Postmidnight flows appear to be triggered by the same mechanism that drives more frequently observed evening flows.
Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics
How Big Data is Helping Environmental and Climate Research
A new special collection invites papers focusing on the processing, modeling, and analysis of all types of big datasets in the Earth and space sciences, including the influence of solar forcing on Earth’s climate.
Machine Learning Helps to Solve Problems in Heliophysics
A new special collection invites papers pertaining to the use of machine learning techniques in all sub-fields of heliophysics.
Modification of Energetic Particles Loss Cone During Storms
The loss cone of energetic particles in the Earth’s inner magnetosphere is substantially modified during disturbed times, with important implications for the radiation-belt and ring current modeling.
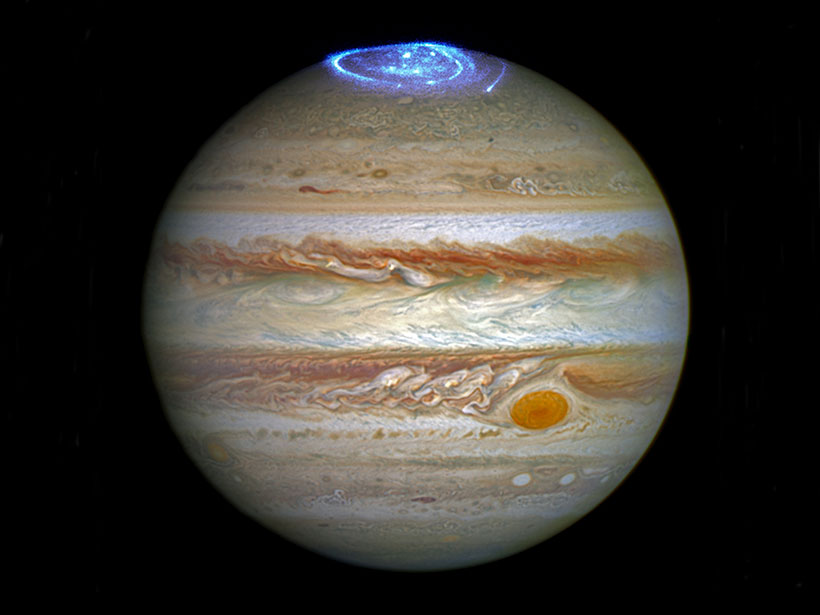
Meteoric Ions Influence Conductance in the Jovian Ionosphere
Meteoric ions dominate the Jovian lower ionosphere due to their long lifetimes. Due to the large densities of the meteoric ions, conductance is enhanced independently of local time.
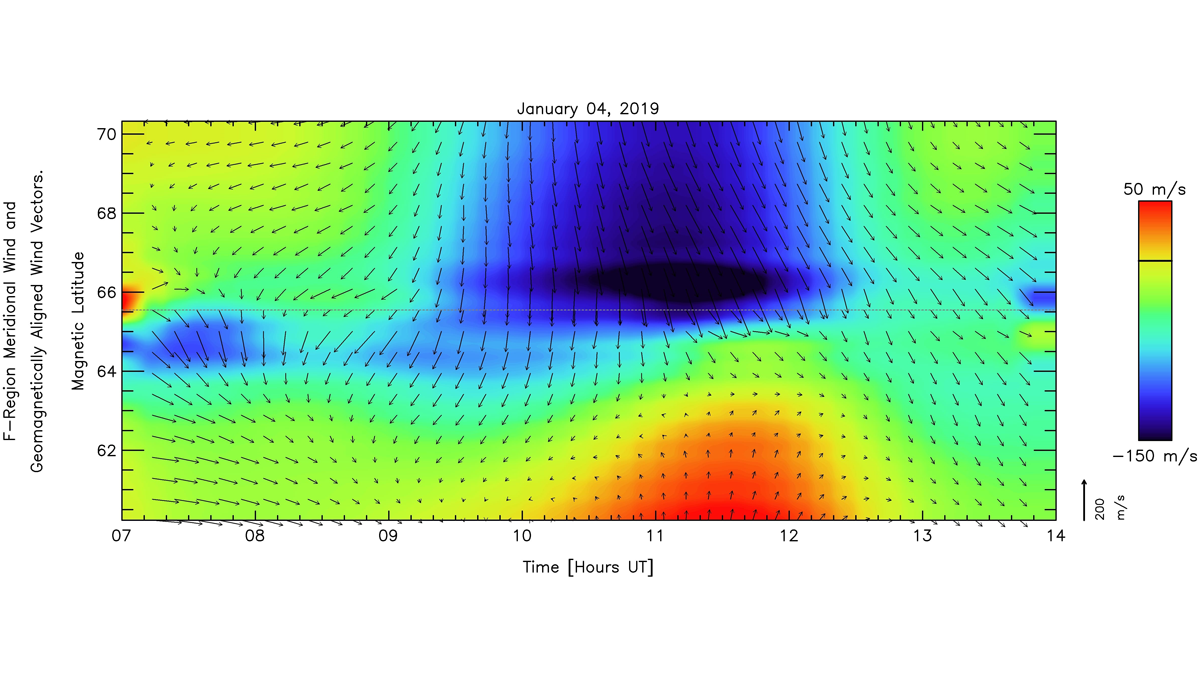
Thermospheric Cross-Polar Winds Observed to Unexpectedly Stall
Observations of cross-polar cap neutral winds near 240 km altitude stalling over short distances in the midnight sector near Poker Flat, Alaska, challenge the standard view of high-latitude dynamics.
Could Low-Altitude Reconnection Power Jupiter’s Polar Aurorae?
Magnetic reconnection events less than 2 Jovian radii above the planet’s cloud tops could explain why Juno has yet to observe a source for Jupiter’s polar aurore.
Filling the Gaps in the SuperDARN Archive
Researchers present a new pattern-finding technique to better estimate missing data on ionospheric plasma velocities.
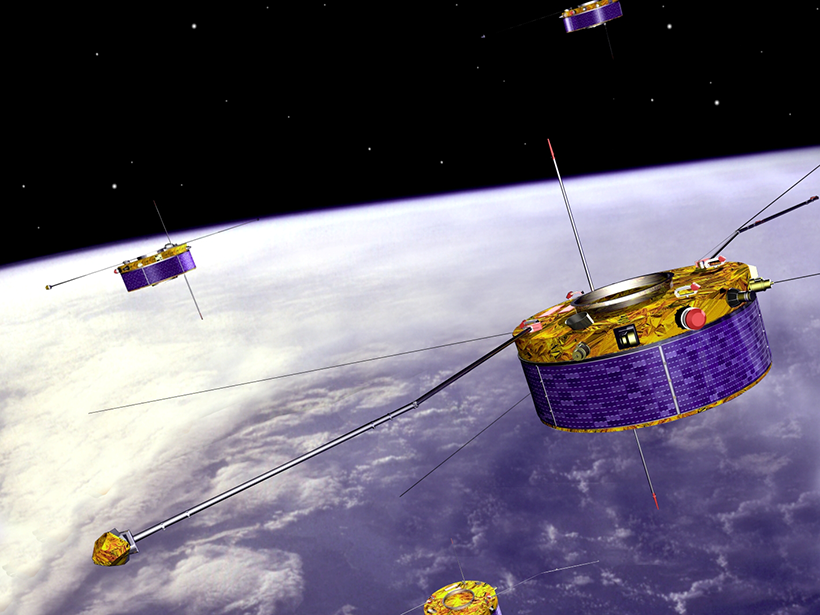
Understanding Aurora Formation with ESA’s Cluster Mission
Over 2 decades, Cluster has shed light on the auroral acceleration region, where parallel electric fields send charged particles on a collision course with the atmosphere.
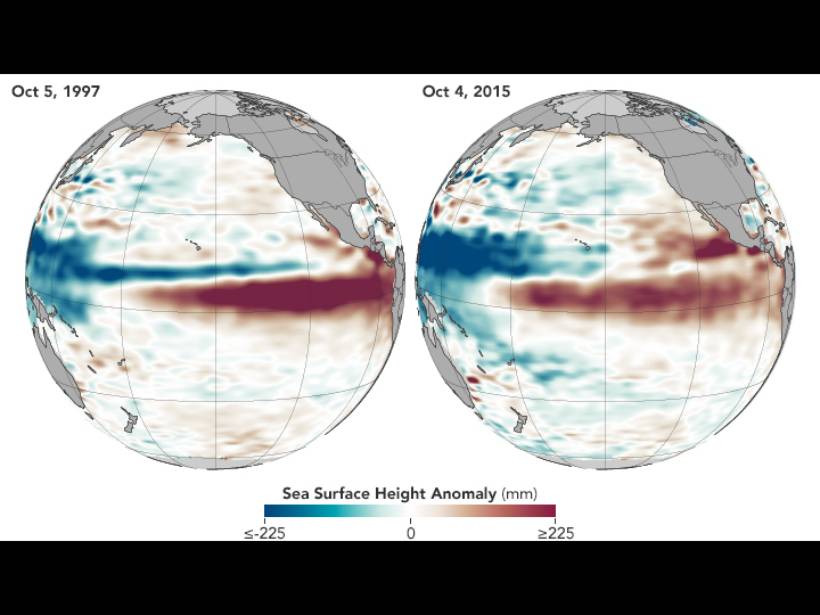
Explaining Thermal Tides in the Upper Atmosphere During the 2015 El Niño
Increased tropospheric heating and reduced dissipation combine to explain an anomalously large thermal tide.