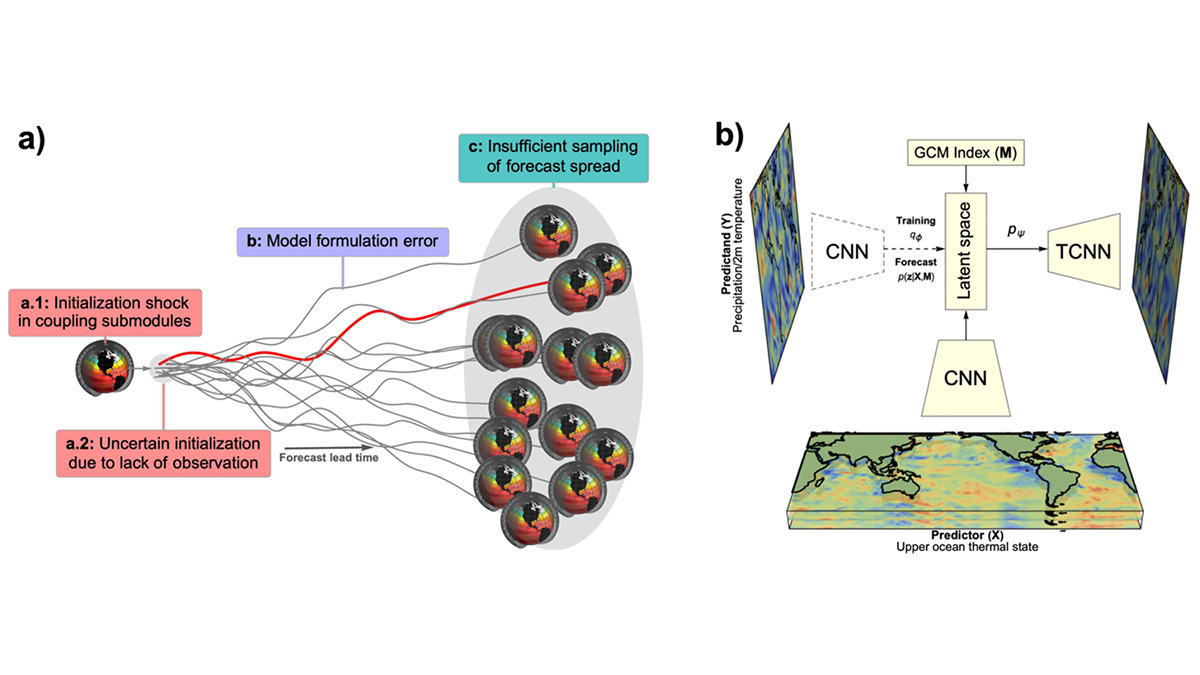
A probabilistic deep learning methodology that learns from climate simulation big data offers advantageous seasonal forecasting skill and crucial climate model diagnosis information at a global scale.
Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems (JAMES)
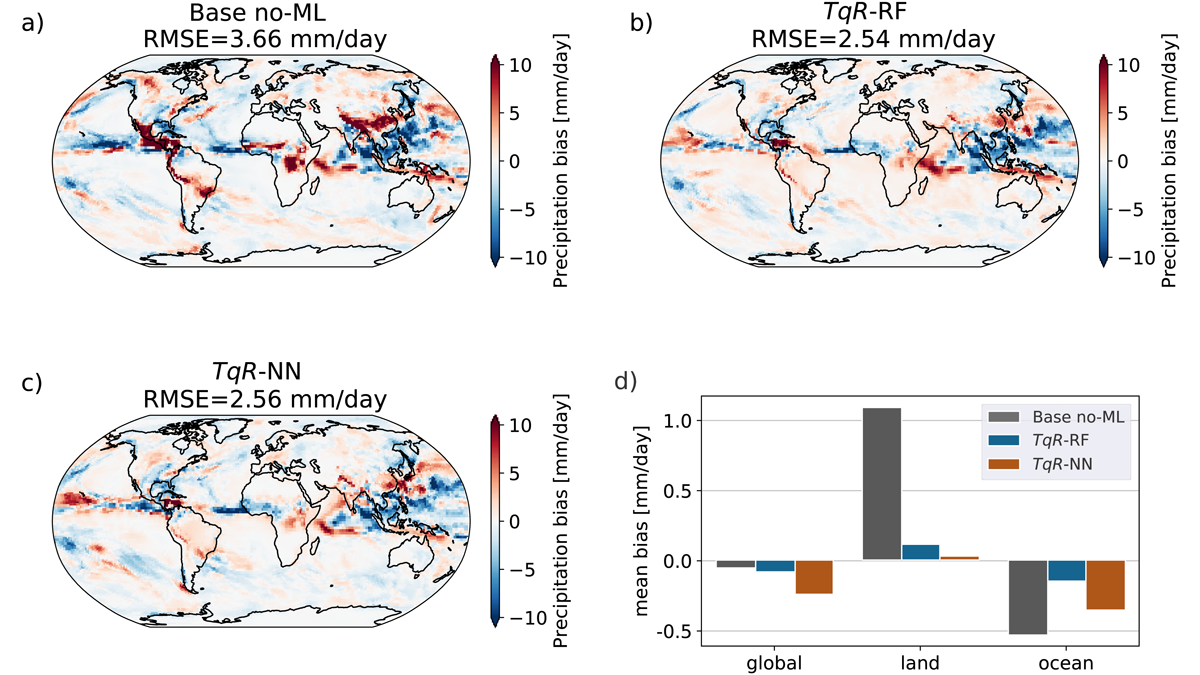
Corrective Machine Learning for Improving Climate Models
A machine-learned correction enables an efficient coarse-grid global atmosphere model to better track the weather and time-mean precipitation of an expensive fine-grid ‘digital twin’ reference model.
The AI Forecaster: Machine Learning Takes On Weather Prediction
A novel approach to weather forecasting uses convolutional neural networks to generate exceptionally fast global forecasts based on past weather data.
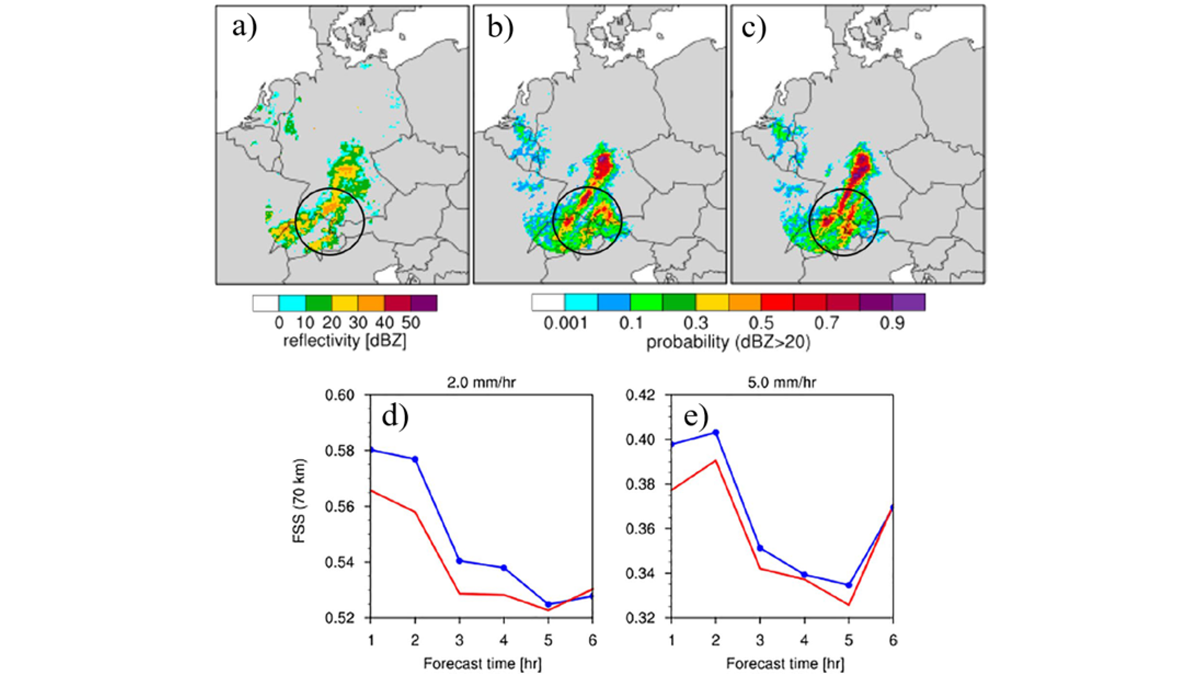
A New Way to Represent Microphysical Uncertainty
A new way of representing microphysical uncertainty in convective-scale data assimilation reduces biases in model states and improves the accuracy of short-term precipitation forecasts.
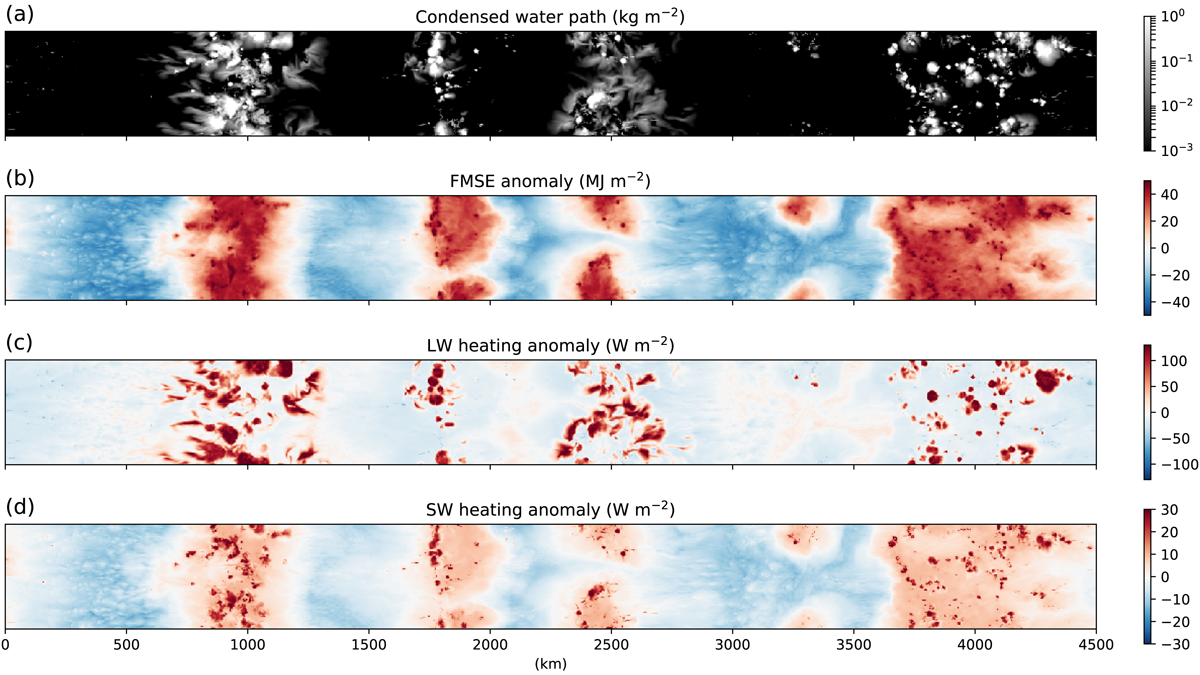
Importance of High Clouds and Moisture in Rainstorm Aggregation
A study of the impacts of radiative interactions with different cloud types on aggregation of rainstorms finds that interactions with high-clouds and water vapor are key.
AeroCom Models Improved with Aerosol and Albedo Constraints
Satellite data has been used to correct the aerosol loading and land surface albedo in several AeroCom models, which has improved shortwave flux biases between models and observations.
Uncovering Hidden Errors in Simulated Precipitation
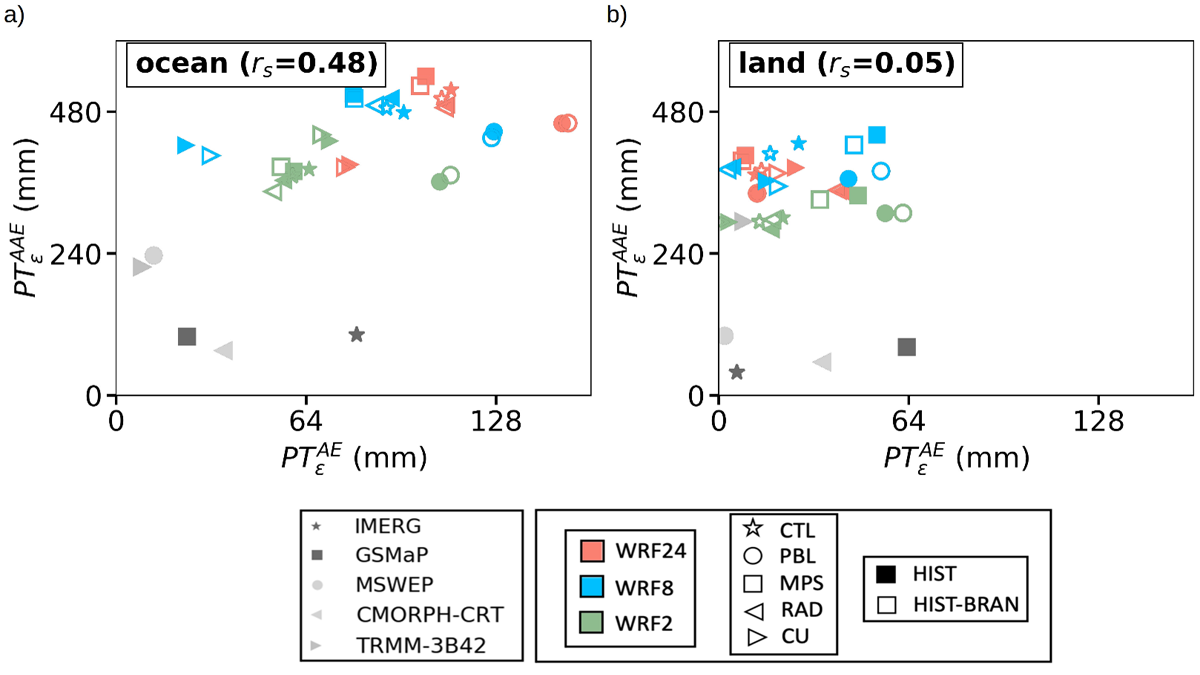
New metrics used to quantify errors in precipitation show that convection permitting simulations outperform coarser resolution simulations.
Introducing the New Editor in Chief of JAMES
Find out about the person taking the helm of AGU’s dedicated earth system modeling journal, JAMES, and his vision for the coming years.
The Past, Present, and Future at JAMES
The outgoing editor in chief of JAMES reflects on his time at the journal, recent developments in Earth system modeling, and the challenges of making modeling data accessible.
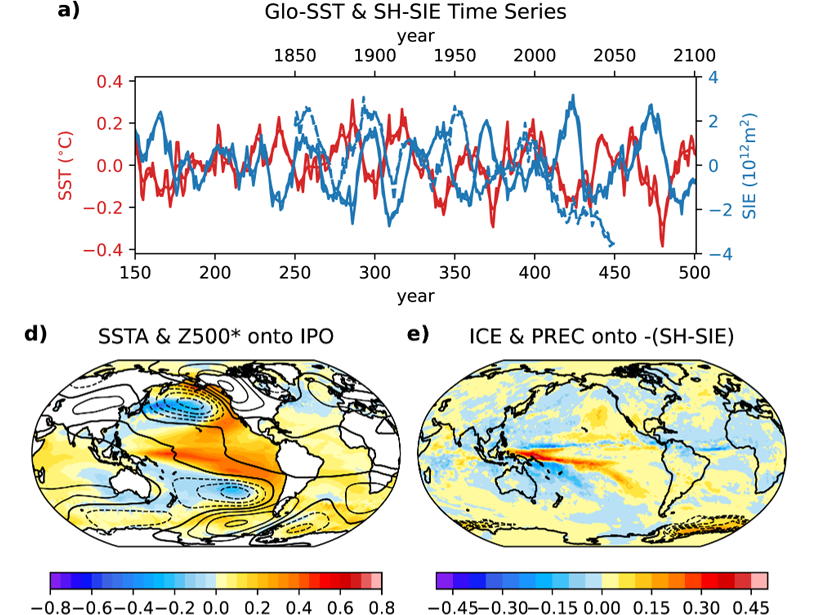
International Collaboration Yields Unique Climate Simulations
Porting and optimizing CESM1.3 to run on the TaihuLight computer enabled an astounding 750 years of simulation with 0.25° grid spacing for land & atmosphere and 0.1° grid spacing for ocean & sea ice.