Tiny microorganisms in the Southern Ocean affect the way the rest of the world’s seas respond to carbon dioxide.
geochemistry
The Catcher in the Ice
There are three ways to extract gases from an ice core. The cleanest one, sublimation, is getting easier.
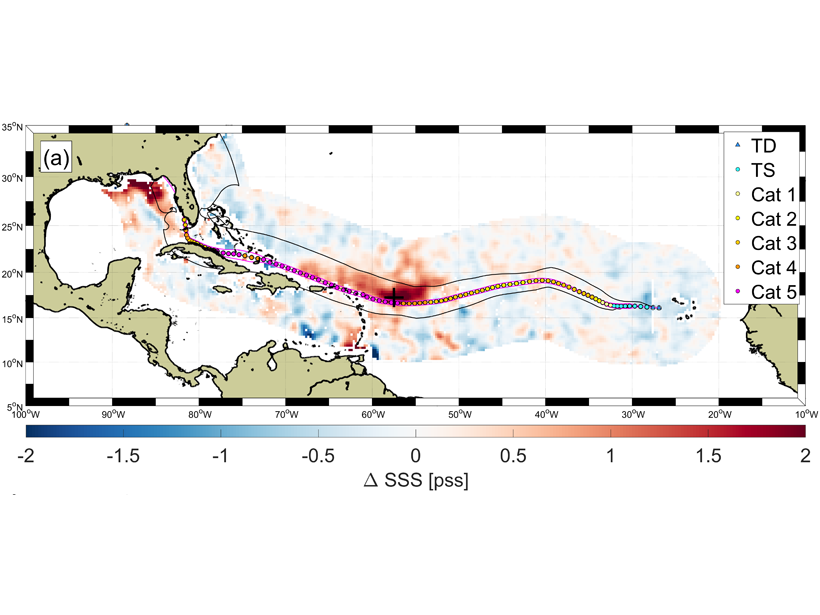
Hurricanes Wakes Show Asymmetrical Response in Ocean Salinity
It’s well known that hurricanes can substantially impact ocean surface temperature, but a new study shows they can also induce an ocean salinity response in unexpected ways.
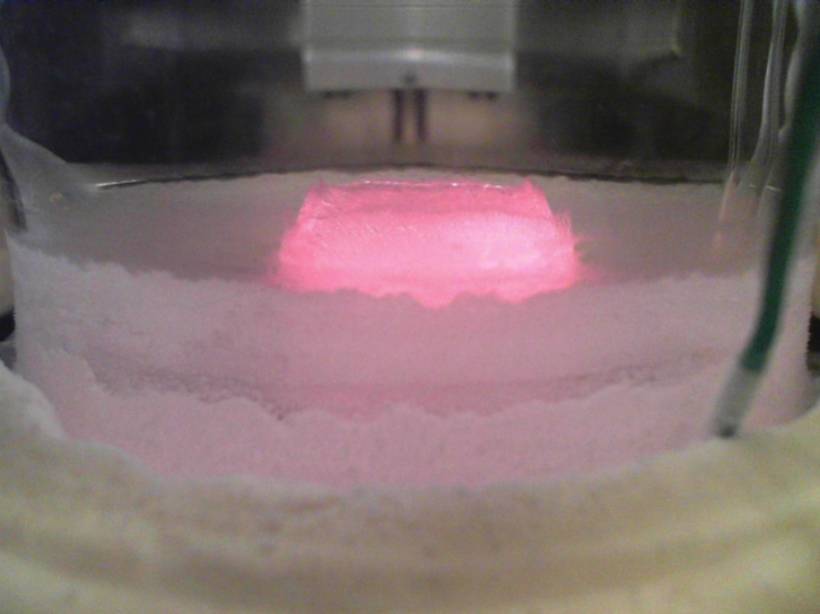
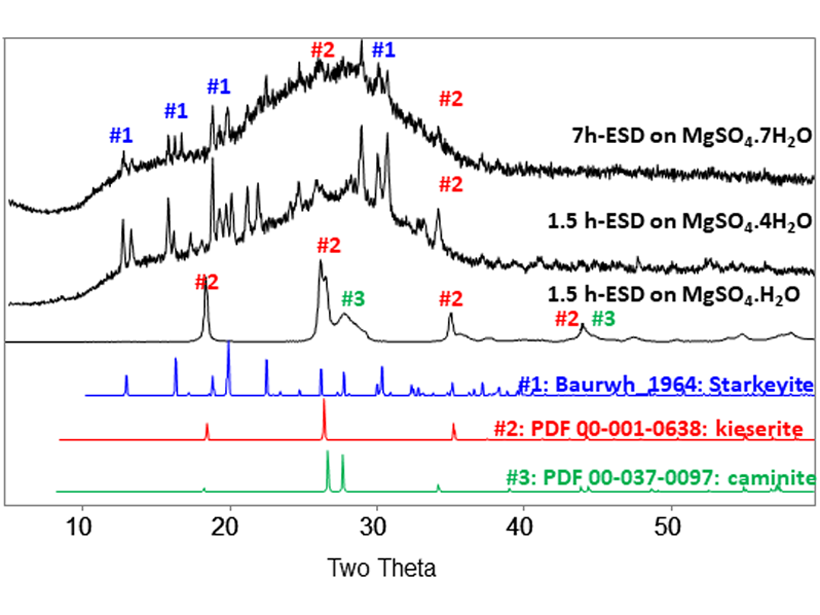
Martian Dust Activities Induce Electrochemistry
Amorphous materials generated from sulfur and chloride salts by electrostatic discharge in a Mars chamber suggest widespread electrical processes during dust activities.
Sinking Fish May Fast-Track Mercury Pollution to the Deep Sea
Isotopic analysis indicates that mercury found in deep-sea organisms may have an origin in carrion from near the surface.
When Did Archaic Humans Control Fire?
A familiar geochemical technique shines a new spotlight on early hominin use of fire.
La Geología y la Química Impulsan la Migración Animal en el Serengueti
Trabajo de campo en Tanzania sugiere que la química del suelo—influenciada por el vulcanismo local y la actividad tectónica—podría ayudar a determinar la migración sin precedentes de más de un millón de ñus.
Acidifying Oceans Could Get Help from Kelp
Forests of fast-growing kelp influence the chemistry of the water in which they live. A new study evaluates their potential to ameliorate ocean acidification in sensitive coastal ecosystems.
Autonomous Minisubmarine Measures Seawater Conditions
Forecasts of carbonate chemistry in coastal ecosystems determined from seasonal robotic measurements can improve fisheries management and help mitigate short-term ocean acidification events.
Tracking Trace Elements in the Ganga River
Levels of dissolved trace and heavy metals, which can be toxic, are highly variable across the river basin, concentrating in urban areas with high pollution but diluted by inflow from tributaries.