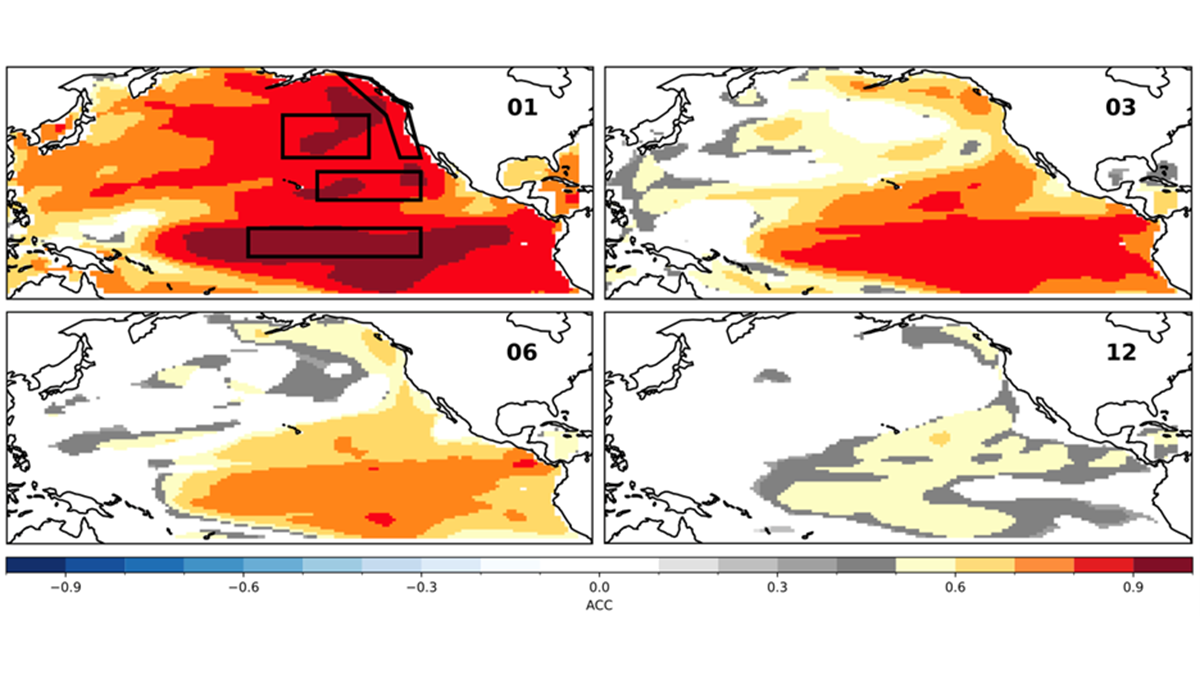
Scientists use a large suite of simulations with an established climate model to predict the Pacific Decadal Oscillation up to one year in advance, but El Niño can still get in the way.
Geophysical Research Letters
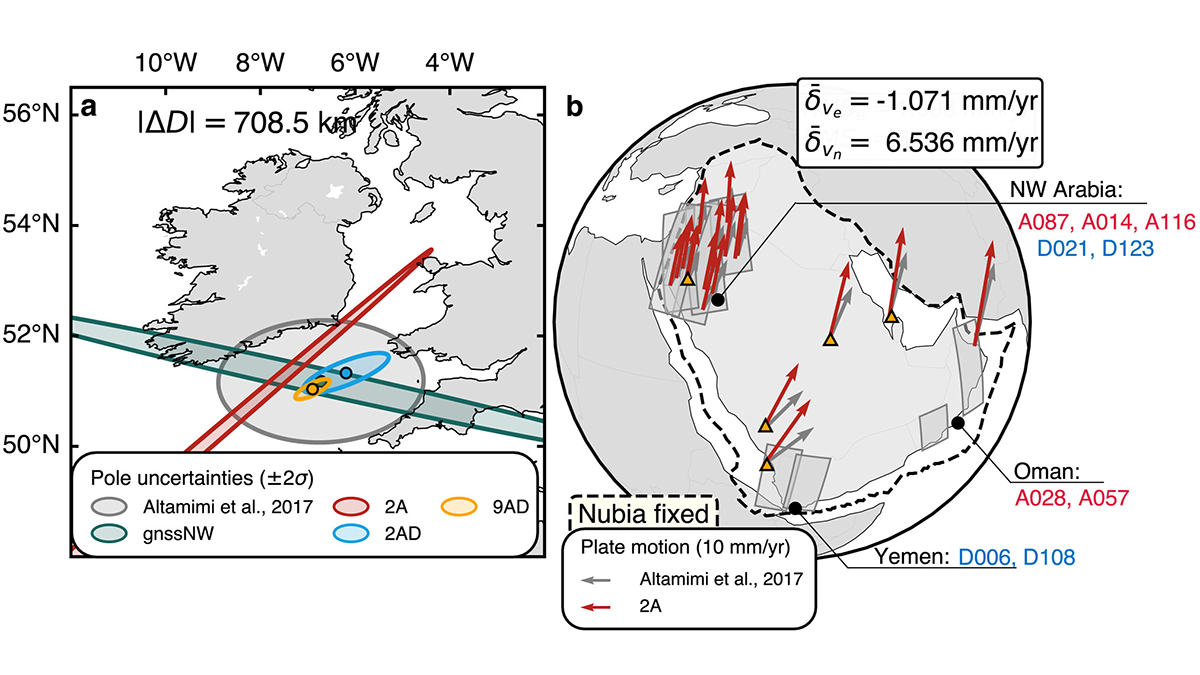
Mapping the Whereabouts of Continents
A new method integrates Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) with conventional ground geodetic networks, taking us closer to high-resolution mapping of plate motions.
A Transatlantic Communications Cable Does Double Duty
A new device enables existing submarine cable networks to measure deep-sea movements. It could ultimately help improve tsunami warnings and climate monitoring.
Un antiguo evento de calentamiento podría haber durado más de lo que pensábamos
Una nueva investigación sobre el Máximo Térmico del Paleoceno-Eoceno usó análisis probabilístico para entender mejor su duración y sobre cuánto tiempo podría afectar el calentamiento moderno al ciclo del carbono.
Water Density Shifts Can Drive Rapid Changes in AMOC Strength
High-latitude variations in density, which appear to be driven by changes in atmospheric pressure, can propagate to midlatitudes and affect the current’s strength within just a year.
Simplicity May Be the Key to Understanding Soil Moisture
A pared-down model that considers only precipitation and net surface radiation seems to solve long-standing problems.
Storm Prediction Gets 10 Times Faster Thanks to AI
Forecasters hope new algorithms will lead to earlier warnings of when dangerous weather is on the way.
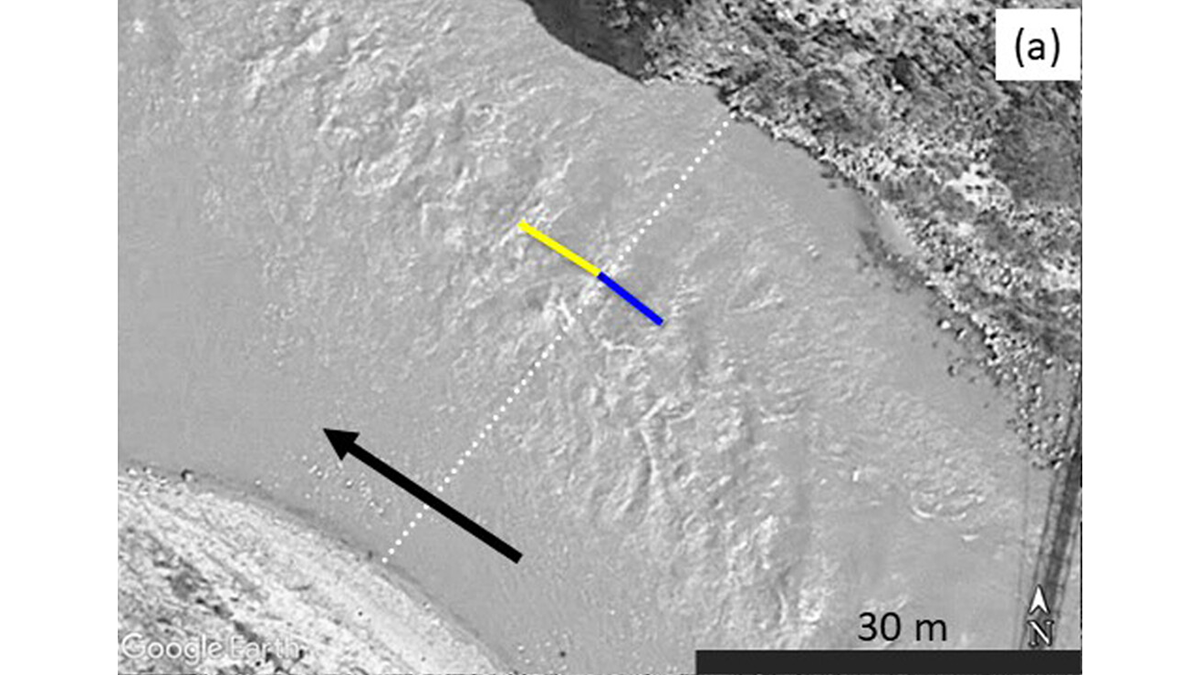
Inferring River Discharge from Google Earth Images
Critical flow theory can predict river discharge based on the spacing of standing waves captured by Google Earth images.
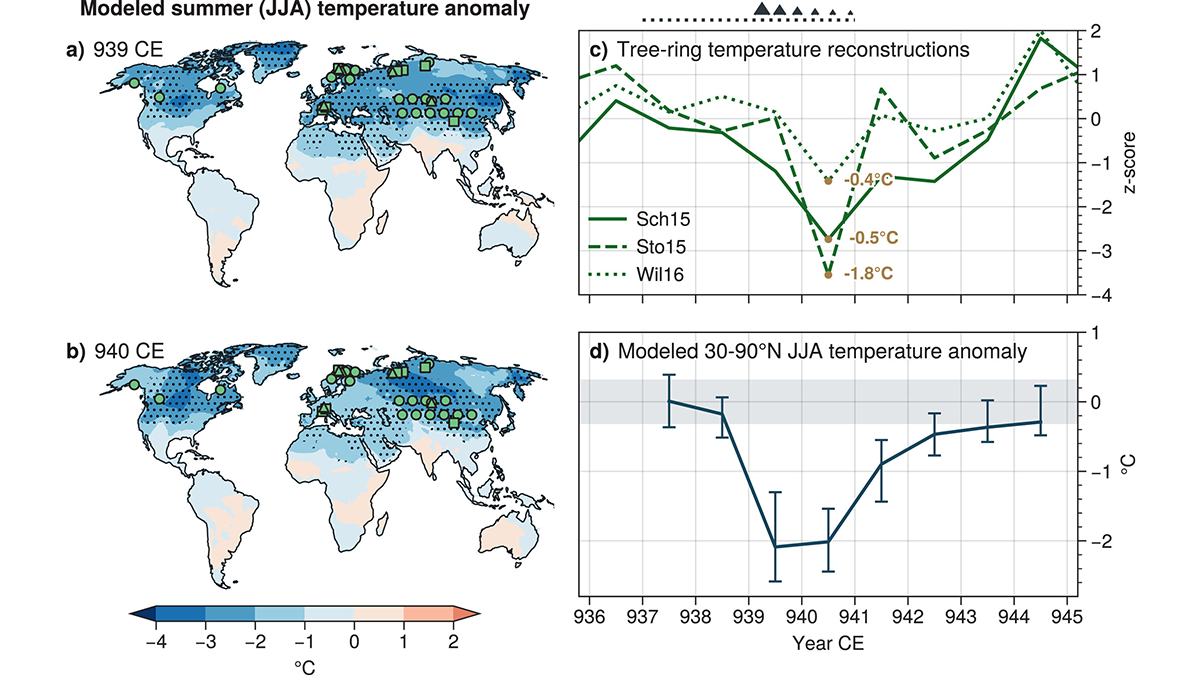
Revised Emissions Show Higher Cooling in 10th Century Eruption
The associated cooling from the Eldgjá eruption is larger than previously predicted and better matches tree-ring temperature reconstructions based on updated estimated emissions.