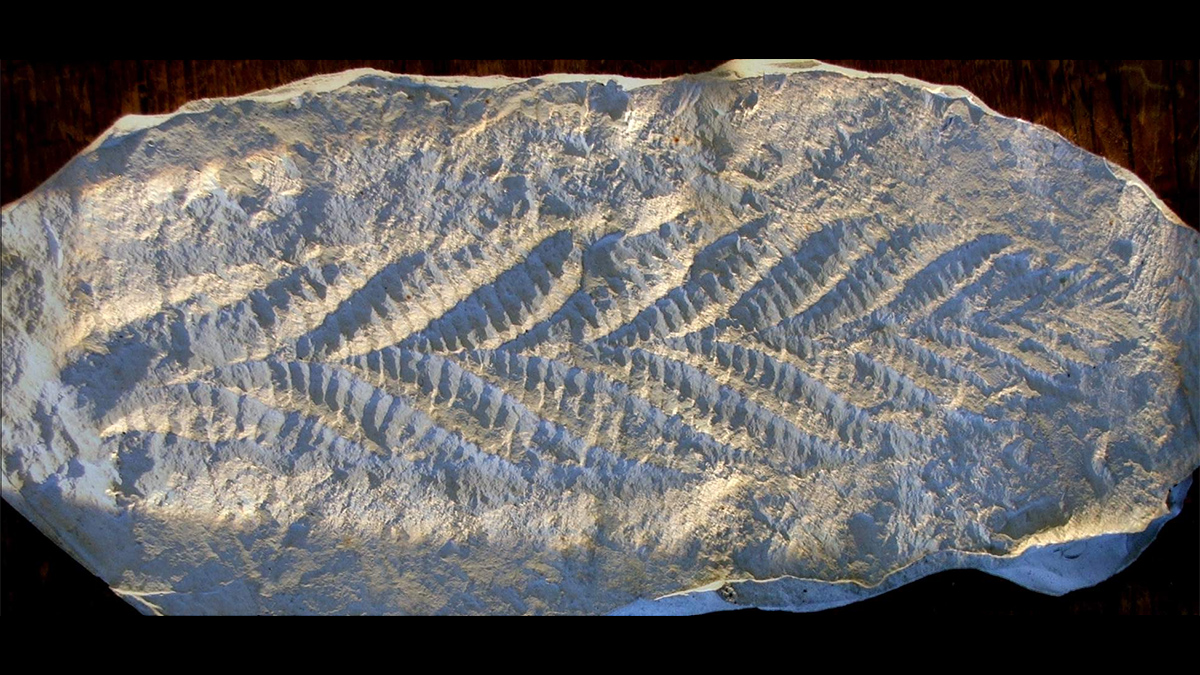
A roughly 70-million-year interval of anomalously weak magnetic field during the Ediacaran period could have triggered atmospheric changes that supported the rise of macroscopic life.
life as we know it
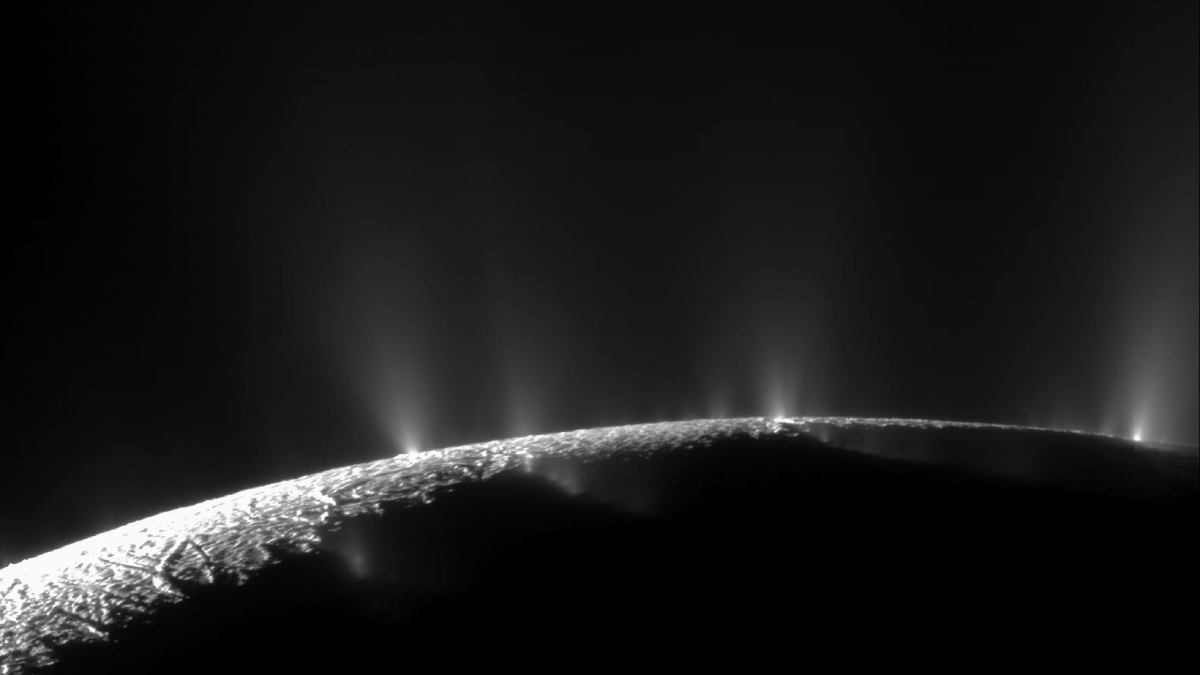
Speedy Flyby Adds New Organics to Enceladus’s “Primordial Soup”
A new analysis of old Cassini data has also verified past detections of complex organics in Saturn’s E ring, strengthening the chemical ties between the ring and its progenitor.
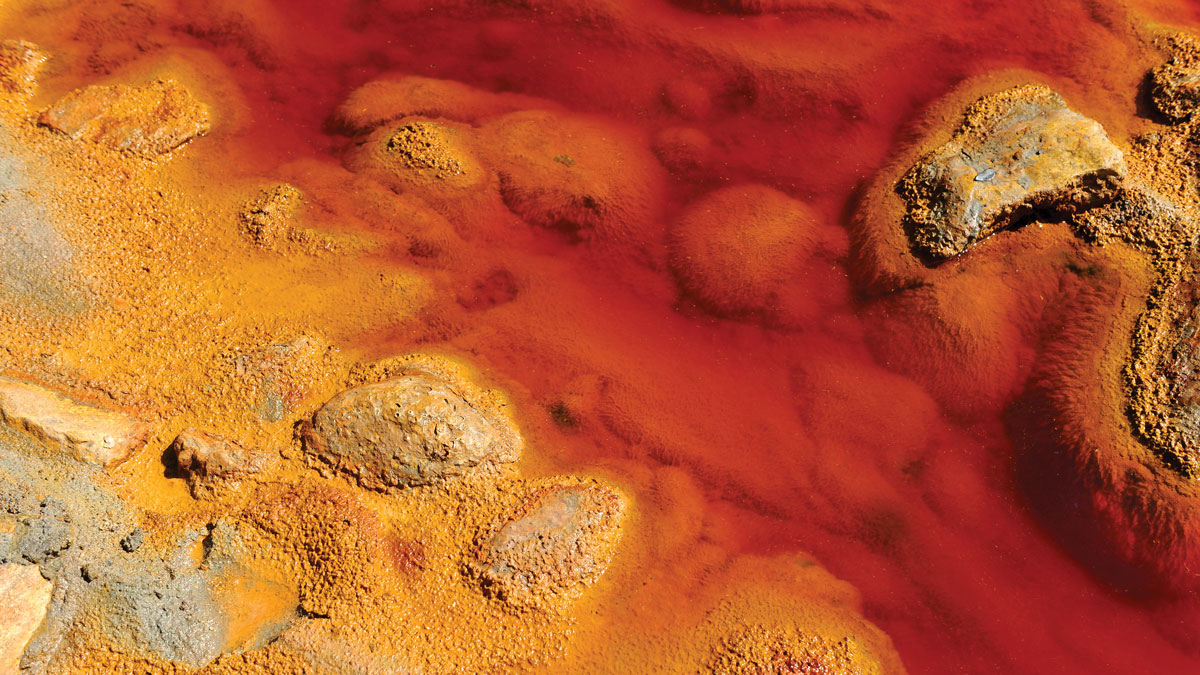
A Flash, a Boom, a New Microbe Habitat
After an asteroid struck Finland long ago, microscopic life colonized the impact site within a few million years, new research reveals.
Asteroid Samples Suggest a Solar System of Ancient, Salty Incubators
The discovery of salty mineral evaporites on Ryugu indicates that watery environments may have been widespread in the early solar system.
Using Algorithms to Help Find Life on Icy Ocean Worlds
Scientists could use machine learning to analyze atmospheric samples in order to help identify microbes on frozen moons. They’re testing the concept using bottles of brine and smelly bacteria.
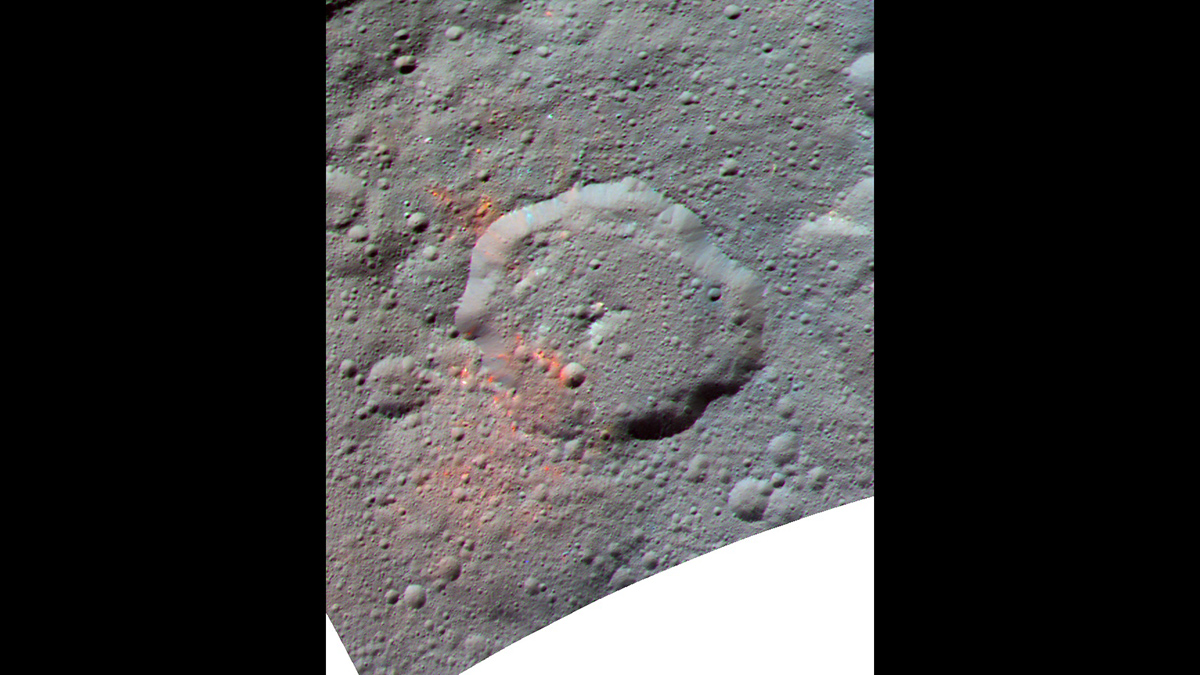
Ceres’s Organics Might Not Be Homegrown After All
Scientists have been unable to determine whether the dwarf planet’s organics were produced by its own chemical processes or delivered by asteroids. New evidence implicates asteroids.
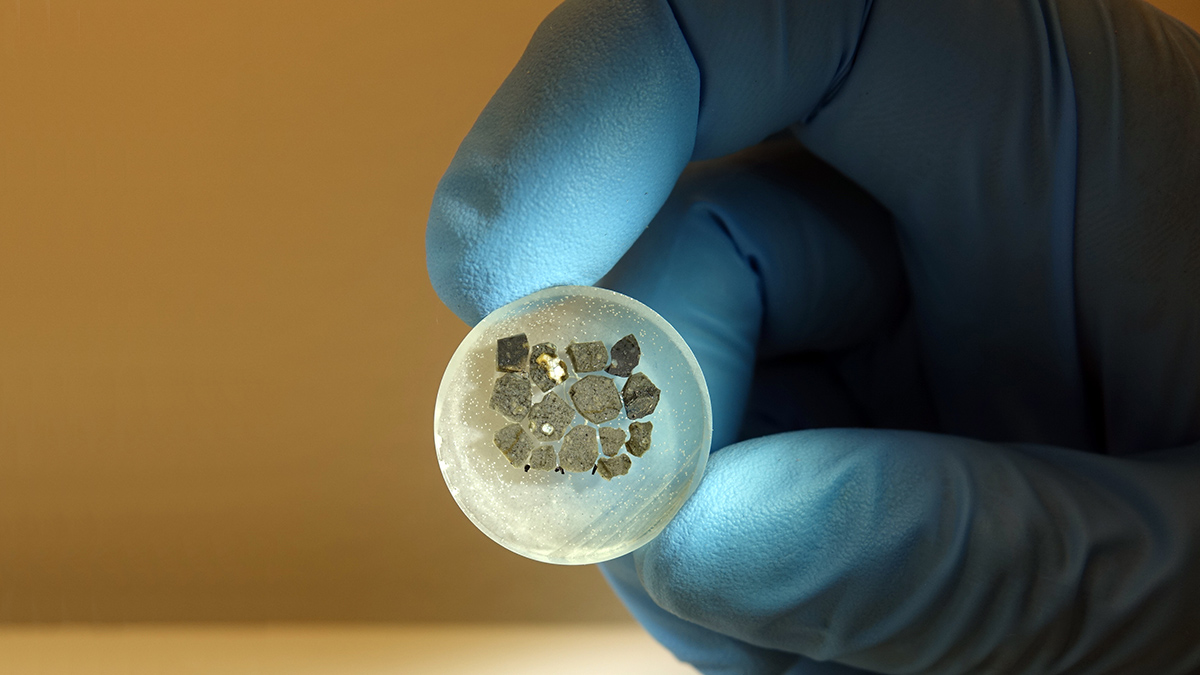
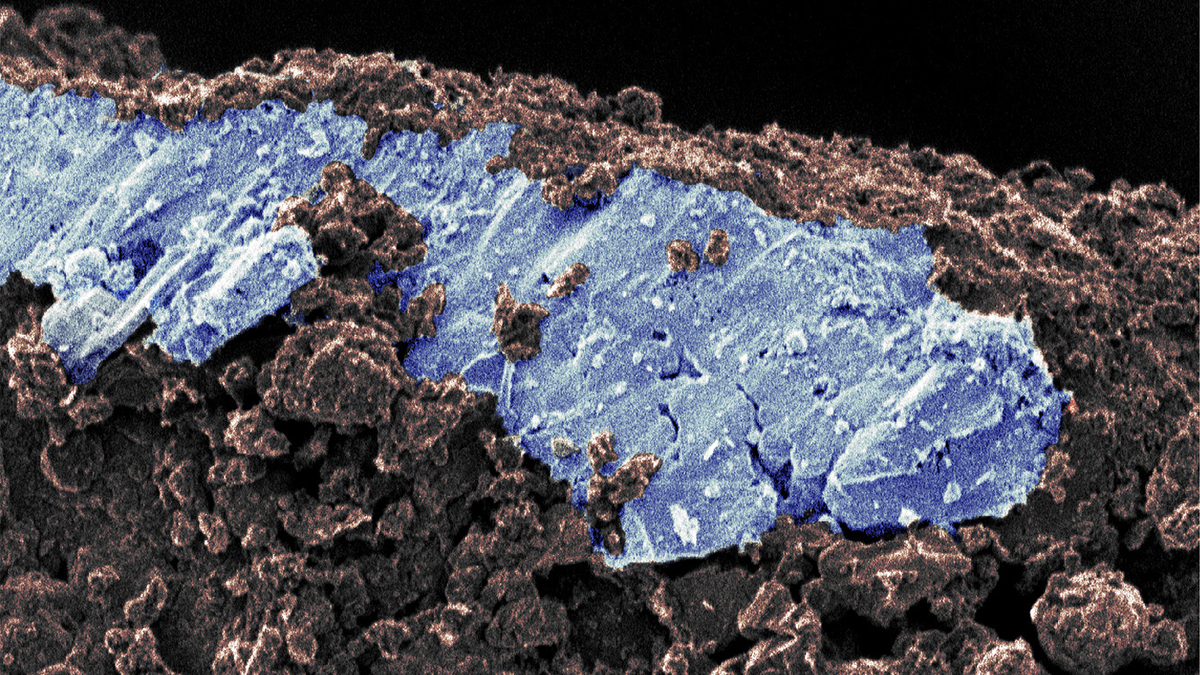
Life’s Building Blocks Found in Bennu Samples
The discovery of amino acids, abundant ammonia, and the bases of DNA and RNA on asteroid Bennu suggest that materials essential to life might be widespread throughout the solar system.
A Planetary Perturbation Like No Other
Scientists are tackling “the most profound questions about life itself” with complex computer modeling, billion-year-old bacteria, and old-fashioned fieldwork.
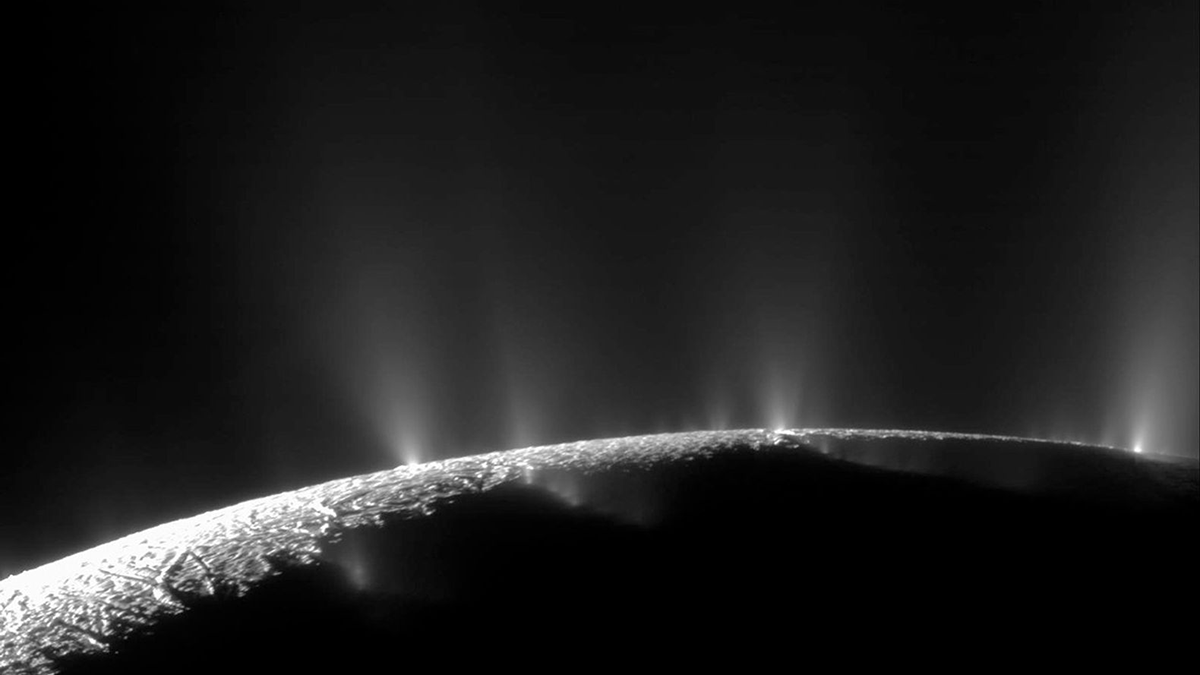
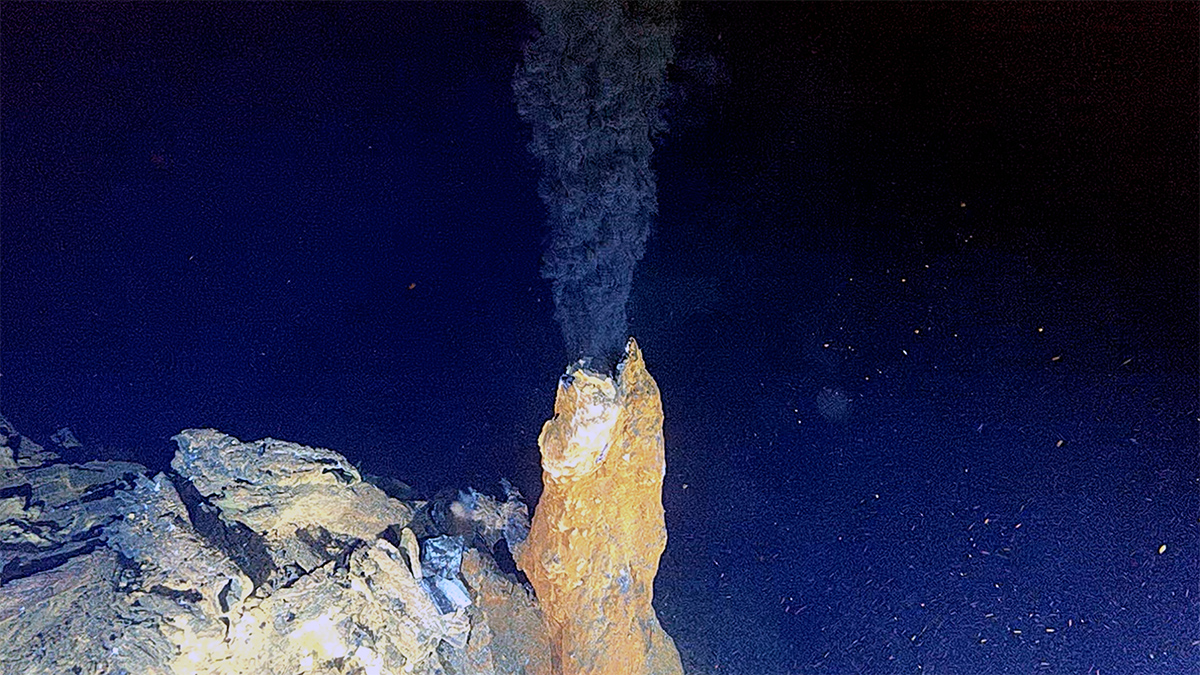
Arctic Hydrothermal Vents May Resemble Those on Enceladus
By studying hydrogen-rich vent sites on Earth, scientists could learn more about the hidden ocean of Saturn’s icy moon—one of our solar system’s likeliest candidates for harboring life beyond Earth.
Planetary Perturbations May Strengthen Gaia
Large-scale disruptions to life may ultimately increase ecological complexity over geologic timescales, though the risk of extinction always looms.