Direct stress measurements inside deforming quartz reveal how its strength changes with temperature, improving models of continental crust deformation.
Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth
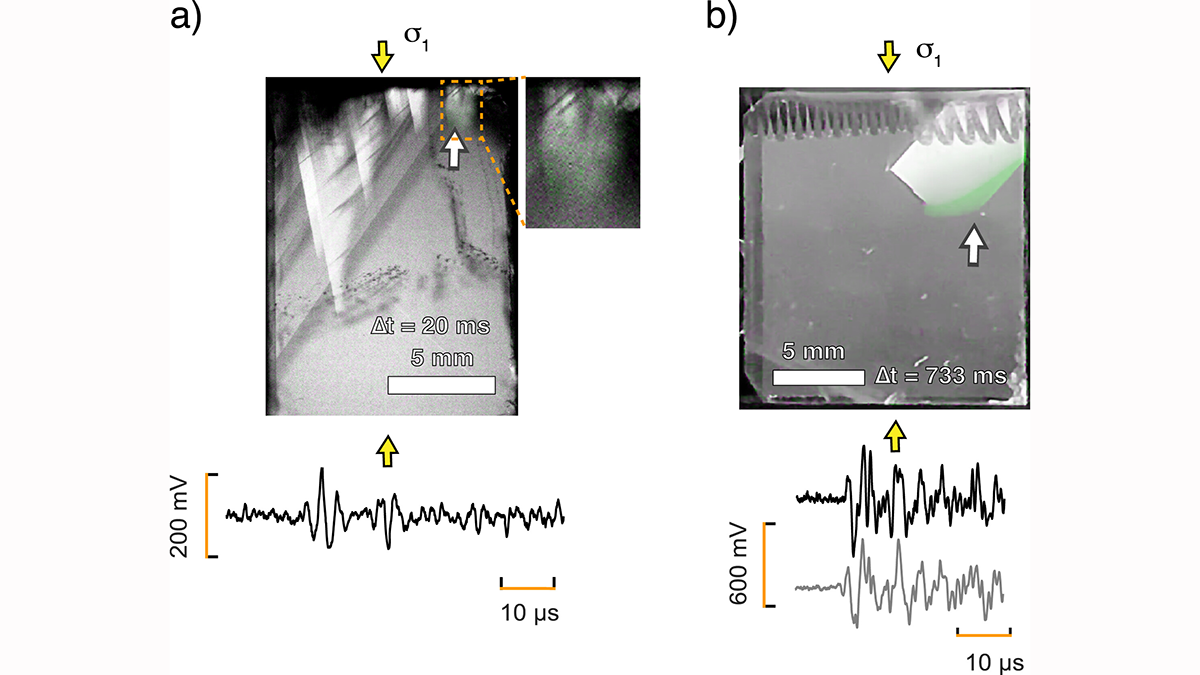
Visualizing and Hearing the Brittle–Plastic Transition
Simultaneous optical, mechanical, and acoustic measurements reveal that brittle microcracking and crystal-plastic twinning in calcite generate distinguishable acoustic signals.
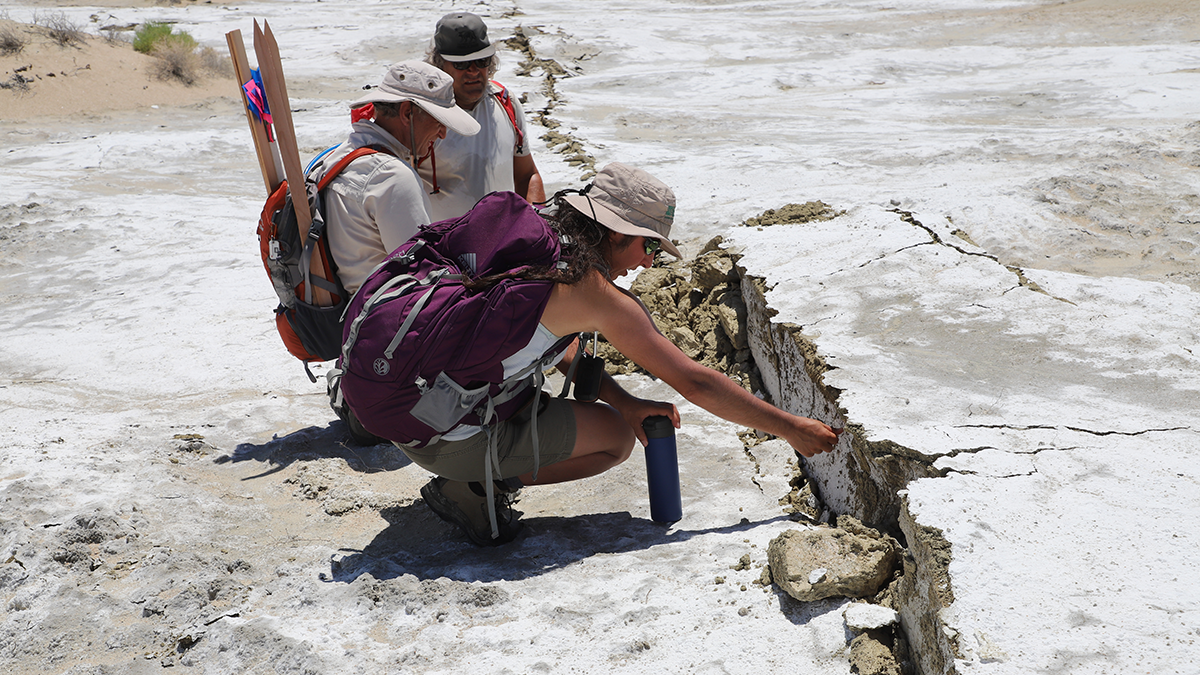
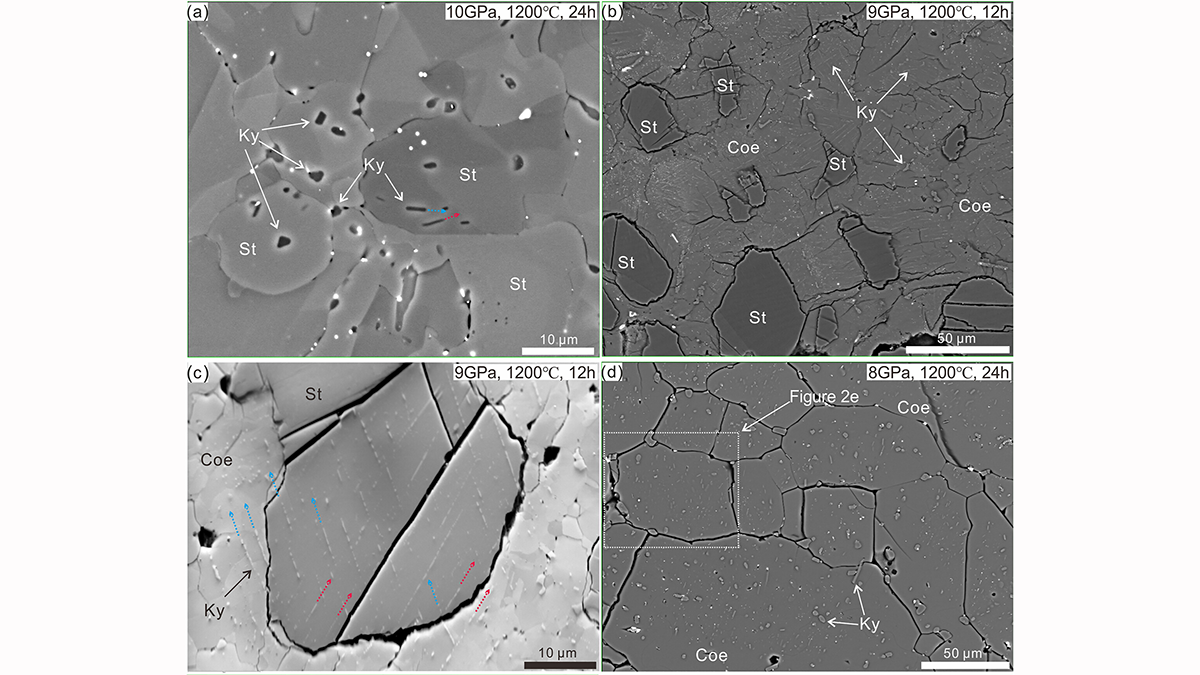
Kyanite Exsolution Reveals Ultra-Deep Subduction of Continents
Laboratory experiments provide the first experimental evidence that continental rocks can be subducted to depths greater than 300 kilometers and return to the surface.
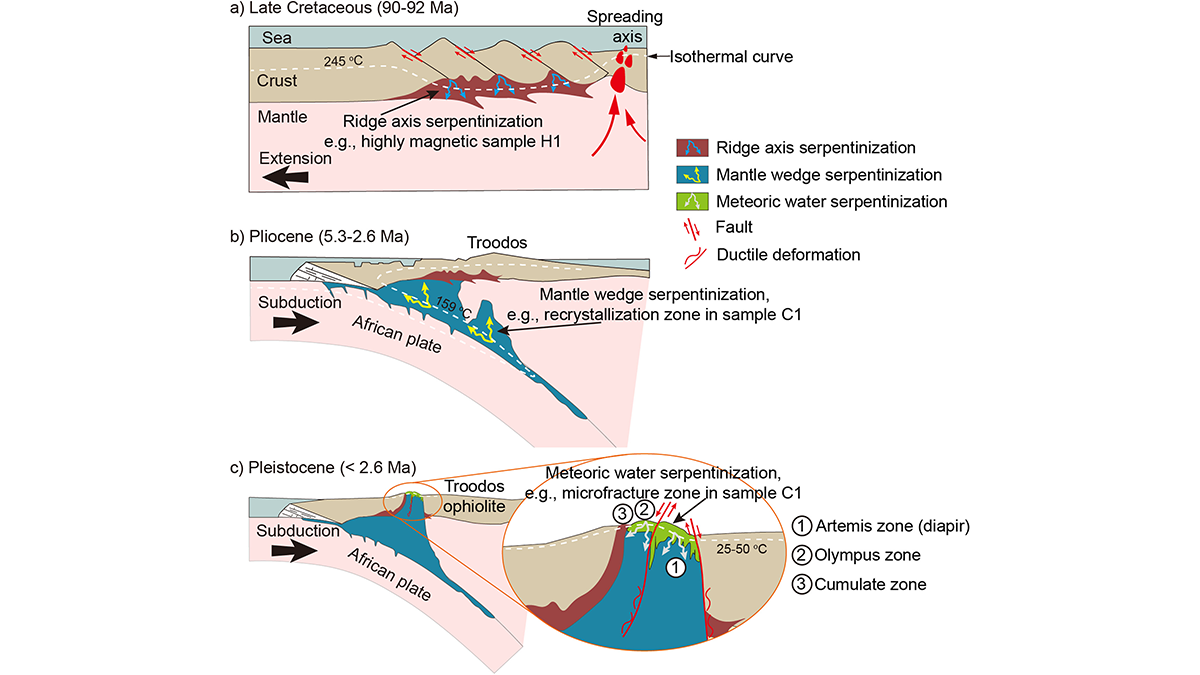
Detecting Remagnetization with Quantum Diamond Microscopy
Scientists reconstruct the magnetization timeline of serpentinized rocks from the Troodos ophiolite by investigating remanent magnetization-carrying structures with a Quantum Diamond Microscope.
Are We Really Seeing More Foreshocks with Enhanced Catalogs?
Different definitions and selection methods can lead to large differences in estimated foreshock rates; however, robust statistical method shows that foreshock rates are similar between standard and enhanced catalog.
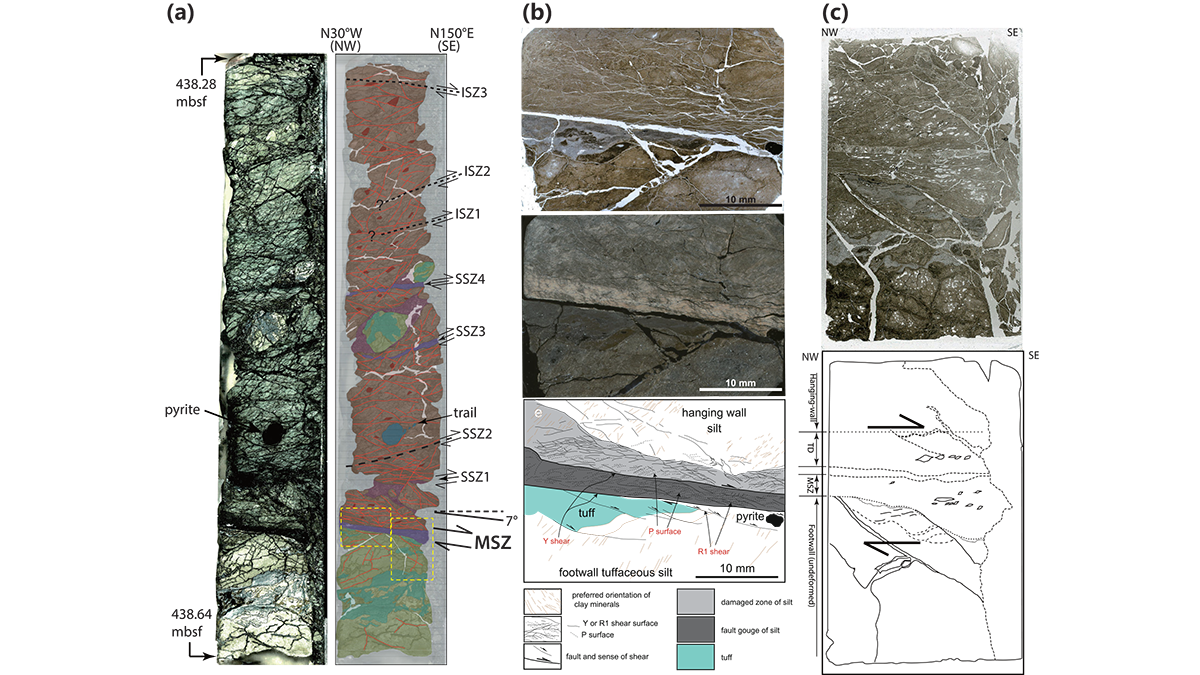
Frictional Properties of the Nankai Accretionary Prism
A database of frictional properties from IODP drilling materials explores the range of slip spectrum and the generation of slow to fast earthquakes in the Nankai subduction zone in light of mineralogy.
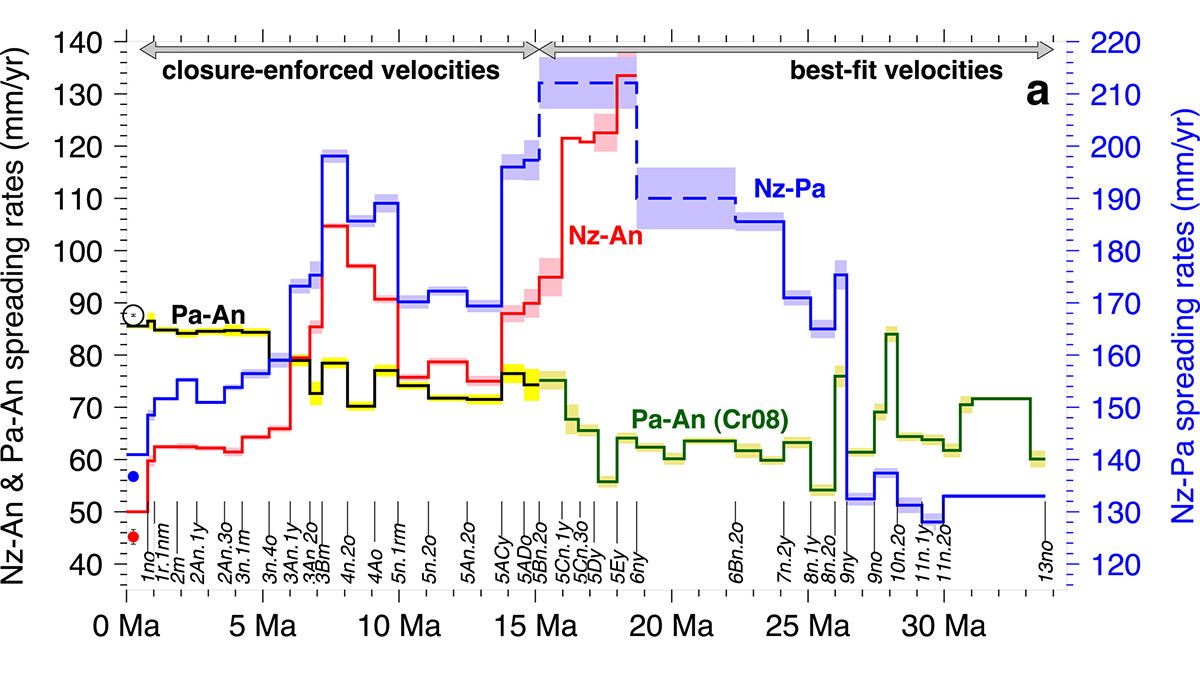
Changes in Slab Dip Cause Rapid Changes in Plate Motion
Periods of slab shallowing in the South American subduction zone appear to cause decelerations in Nazca plate motion.
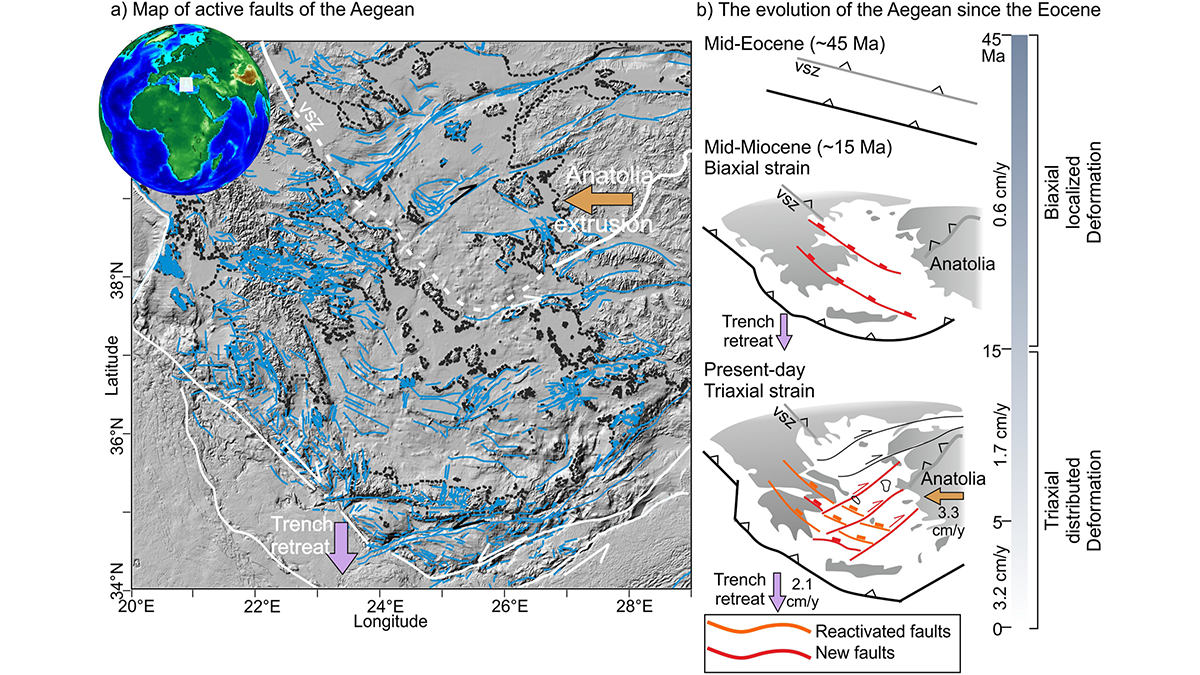
The Language of the Crust: Investigating Fault-to-Fault Interactions
Faults don’t just form—they respond, resist, and reshape the crustal narrative.
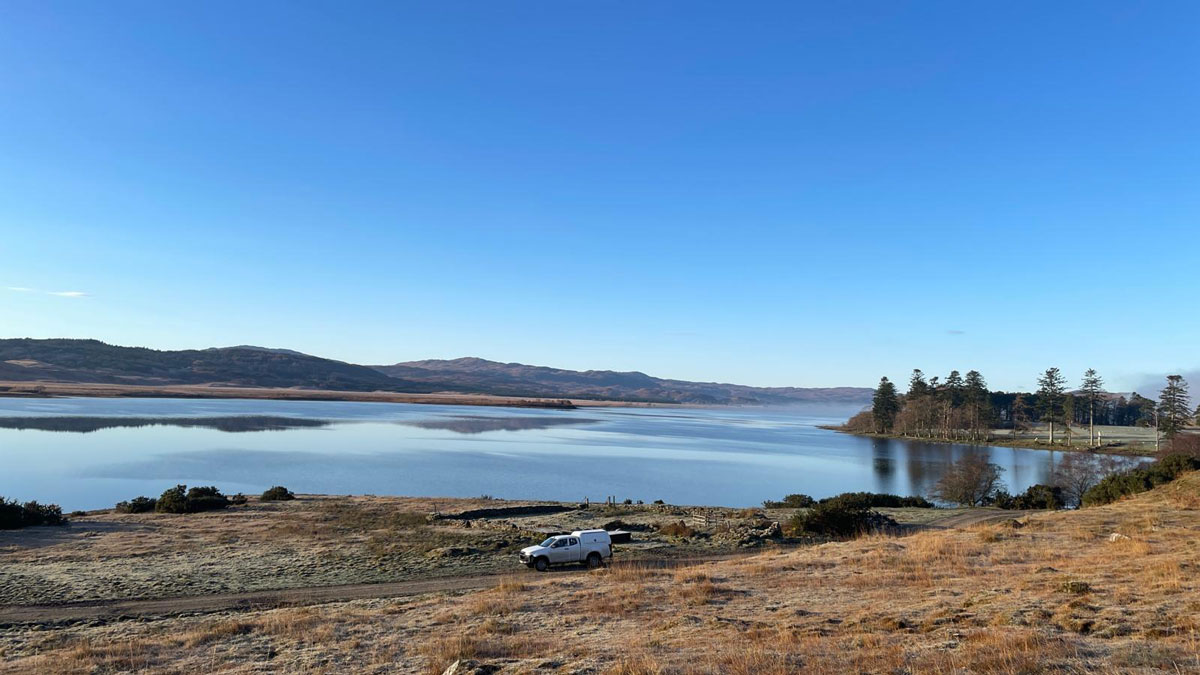
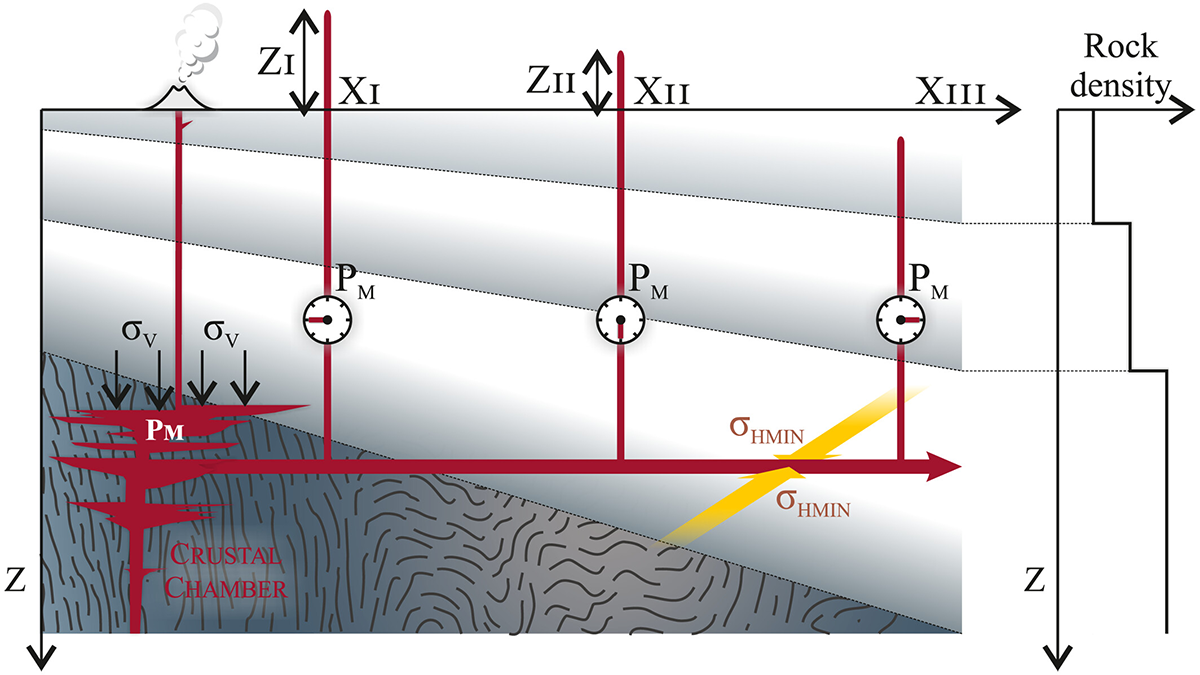
The Invisible Brake: Near‑Surface Cooling Stalls Giant Dyke Swarms
Sill-based pressure reconstructions show Mull’s giant dykes had eruption-capable pressures, but near‑surface groundwater cooling increased magma viscosity and stalled lateral propagation.
New 3D Model Reveals Geophysical Structures Beneath Britain
Using magnetotelluric data to identify subsurface electrically conductive and resistive areas, scientists can identify underground features and predict how space weather may affect infrastructure.