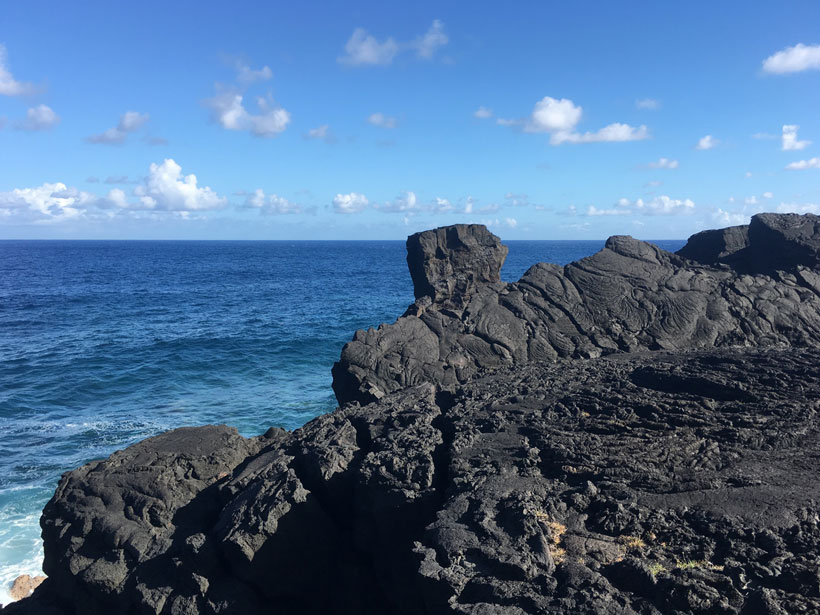
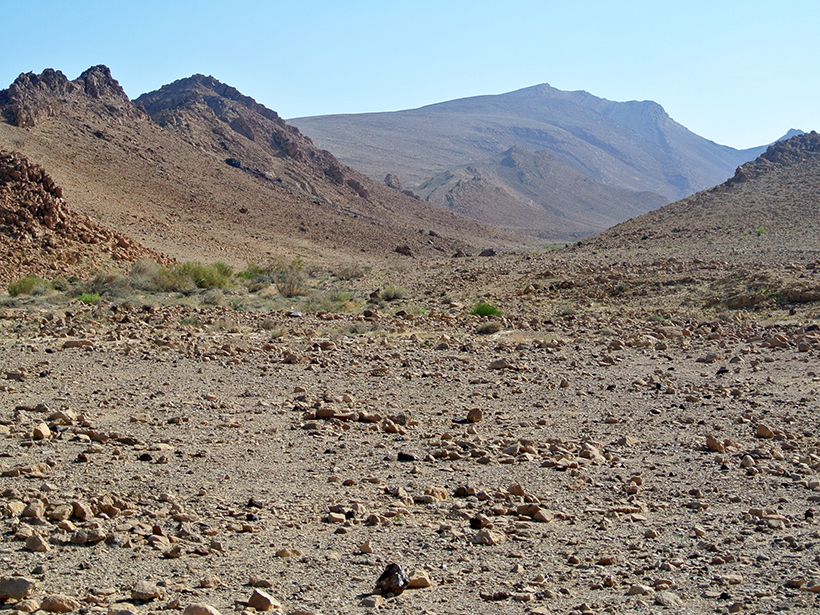
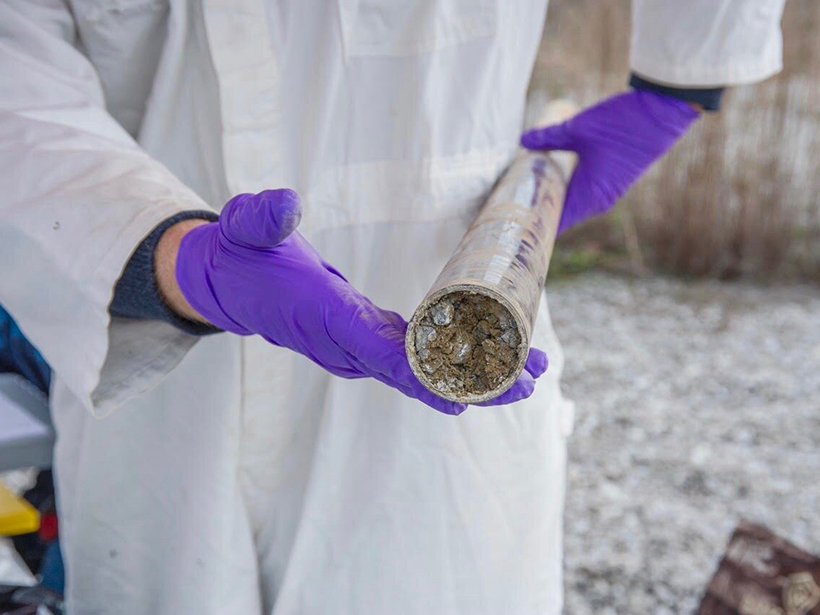
New research on the geochemistry of Canary Islands paleosols shows that the Sahara has been an arid dust producer for at least 4.8 million years.
geochemistry
Interstellar Interloper Borisov Looks Like a Regular Comet, for Now
A first look at the chemical composition of the interstellar comet Borisov reveals ingredients that look a lot like those found in solar system comets. That’s not likely to last very long.
Leaky at the Core
New evidence from deep mantle plumes suggests that Earth’s liquid outer core might be leaking tungsten isotopes into the lower mantle.
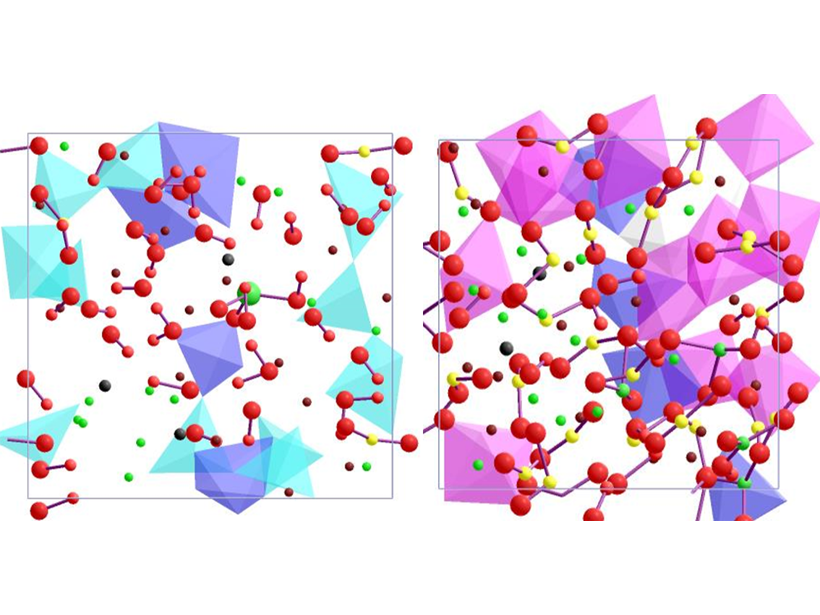
Hiding Deep Hydrous Melts at the Core-Mantle Boundary
Silicate melts containing H2O in the lowermost mantle are surprisingly dense and may stagnate there, trapping primordial volatiles and potentially causing some of the ultra-low velocity zones.
How Land Use Affects Nutrient Pollution in a Changing Climate
As heavy rain falls more frequently, the land alongside a river has a greater effect on the waterway’s nutrient levels—for better or worse.
Organic Gases Released and Taken Up by Soil Lack Quantification
Soils both emit and take up different biogenic volatile organic compounds, altering the chemical composition of the atmosphere and influencing local, regional, and global climate.
The Dawning of the Age of Old Aquifers
A new technique using 81Kr can measure the age of old groundwater in arid regions. The method can be used as a proxy for past climates and weather patterns.
New Tool Reveals That Soils Are Teeming with Active Microbes
BONCAT, a new type of amino acid tagging, highlights and categorizes active soil microbes in situ.
How Ice Cores Are Helping to Track Preindustrial Ozone
Research helps allay concerns about discrepancies between atmospheric chemistry models and historical direct measurements.
The Jail That Keeps Oxygen in the Air
Oxygen shouldn’t be in the air we breathe. But it is, and the reason why is almost criminal.