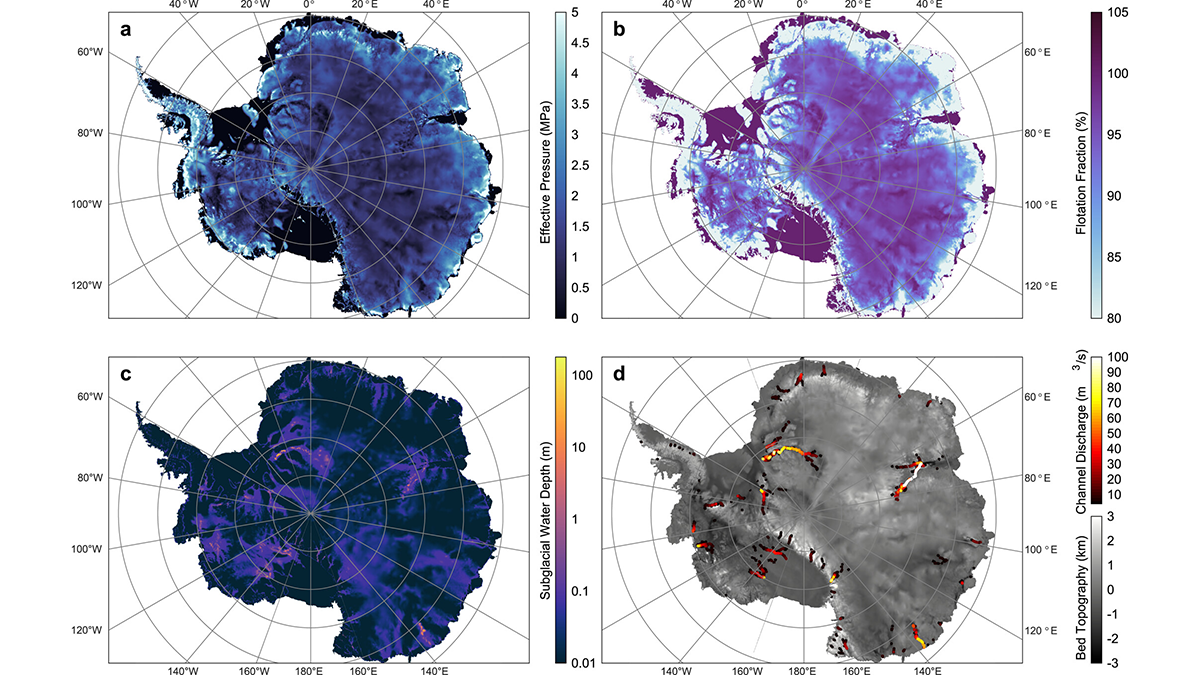
Using simulations of subglacial hydrology, a new study shows the volume and movement of meltwater underneath the Antarctic Ice Sheet.
Geophysical Research Letters
Los lagos y estanques de Alaska revelan los efectos del derretimiento del permafrost
Un nuevo conjunto de datos proporciona un método poderoso para rastrear fácilmente los cambios en el permafrost.
Heating Mechanism at Earth’s Bow Shock Depends on Shock Speed
A new technique shows that the dominance of gradual versus chaotic electron heating processes at Earth’s bow shock is controlled by how fast the shock is moving.
Alaska’s Lakes and Ponds Reveal Effects of Permafrost Thaw
A new dataset provides a powerful method for easily tracking changes in permafrost.
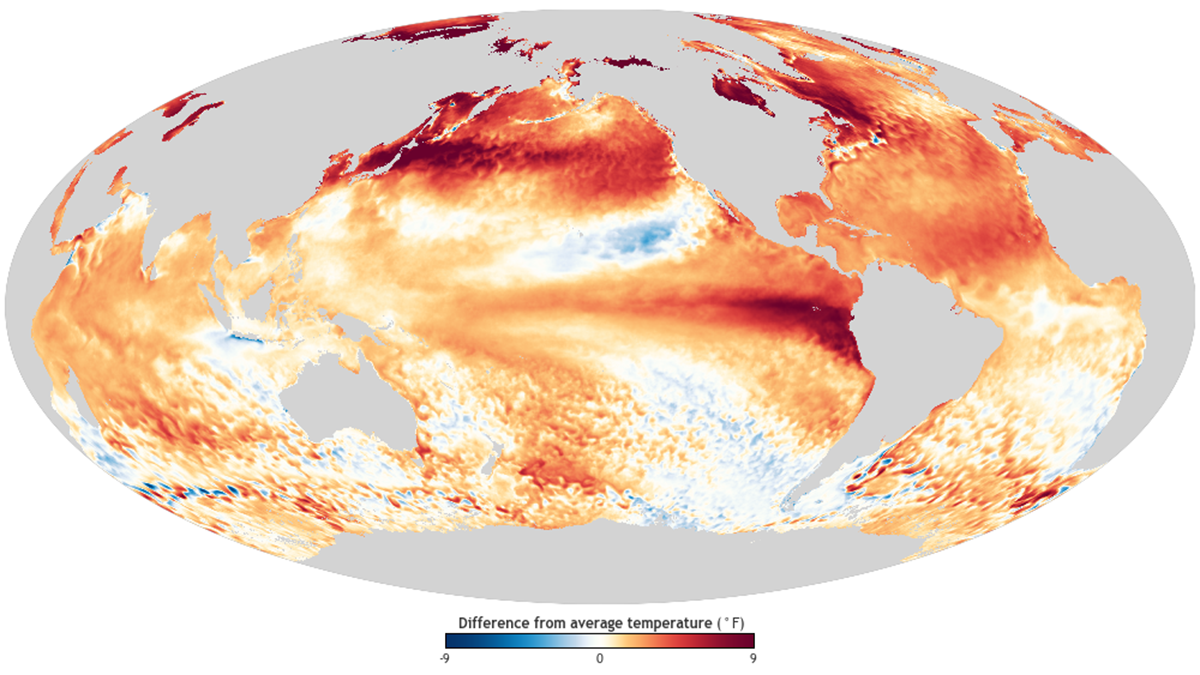
Three Studies Point to El Niño as Key to 2023 Record Global Heat
Three recent studies reveal how the interplay between El Niño and long-term global warming drove the record-breaking global temperatures of 2023.
Steering Geophysical Research Letters Forward: A Focus on Excellence and Global Inclusivity
Meet the new Editor-in-Chief of Geophysical Research Letters and discover his plans to shape the journal’s role in advancing the Earth and space sciences.
Deep Beneath California’s Sierra Nevada, Earth’s Lithosphere May Be Peeling Away
Evidence for lithospheric foundering, or the process of denser material sinking into the mantle, is emerging.
Modeling the Long and Short of Subduction Zones
A new subduction model could reveal important insights about megathrust earthquakes.
Magmatic Fluids and Melts May Lie Beneath Dormant German Volcanoes
New processing strategies applied to old seismic data reveal potential pockets of magmatic fluids or melts from the upper mantle.
Massive Antarctic Icebergs May Calve at Random
The first analysis of extreme calving events in Antarctica finds no correlation with climate change, highlighting the significance of common, smaller calving events for ice loss and instability.