火星上甲烷的峰值可能来自盖尔陨石坑内部,NASA的“好奇号”探测器目前正在那里进行探测。
Earth and Space Science
The Mystery of Methane on Mars Thickens
Two recently published papers zoom in on the mystery source of methane in the Martian atmosphere.
Introducing the New Editor in Chief of Earth and Space Science
Find out about the person taking the helm of Earth and Space Science and her vision for the coming years.
Scientists Turn Back Time to Track Methane Emissions on Mars
Period spikes of methane on Mars could originate inside Gale crater, where NASA’s Curiosity rover is currently exploring.s
Machine Learning Algorithms Help Scientists Explore Mars
Researchers applied machine learning algorithms to several distinct chemical compositions of Mars and suggest that these algorithms could be a powerful tool to map the planet’s surface on a large scale.
Polar Vortex Linked to Atmospheric Circulation at Daily Scale
A simplified representation of polar vortex at monthly scale was revised using a new method, and its daily association with air-sea teleconnections was analyzed to study weather impacts.
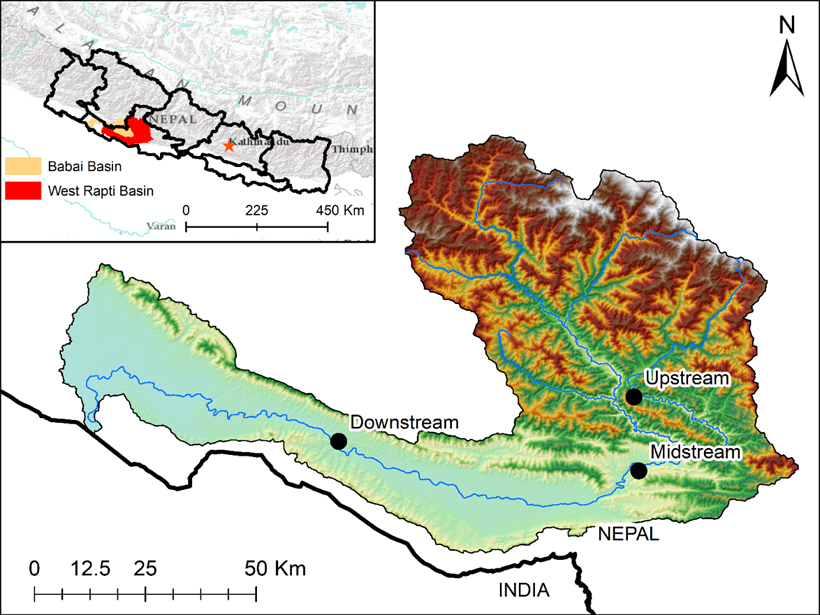
Satellite Estimates for Hydroclimatic Extremes
A new study corrects poor-performing satellite-based rainfall estimates with gauge data and also fills gauge data gaps using well-performing satellite-based rainfall estimates.
Understanding and Anticipating Induced Seismicity
A new special collection in JGR: Solid Earth and Earth and Space Science seeks papers from across disciplines that provide insights into induced seismicity at different spatial and temporal scales.
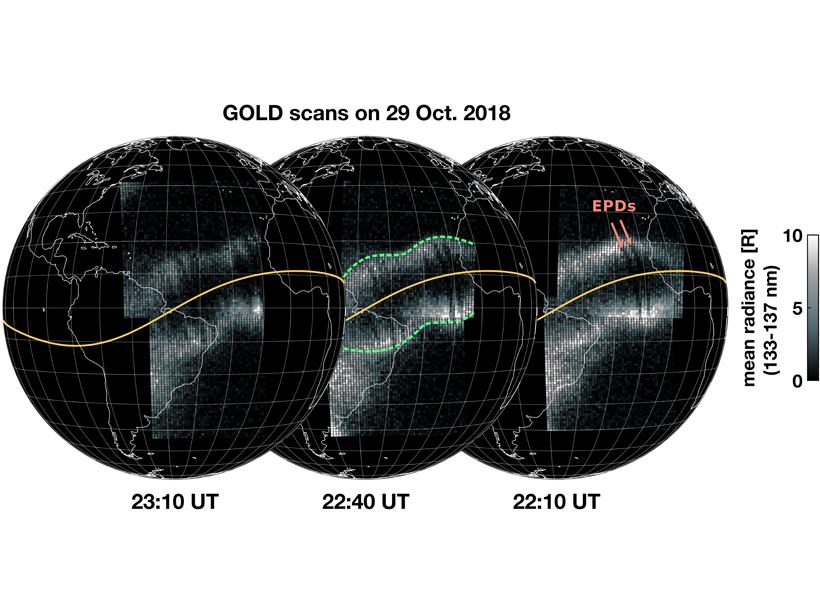
GOLD Sees Quasi-Stationary Waves in the Nighttime Ionosphere
The wave-like features in the pre-midnight ionosphere are not moving, vary strongly from day-to-day, and are often associated with the equatorial plasma bubbles, but their origin is still unknown.
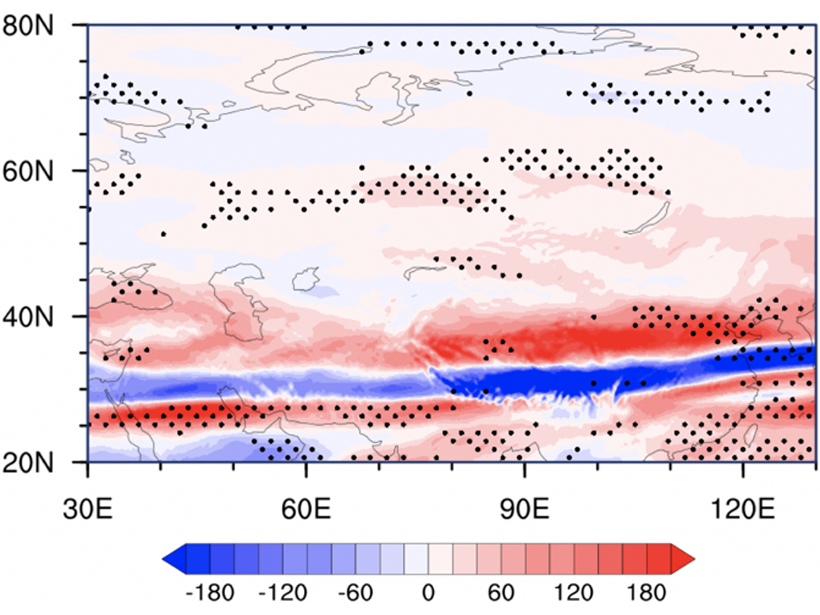
Global Warming Intensifies Turbulence Over Northern Eurasia
A significant increasing trend of turbulence in upper atmosphere over northern Eurasia is attributed to intense anthropogenic activities.