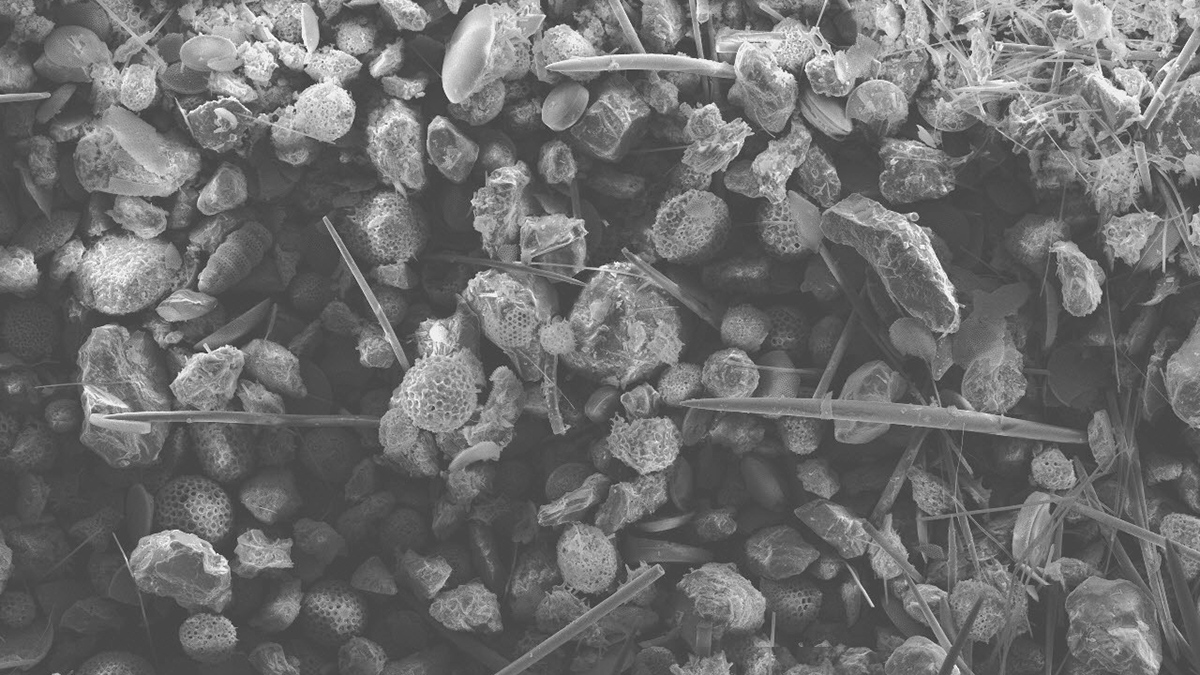
Clays May Have Slowed Earth’s Recovery After the Great Dying
Without tiny marine organisms using silica for shells, Earth’s oceans generated more clay, released more carbon dioxide, and kept Earth warmer for longer.
A Long-Lost Tropical Island Lies Off Brazil’s Coast
An undersea volcanic plateau in the southwestern Atlantic was a tropical island 45 million years ago.
Extreme Lithium Isotope Fractionations During Intense Weathering
Extreme lithium fractionation is observed when primary minerals in andesite are transformed to secondary clay minerals and then to oxides with intensive chemical weathering in a tropical climate.
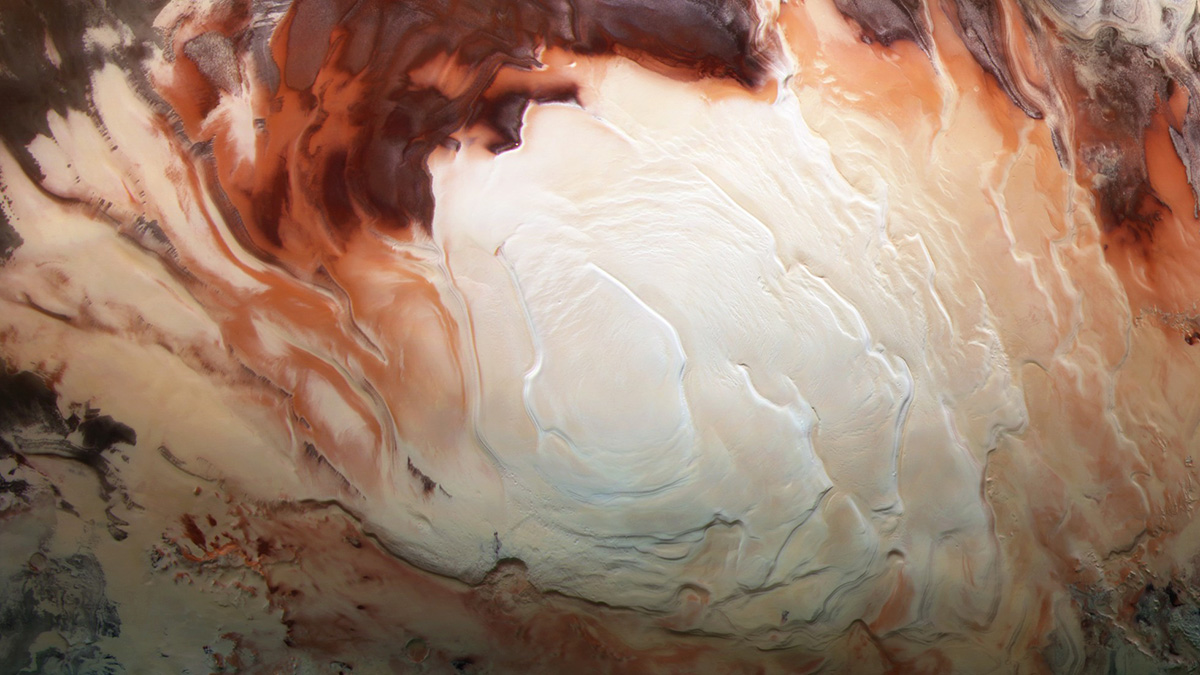
The Bumpy Search for Liquid Water at the South Pole of Mars
Studies since 2018 have provided competing explanations of bright radar reflections from the base of the south polar ice cap.
Clay Type, Not Just Content, Crucial for Fault Zone Permeability
Faults containing clays are often considered as barriers to fluid flow but new work shows that fault processes leading to the formation of clays can increase permeability relative to the host rock.
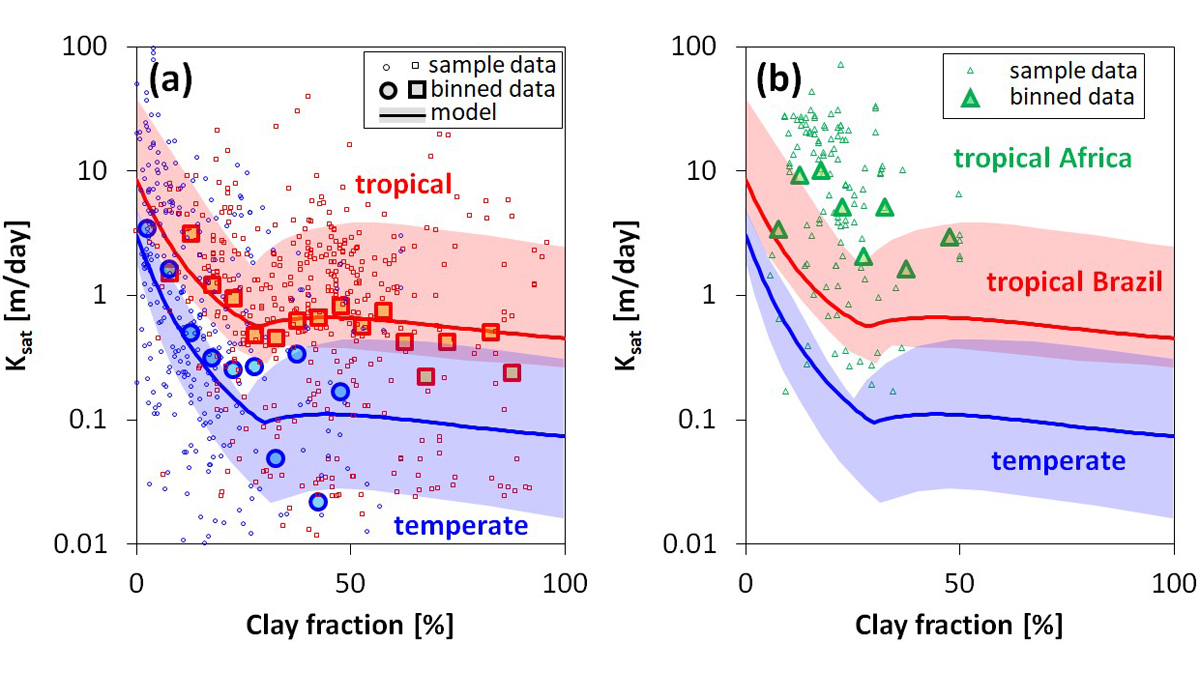
Not All Clays are Made Equal – and it Matters for Hydrology
Soil clay content is an important characteristic that affects many hydraulic and mechanical properties of soil; clay mineral type is important for their prediction.
Tracking Reverse Weathering
Using beryllium isotopes to track in situ formation of clays in the ocean, known as reverse weathering, will improve global models of atmospheric carbon dioxide and ocean alkalinity.