Pulses of activity, from tides to precipitation swings, play a crucial, changing role in ecosystems worldwide.
deserts
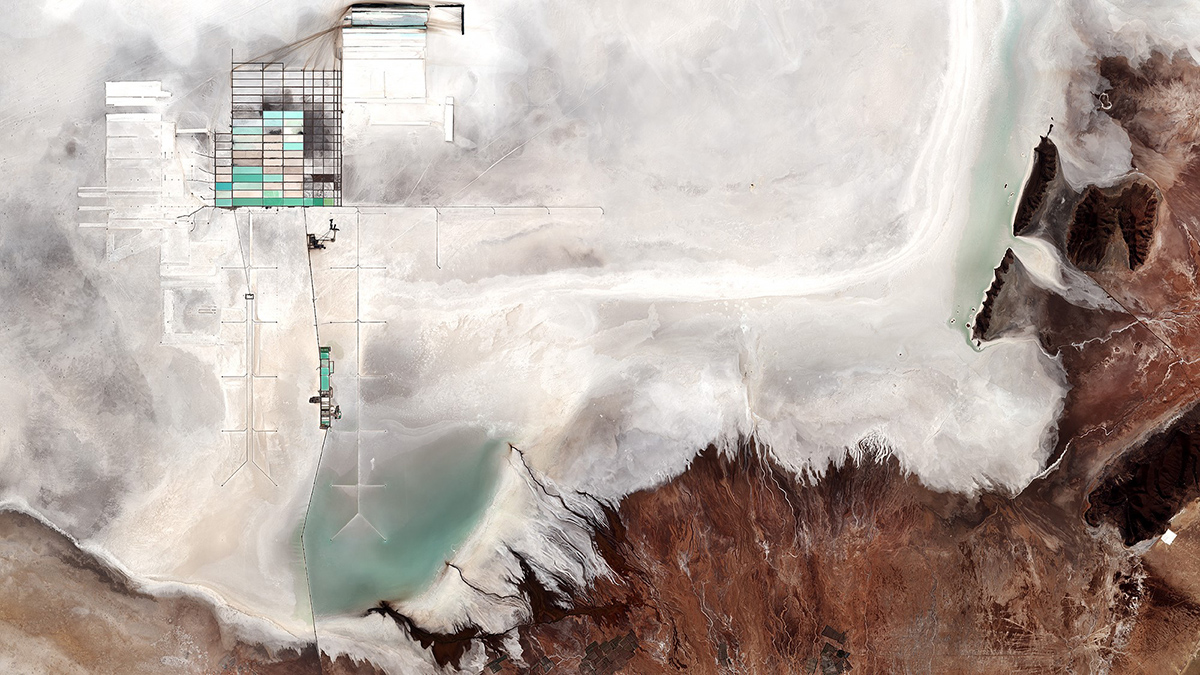
Preocupaciones sobre el litio, el agua y el clima en los dos desiertos más altos de la Tierra
La extracción de salmuera para satisfacer la demanda de recursos en medio de la transición a energías renovables está afectando los recursos hídricos en Sudamérica y China. Los hidrólogos pueden ayudar a comprender cómo y a sumarse a la búsqueda de soluciones.
Why the Southern Alps Turned Red During the Summer of 2019-2020
Snow on the Southern Alps turned from white to red in 2019-2020. New geochemical evidence points to the color change resulting from red Australian desert dust carried across the Tasman Sea.
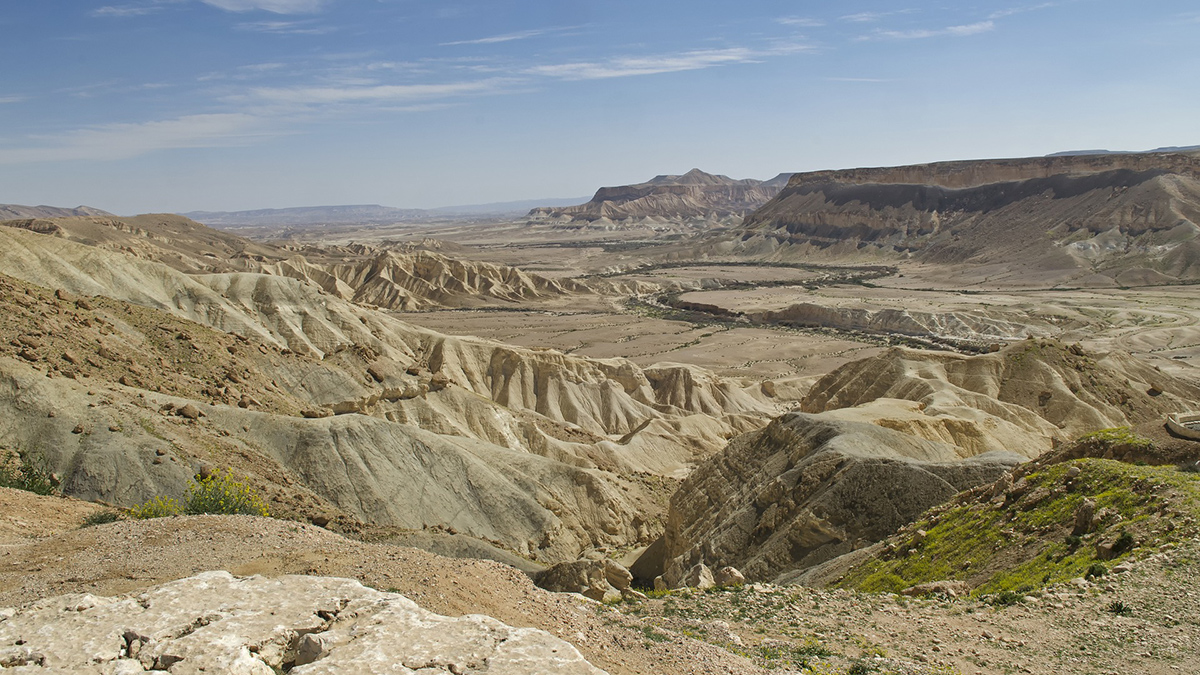
Climate Shifts Drive Episodic Drainage Changes
Drainage divide migration is influenced by tectonics and climate over long periods. New research in Israel shows that even shorter-term wet-dry cycles can move divides.
Lots of Dust Gets Sucked Up by Jet Engines
Changing flight times and holding altitudes could substantially reduce the amount of wear-inducing dust ingested by jet engines.
Concerns over Lithium, Water, and Climate in Earth’s Two Highest Deserts
Brine mining to meet resource demands amid renewable energy transitions is affecting water resources in South America and China. Hydrologists can help understand how and join the search for solutions.
Rainstorm Intensity Drives Desert Landscape Evolution
New mathematical models show that the persistence of near-vertical cliffs in arid landscapes is maintained by infrequent, but high-intensity rain storms.
Desert Landscape Evolution Controlled by Storm Intensity
A new study in the Negev Desert finds that long-term erosion of a desert escarpment occurs in drier areas where intense storms are most frequent.
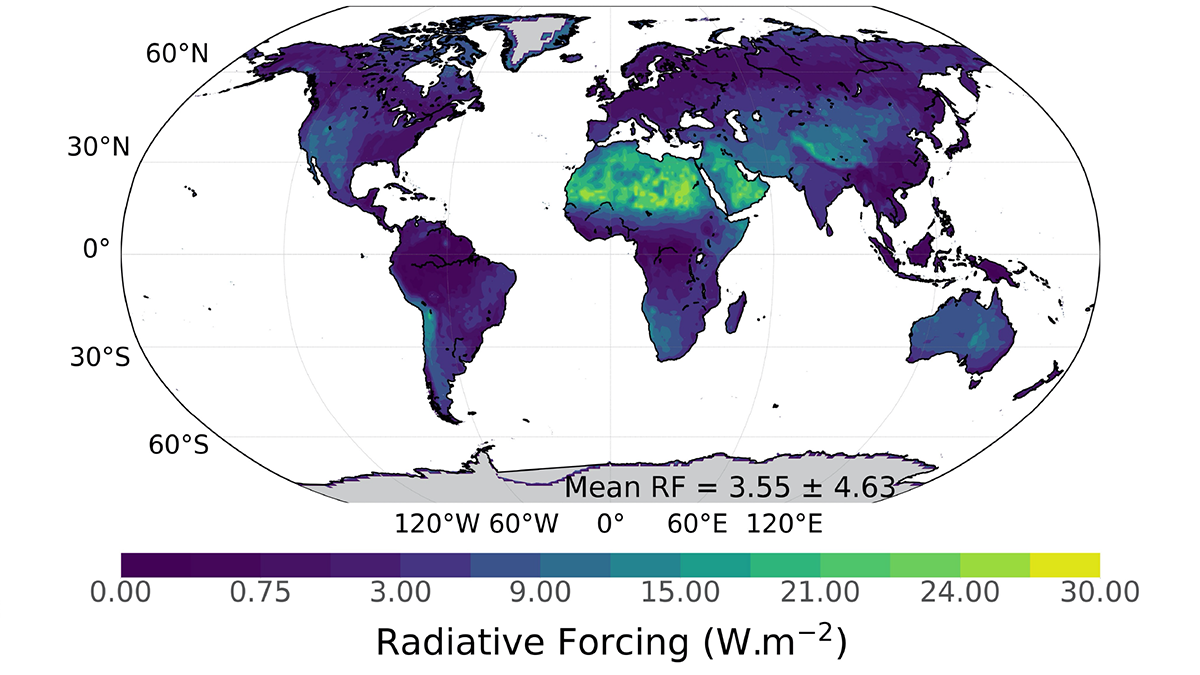
Sensing the Color of Soil for Climate Modeling
The color of soil reflecting the Sun’s rays affects the Earth’s climate and water cycle. Using satellite data that senses many wavelengths improves soil reflectivity estimates, especially in deserts.
Solar Panels Nurse Desert Soil Back to Life
Cultivating delicate soil crust in the shade of solar panels might boost the recovery of arid land.