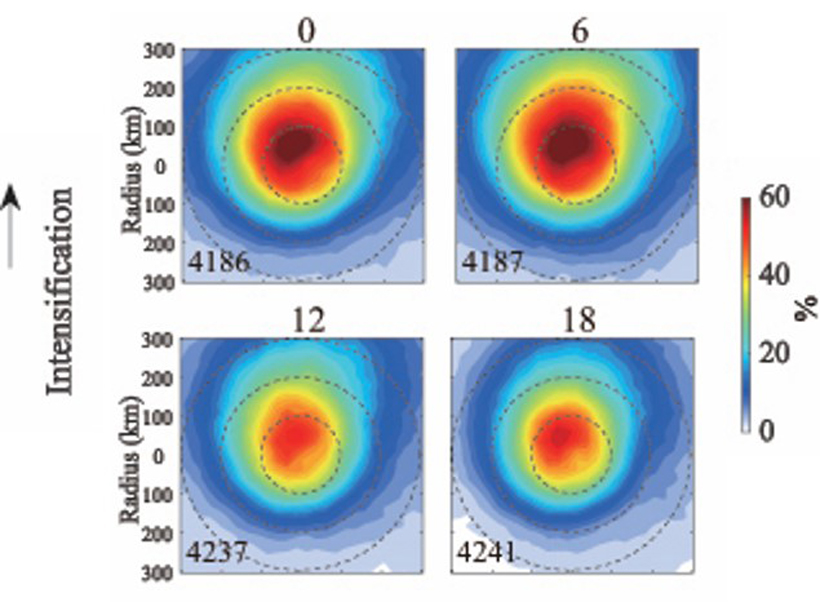
The diurnal variations of tropical cyclone intensification and decay are analyzed using satellite data for deep convective clouds.
hurricanes, typhoons, & cyclones
Post-Tropical Cyclones Influence on European Windstorm Risk
Comparing the importance of midlatitude cyclones and post-tropical cyclones on European windstorms during the Atlantic hurricane season using ERA-5 reanalysis.
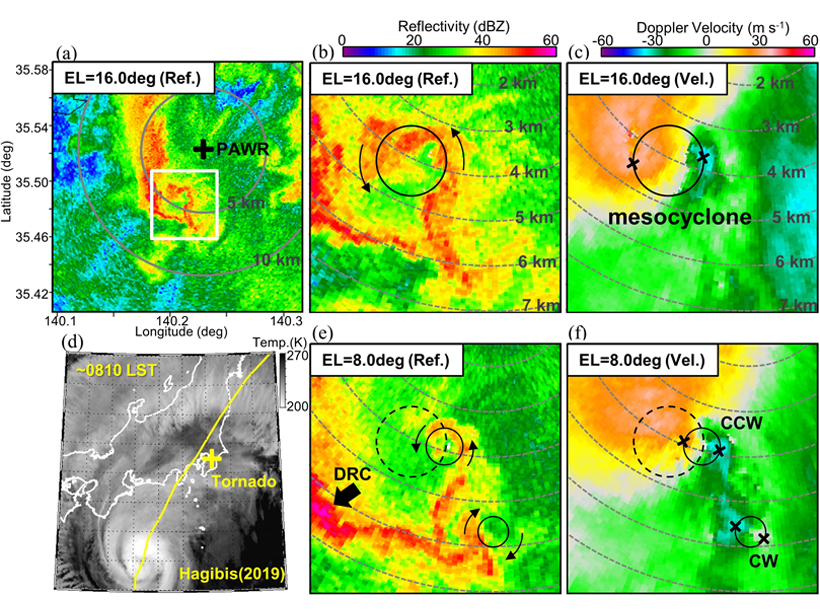
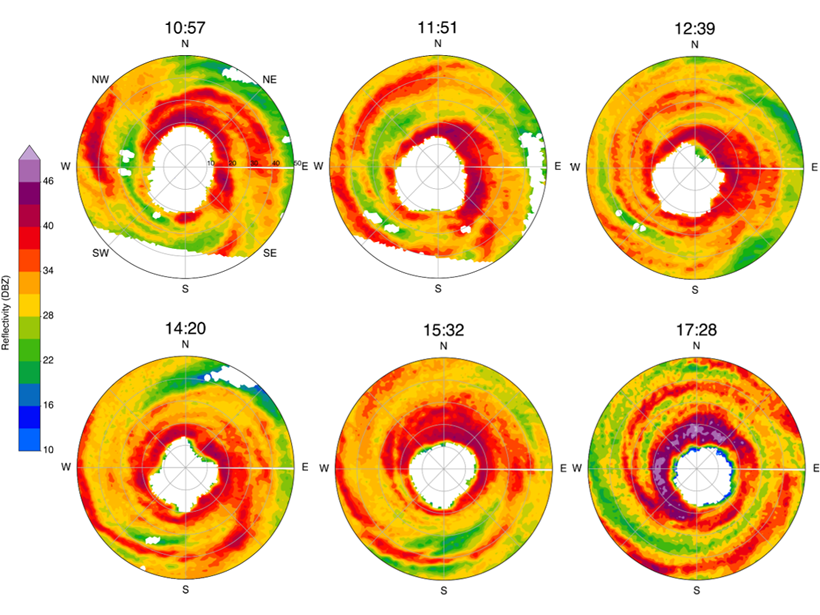
Radar Observations of a Tornado Associated with Typhoon Hagibis
Analysis of tornadogenesis processes on a shallow supercell associated with Typhoon Hagibis using finely resolved rapid-scan radar observations at a very close range.
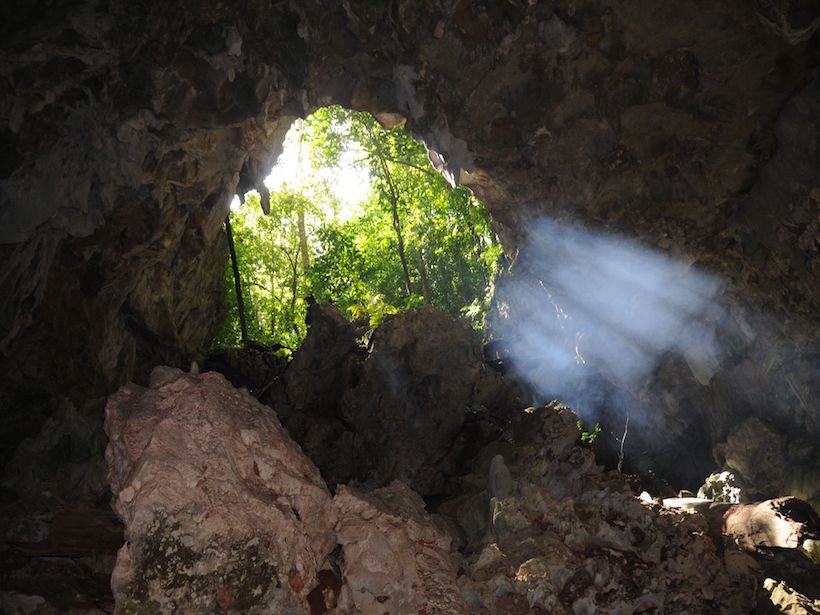
Bat Guano Traces Changes in Agriculture and Hurricane Activity
Researchers hiked and rappeled into two caves in Jamaica to collect over 40 kilograms of excrement.
Tropical Cyclones Suppress Rainfall in Their Wakes
Passing storms dredge up colder ocean water, curbing evaporation and decreasing cloud coverage and rainfall for weeks, satellite data reveal.
What the Upper Ocean Looks Like During a Hurricane and Why It Matters
High-resolution measurements reveal the structure of the upper ocean under a hurricane and its feedback on storm intensity.
The Evolution of Observed Hurricane Eyewall Shapes
The observational evidence of the wind field of Hurricane Michael using radar imagery showed an eyewall structure evolution with elliptical, triangular, and square shapes for the first time.
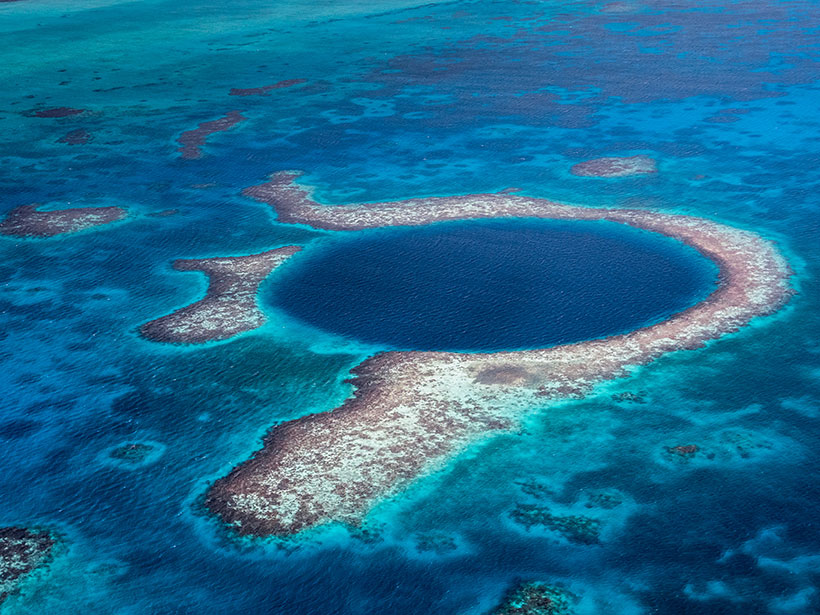
Severe Cyclones May Have Played a Role in the Maya Collapse
Sediment cores from the Great Blue Hole reveal that a series of extreme storms hit the region after 900. The storms may have irreparably damaged an already stressed Maya population.
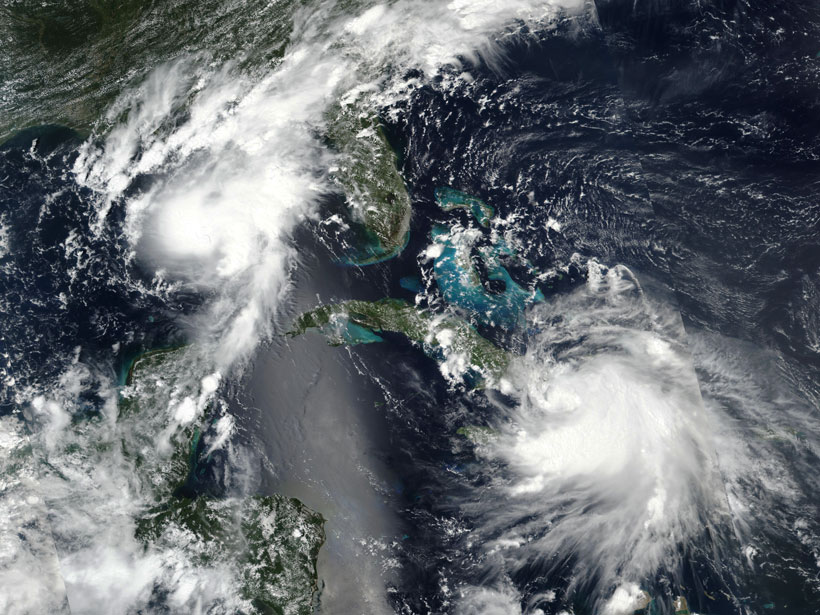
Storms Interact but Rarely Merge into Bigger Tempests
The Fujiwhara effect—complex interactions between large storms nearby each other—can steer hurricanes and tropical storms but doesn’t typically create colossal tempests.
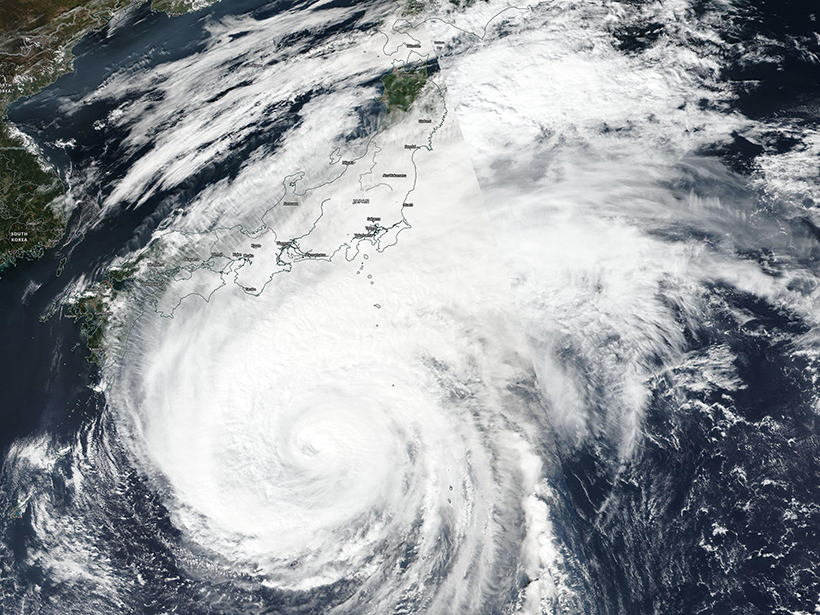
Typhoons Getting Stronger, Making Landfall More Often
New research shows a growing threat from Pacific storms amid climate change.