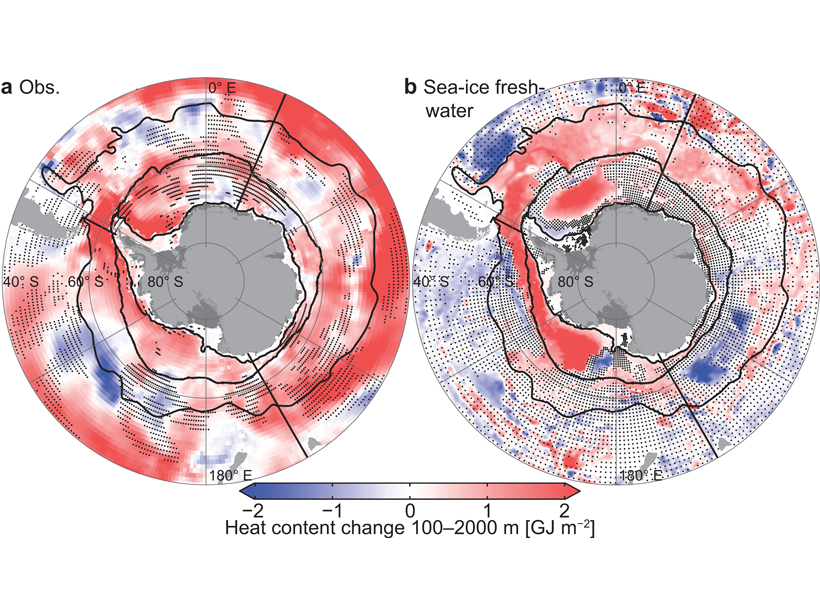
Global climate models do not reproduce observed trends of the Southern polar ocean surface, but an increase in wind-transported sea ice that melts and inhibits mixing may account for the disparity.
geochemistry
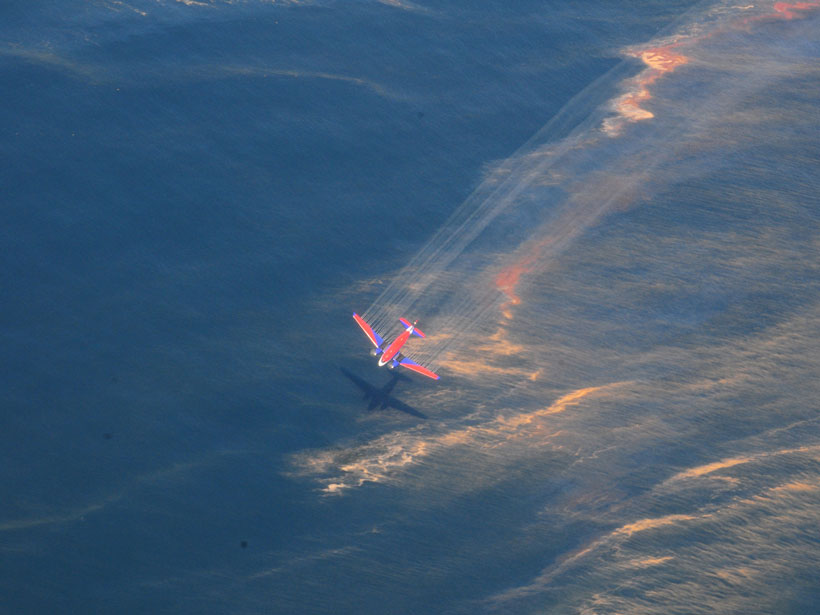
Why Sunlight Matters for Marine Oil Spills
A decade of research since the Deepwater Horizon disaster has revealed how sunlight—its importance long understated in oil spill science—substantially alters petroleum floating at the sea surface.
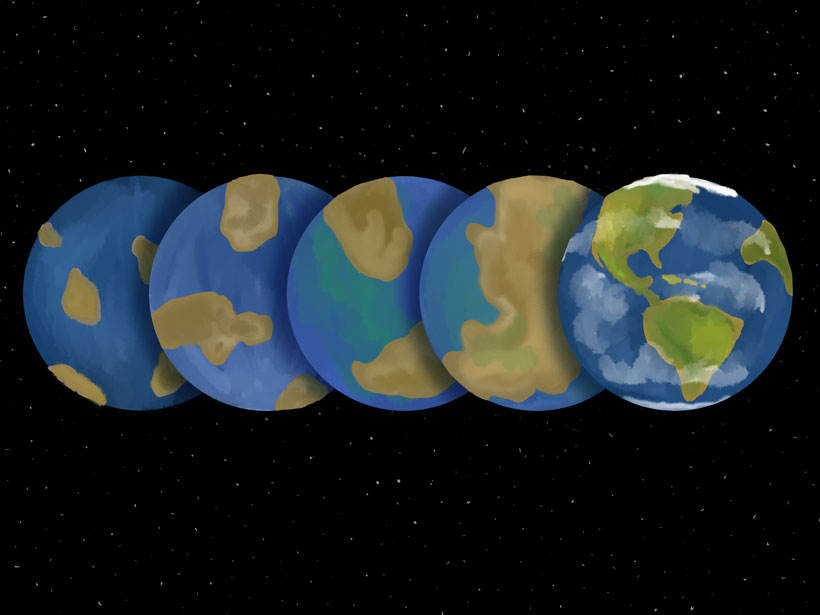
Looking Back at Our Pale Blue Dot
Astronomers model changes in Earth’s chemical signature over the past 4 billion years to improve the search for Earth-like exoplanets.
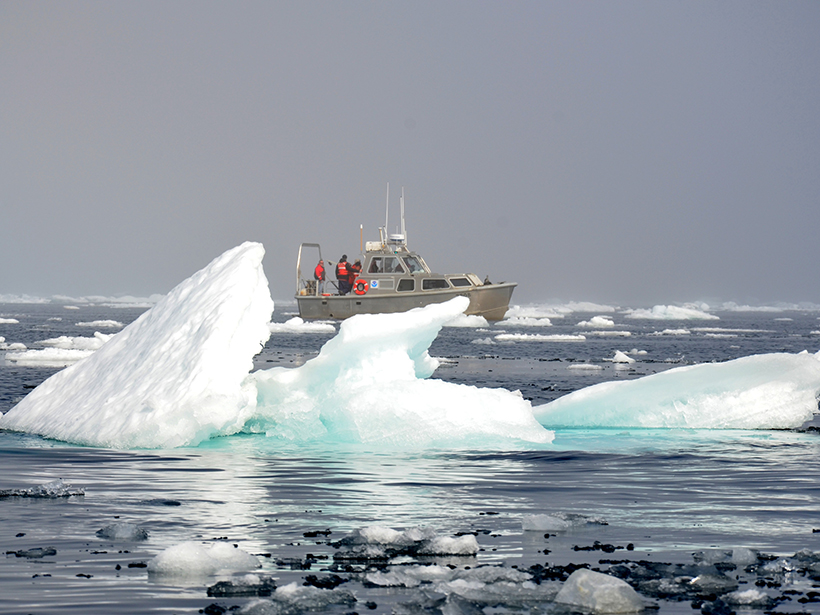
The Arctic Ocean May Not Be a Reliable Carbon Sink
The rapid changes happening in the Arctic Ocean, including increasing freshwater input, could dramatically affect its ability to store carbon.
Taro Takahashi (1930–2019)
This giant in geochemistry also pioneered early high-pressure, high-temperature studies that launched the field of mineral physics.
Tracking Reverse Weathering
Using beryllium isotopes to track in situ formation of clays in the ocean, known as reverse weathering, will improve global models of atmospheric carbon dioxide and ocean alkalinity.
Earth Rocks and Moon Rocks Are More Different Than We Thought
New analyses of oxygen isotopes reveal terrestrial and lunar rocks aren’t as similar as previously thought, potentially changing the way we think the Moon formed.
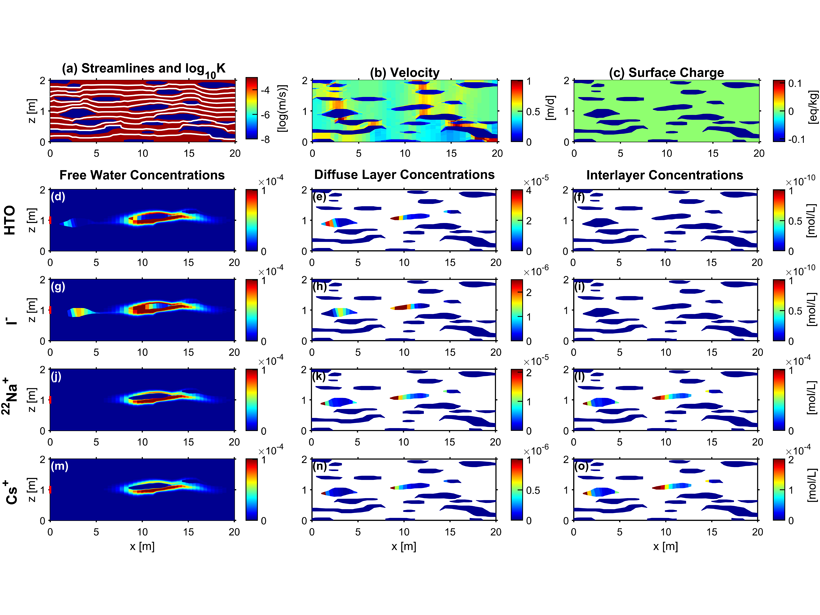
Modeling Transport and Charge Effects in Heterogeneous Media
Simulation of charged species reactive transport in complex physically and electrostatically heterogeneous porous media is possible with a multiple continua approach coupled to a geochemical code.
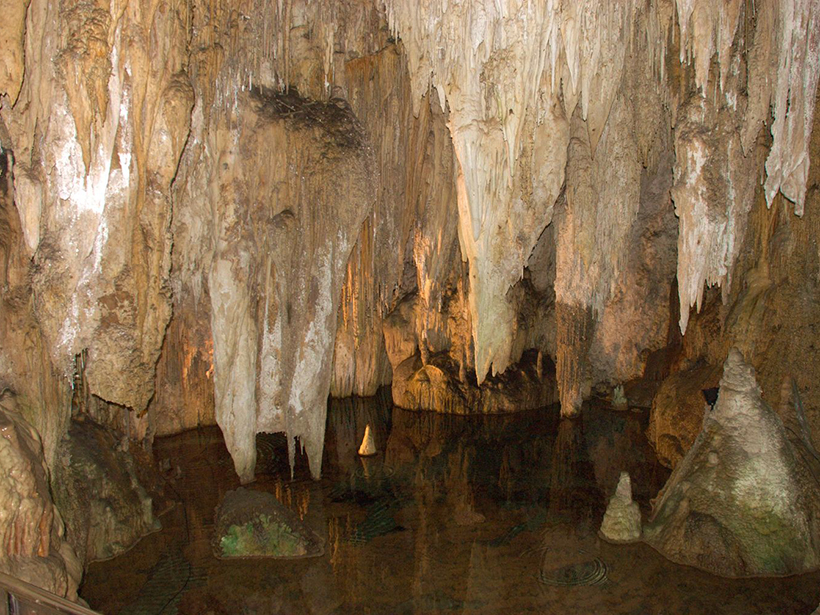
How to Read Atmospheric History Written in Flowstones
Oxygen isotope ratios in cave deposits reflect past climates, but interpreting these data is not straightforward. A new study explores what these ratios really tell us.
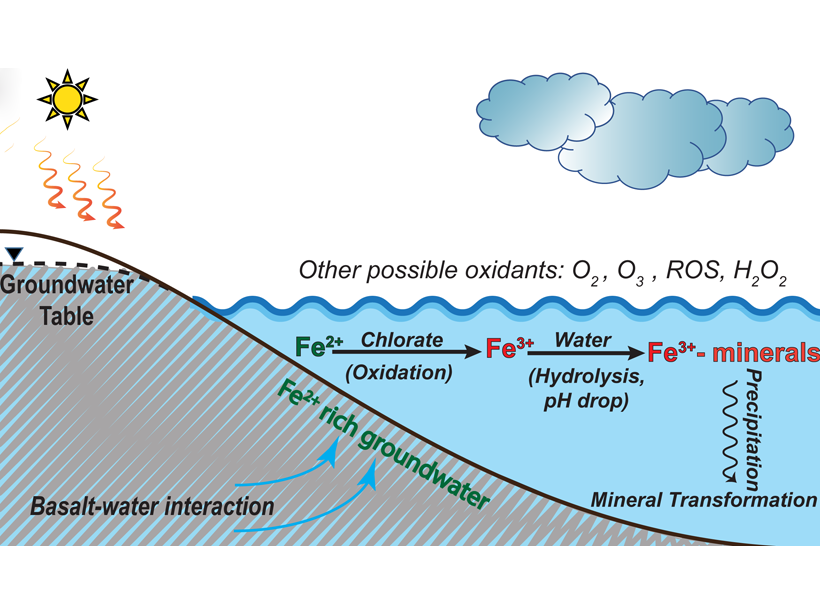
Why Is the Red Planet Red? Chlorate May Oxidize Mars’ Surface
Laboratory experiments and geochemical model suggest that chlorate is very effective to oxidize reducing iron to reddish iron oxides on Mars when liquid water was present on the surface.