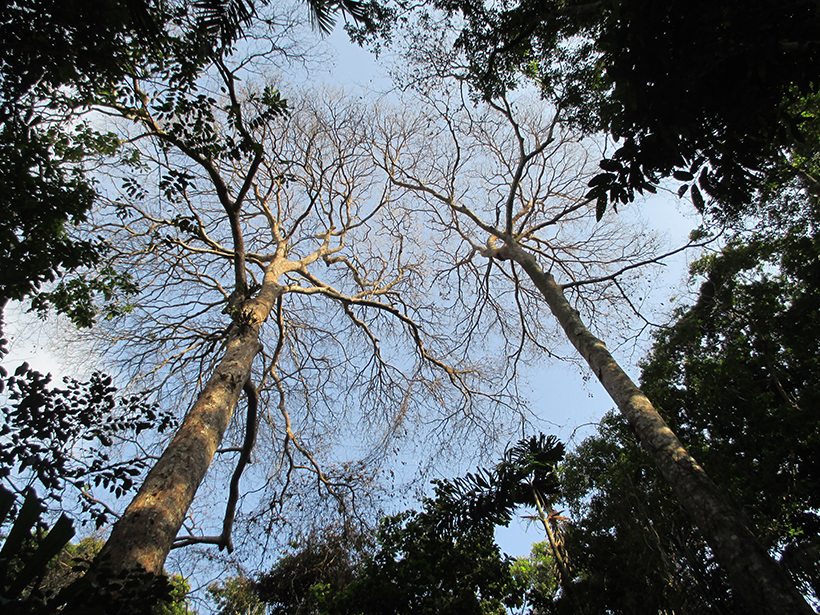
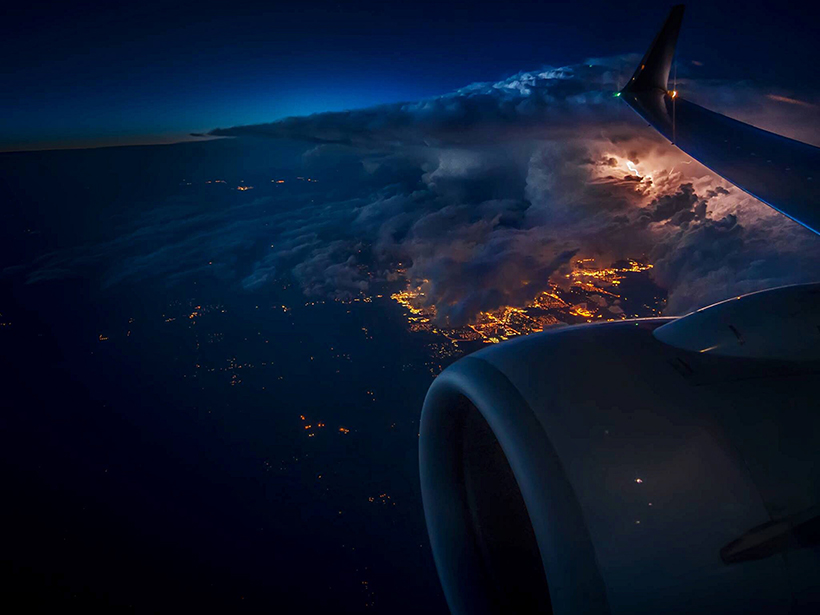
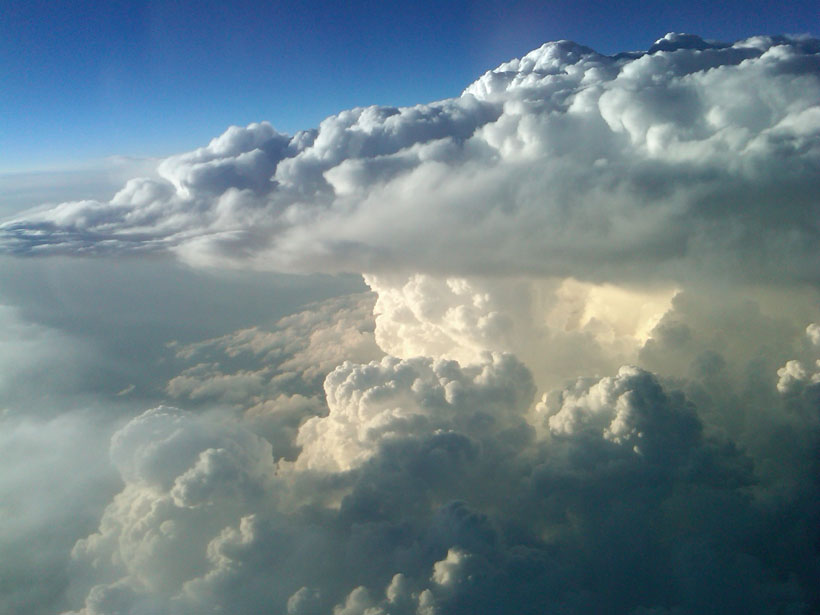
On Barro Colorado Island in the Panama Canal, scientists map lightning strikes and find that they kill mainly the loftiest trees, likely disturbing the forest ecology.
lightning
How Storm Turbulence Can Spark Lightning
The turbulent pockets of air inside storms can help to build up static electricity in the atmosphere, according to a new study.
Antenna Towers Attract Additional Lightning Strikes
Atmospheric scientists evaluate the influence of human-made structures on lightning data.
How Lightning Creates "Killer Electrons" in Earth's Radiation Belts
New calculations show that lightning-triggered plasma waves in Earth's magnetosphere absorb energy from slow particles and energize electrons to levels that can damage satellites severely.
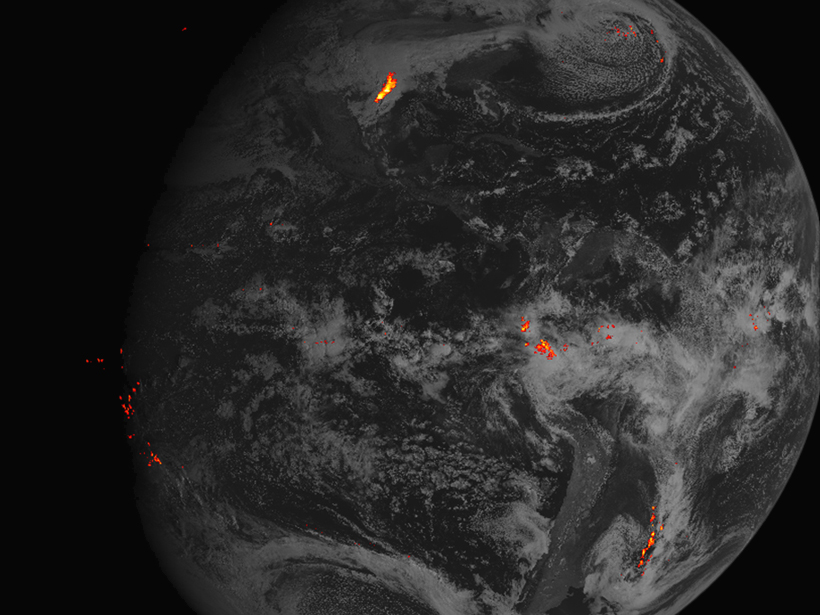
GOES-16 Satellite Lights Up Lightning Flashes in New Video
The satellite's lightning mapper instrument will help scientists forecast extreme weather.
New Way to Gauge Lightning's Role in Ozone Formation
Comparing satellite data on a key airborne ozone precursor to readings from a lightning sensor network reveals how much different types of lightning strokes affect atmospheric ozone chemistry.
Searching for Lightning's Signature on Venus
How energetic would lightning on Venus have to be to be detected by sensors? A new model sheds light.
Storms Cause Infrequent Turbulence for Aircraft, New Study Finds
Scientists using lightning sensors to automate air-turbulence detection have found evidence that storms jostle aircraft much less than previously thought.
Scientists Find Dead Lightning Branches That Come Back to Life
The detached bursts of brilliance might explain why the lowest point of a lightning bolt will sometimes suddenly brighten by up to 50% and double its speed as it hurtles to Earth.
Connecting Thunderstorms and Climate Through Ozone
New data links thunderstorms to climate via their impacts on aerosols, ozone, and water vapor in the stratosphere.