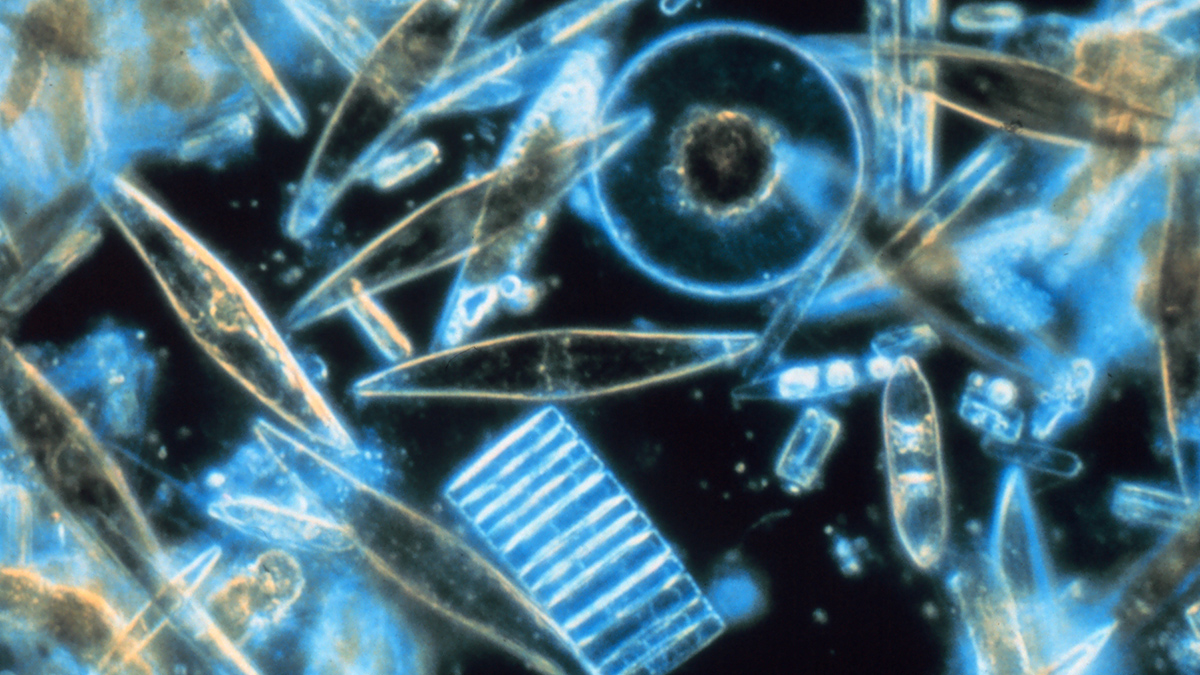
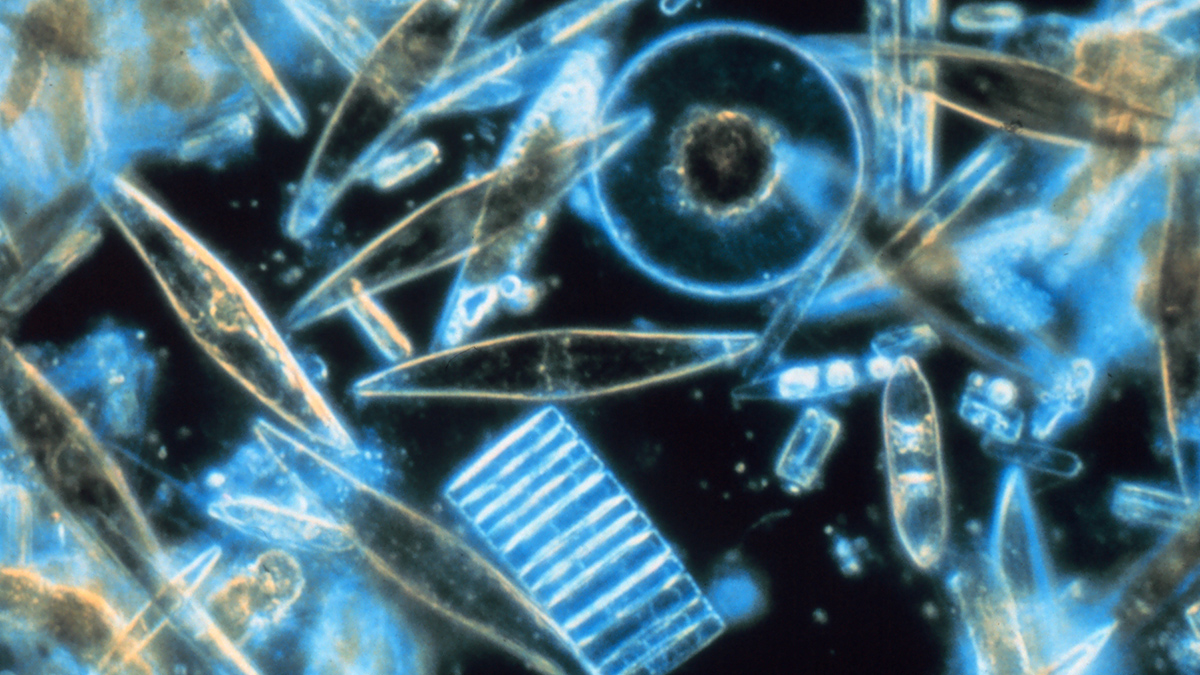
New observations highlight how abiotic and biotic processes influence the tiny oceanic particles.
Global Biogeochemical Cycles
New River Chemistry Insights May Boost Coastal Ocean Modeling
By more realistically accounting for river inputs, researchers reduced overestimation of the amount of carbon dioxide absorbed by coastal waters.
What Could Happen to the Ocean’s Carbon If AMOC Collapses
Mass glacier melting may have led this influential ocean current system to collapse at the end of the last ice age. A pair of modeling studies examines how such a collapse could affect dissolved inorganic carbon and carbon isotopes in Earth’s oceans.
Mysteriously Bright Waters near Antarctica Explained
Shiny-shelled diatoms make a remote part of the Southern Ocean appear especially reflective in satellite imagery.
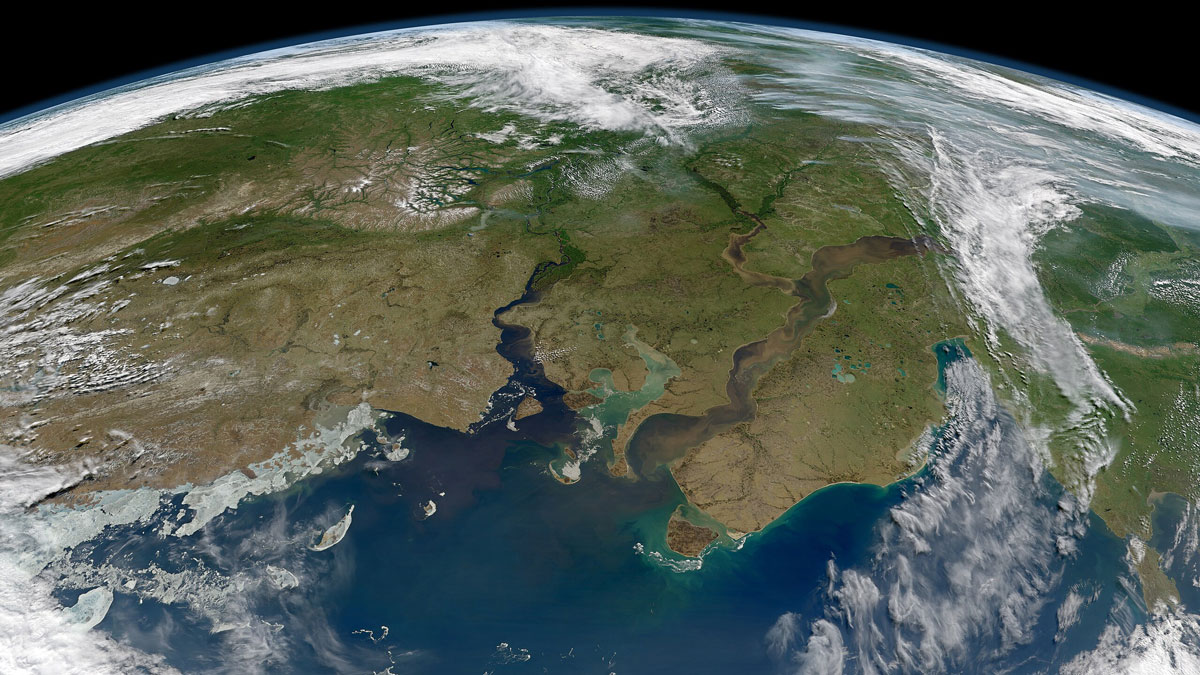
Arctic Rivers Trade Inorganic Nitrogen for Organic
Climate change is shifting the makeup of a key nutrient in rivers across Russia, Alaska, and Canada, with the potential for ecosystem-wide impacts.
When Rain Falls in Africa, Grassland Carbon Uptake Rises
Satellite data suggest an explanation for the continent’s high year-to-year variability in carbon uptake.
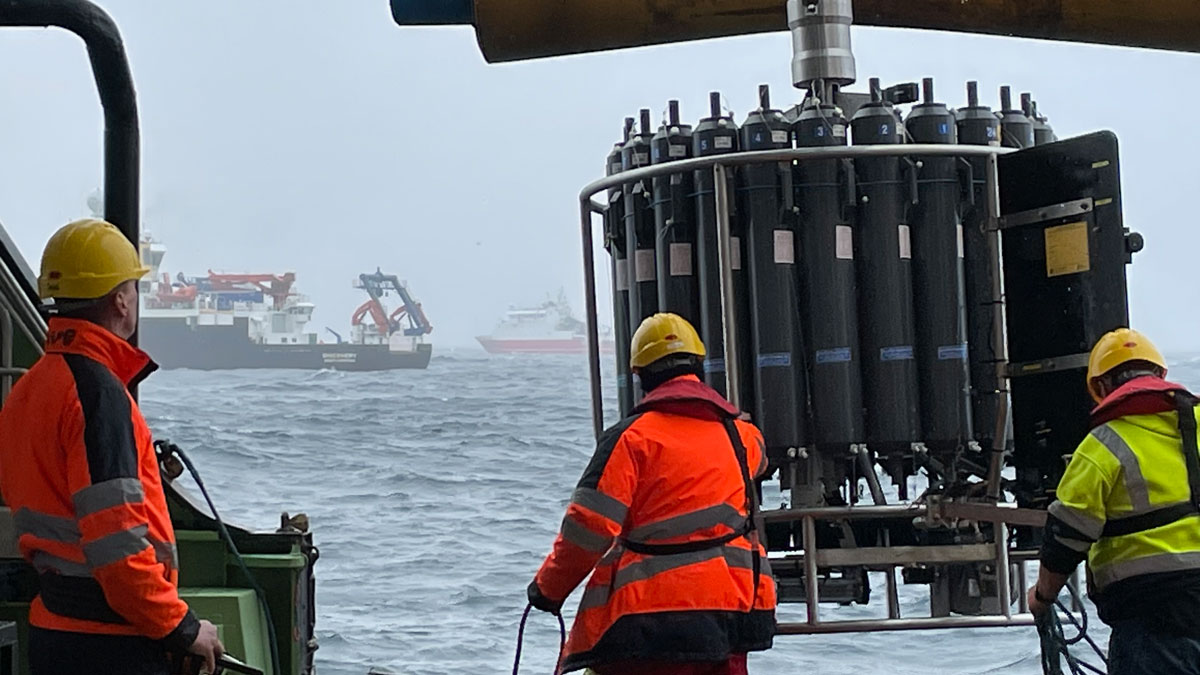
Tracing Black Carbon’s Journey to the Ocean
Scientists surveyed a trio of estuaries in pursuit of a missing source of oceanic dissolved black carbon.
More Bubbles Means More Variation in Ocean Carbon Storage
A new model accounting for the role of bubbles in air-sea gas exchanges suggests that ocean carbon uptake is more variable than previously thought.