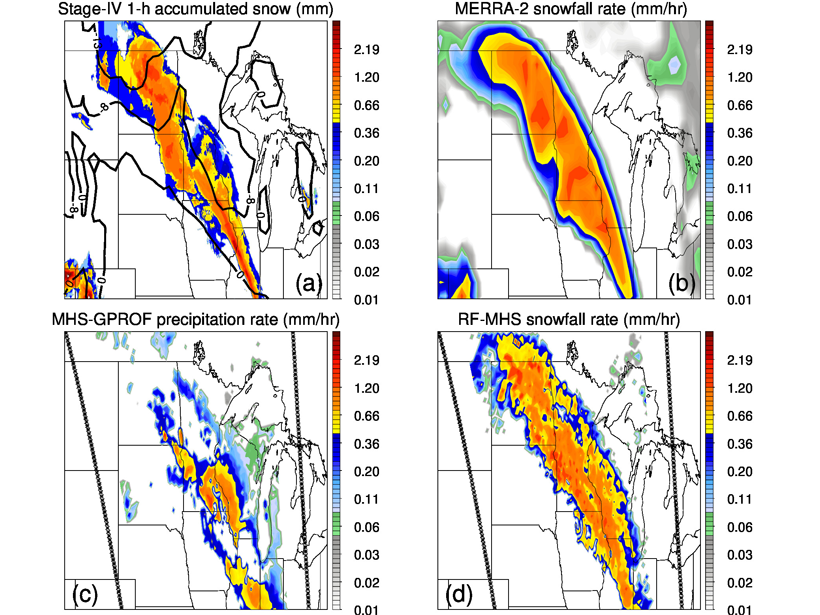
Machine learning is used to retrieve global snowfall occurrence and rate from satellite-based passive microwave sounder observations, trained by snowfall data from a high-quality space borne radar.
Earth and Space Science
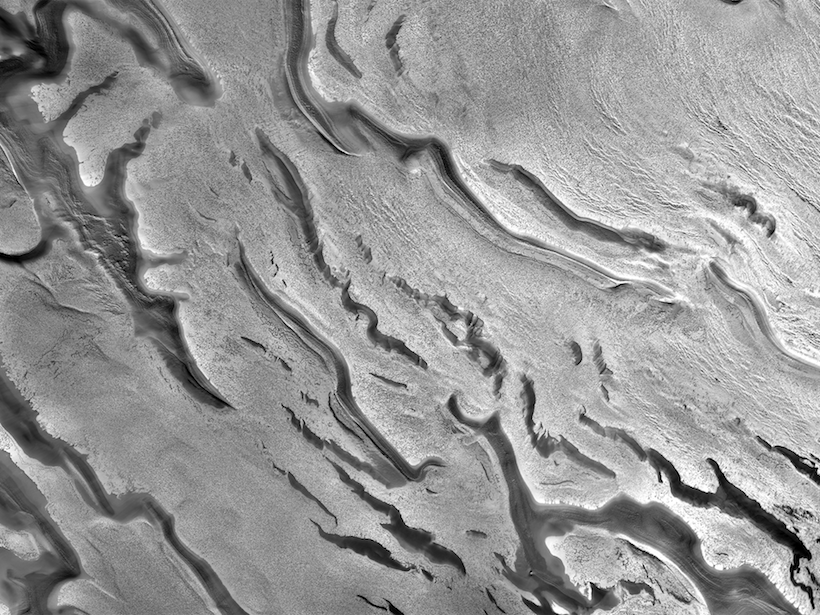
A Precise Mosaic View of Mars’s South Pole
A new workflow improves the process of creating massive, accurate mosaics from spacecraft-captured images of a planet’s surface.
Zero-valent Iron in the Oxidizing Atmosphere?
A comparative study of urban, semi-urban, and rural sites reveals that the species of atmospheric iron varies depending on location.
Up Close with an Active Asteroid
A new journal special collection investigates the ejection of particles from the asteroid Bennu and the implications of these observations for asteroid science.
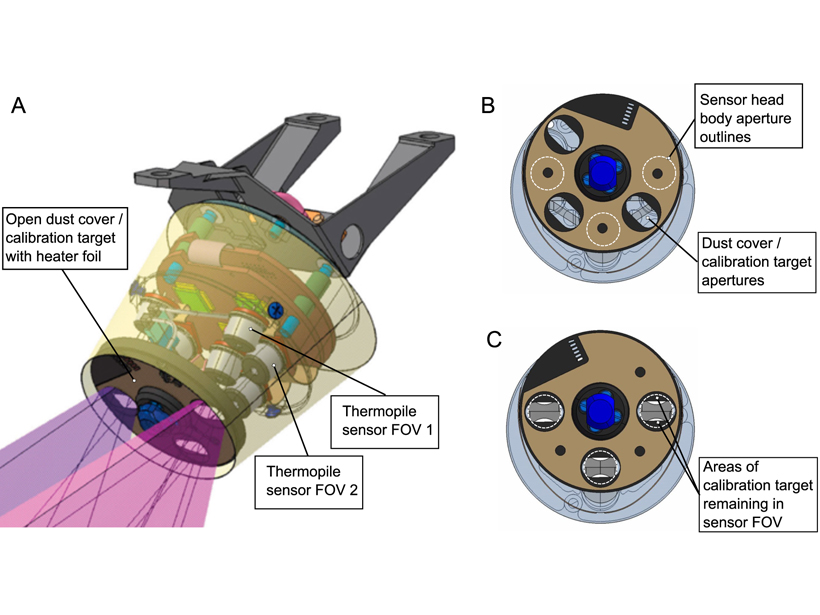
Insights from Calibration of the HP³ Radiometer on InSight
A detailed analysis of Heatflow and Physical Properties Package Radiometer on the Mars InSight lander, including changing instrument sensitivity and calibration coefficients.
Who Wants to Count All the Craters on Mars? Not Me!
Humans found hundreds of thousands of craters on Mars greater than 1 kilometer in diameter, but now computers automate the process delivering crater counts as well as geologically meaningful ages.
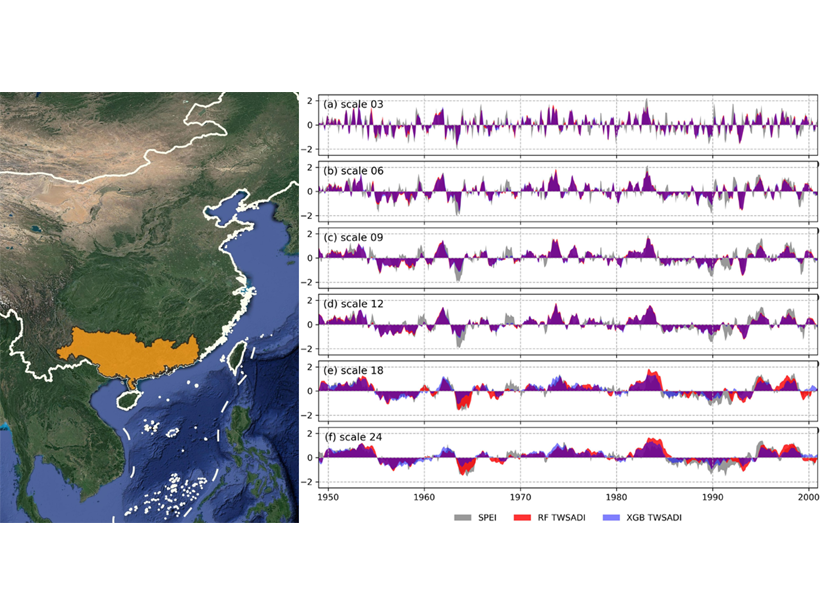
Ensemble Learning Estimates Terrestrial Water Storage Changes
Ensemble learning models for estimating past changes of terrestrial water storage from climate are presented and tested in the Pearl River basin, China.
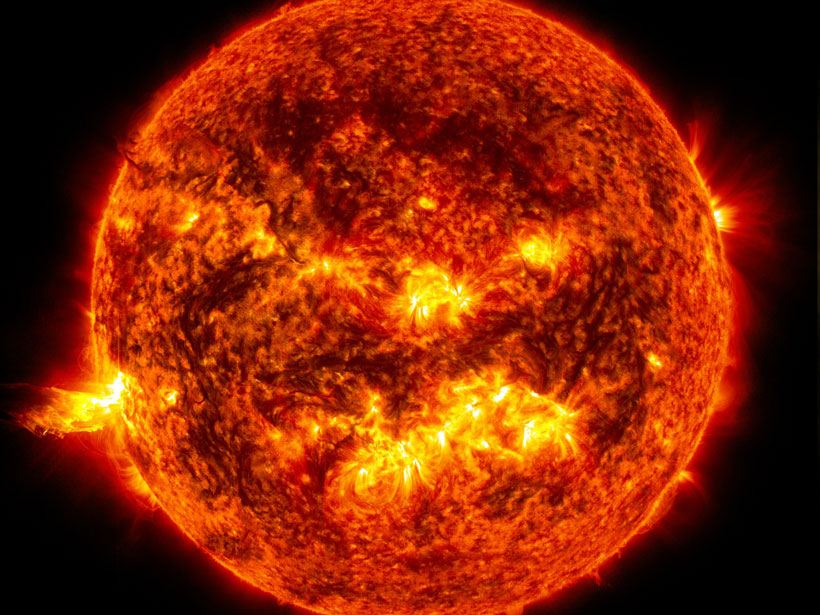
How Accurate Are Our Measurements of the Sun’s Energy?
As instruments collecting solar data degrade, researchers must correct for errors. A new study compares several methods to correct solar spectral irradiance measurements.
Mapping Martian Dunes from Orbit
New research shows how fast the sands shift on the Red Planet and how useful imagery from different orbiting cameras can be in studies of Mars’s dunes.
Evaluating Cloud Cover Predictions in Climate Models
A new analysis highlights progress in predictions of cloud cover from models that are part of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project.