What happens when subduction stops? A team of scientists installed a dense seismic network in Borneo to investigate causes and consequences of subduction termination.
landscape & topography
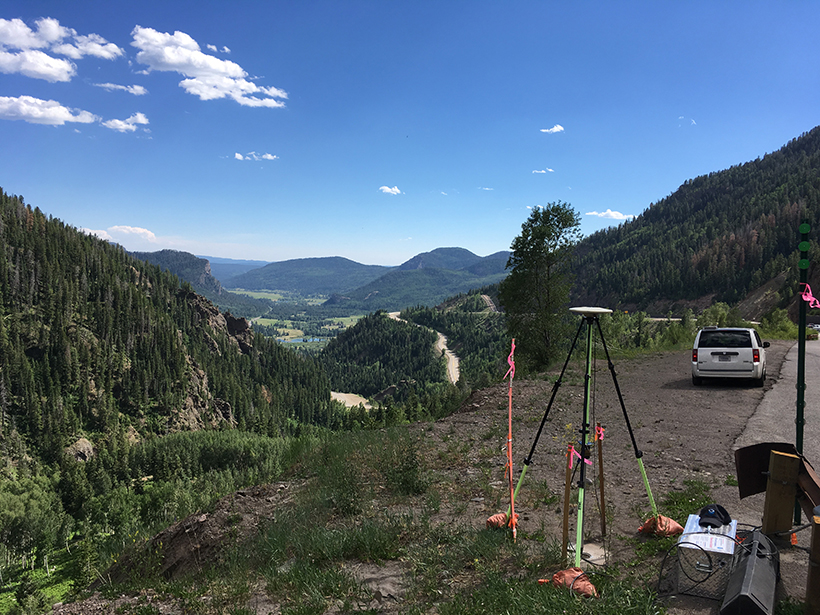
Airborne Gravity Surveys Are Remaking Elevations in the U.S.
Measuring gravity’s tiny fluctuations is giving the United States an upgraded system of elevations.
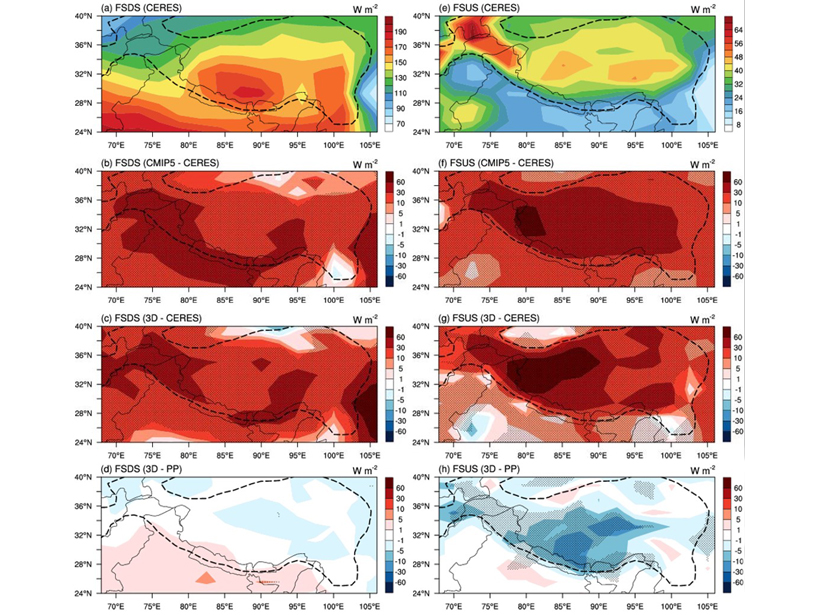
3D Radiation-Topography Interaction Warms Up Tibetan Plateau
3-D radiation-topography interaction, which can increase the sunlight absorption by the surface, is missing in all climate models, causing strong cold biases over the Tibetan Plateau.
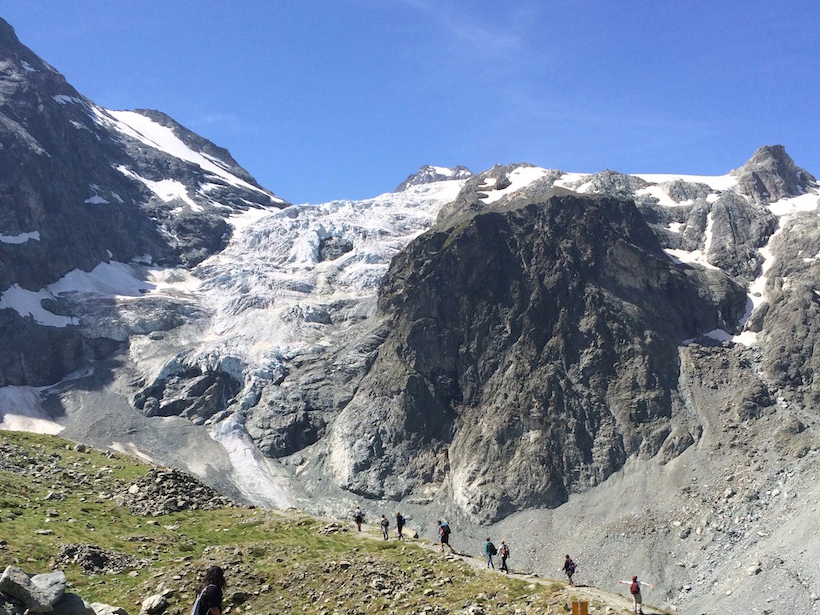
Decadal Changes in Glacial Discharge in the High Alps
A new statistical analysis of daily, glacial runoff cycles offers a unique way of examining how Alpine glaciers have responded since the onset of rapid regional warming in the 1980s.
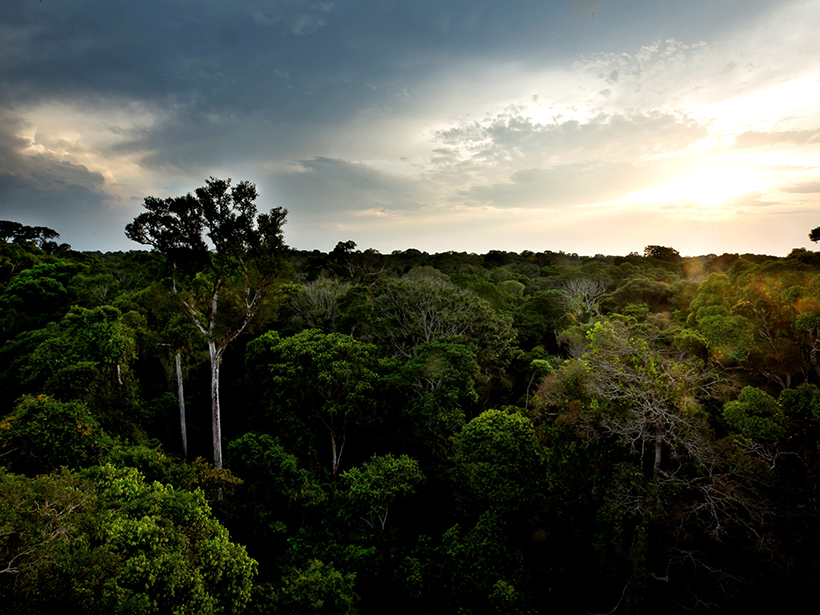
A Simplified Model of Water Vapor Exchange in the Amazon
Evapotranspiration is the exchange of water vapor between land and the atmosphere, and it is hard to measure and model. A new study shows promise for its estimation over large, vegetated landscapes.
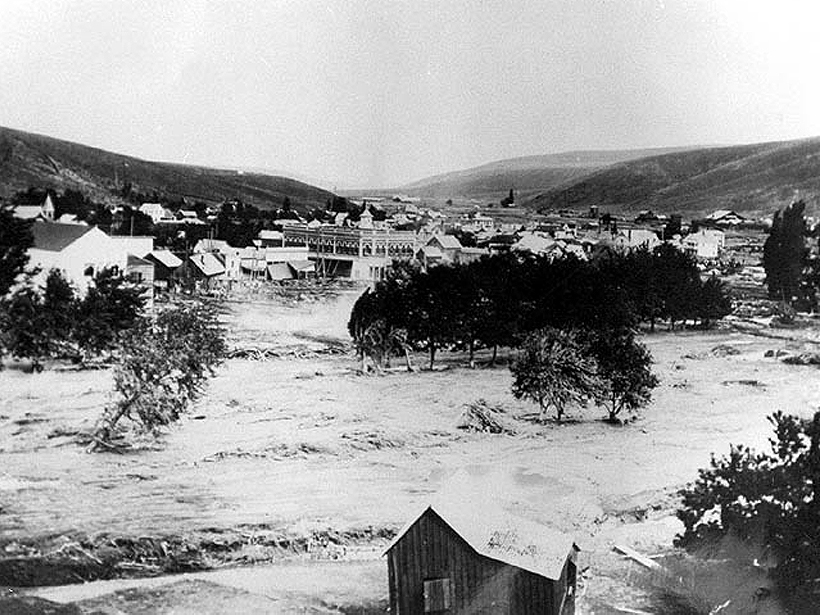
The Meteorological Culprits Behind Strange and Deadly Floods
A new study examines how unusual meteorology interacted with topography and other local conditions to generate some of the most devastating floods in American history.
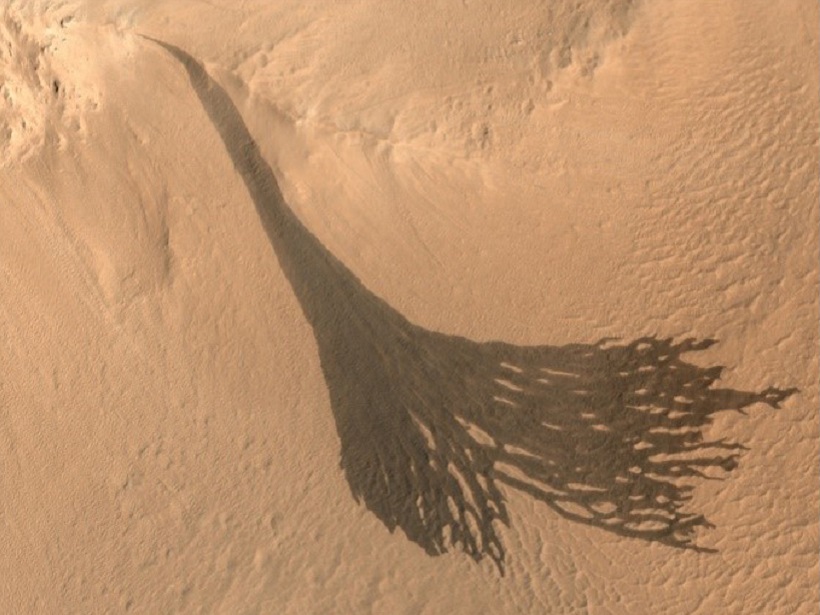
Revisiting Enigmatic Martian Slope Streaks
Slope streaks of different sizes and shapes are a common feature on the surface of Mars, but scientists disagree about the mechanisms for their formation and development.
Dennis P. Lettenmaier Receives 2018 Robert E. Horton Medal
Dennis P. Lettenmaier was awarded the 2018 Robert E. Horton Medal at the AGU Fall Meeting Honors Ceremony, held on 12 December 2018 in Washington, D. C. The medal is for “outstanding contributions to hydrology.”
The ILAMB System for Benchmarking Land Surface Models
An evolving set of tools helps land surface model developers optimize the realism of their parameterizations for the next generation of weather and climate models.
Scanlon Receives 2018 Hydrologic Sciences Award
Bridget Scanlon will receive the 2018 Hydrologic Sciences Award at AGU’s Fall Meeting 2018, to be held 10–14 December in Washington, D. C. The award is for “outstanding contributions to the science of hydrology.”