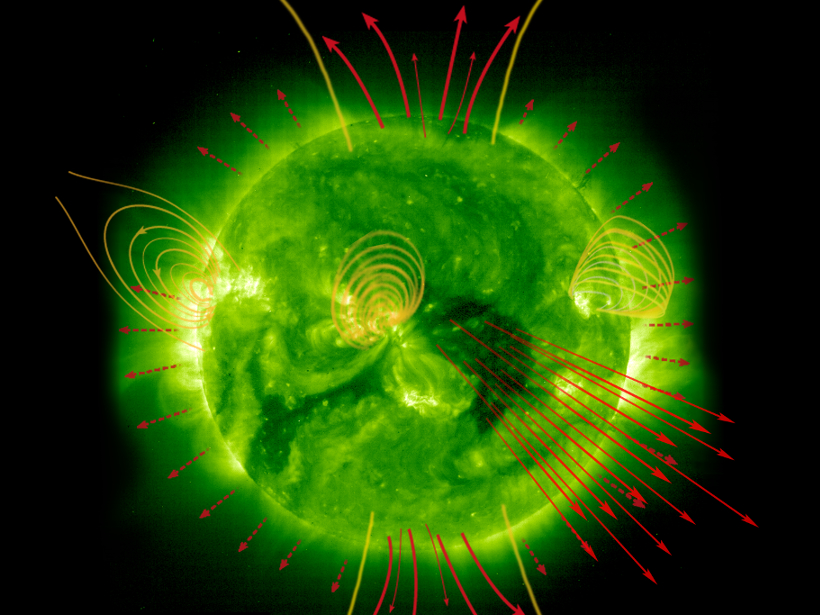
When the Earth's and the Sun's magnetic fields meet, they realign in explosive and mysterious reconnections. Data suggest that plasma waves called kinetic Alfvén waves play a key role.
magnetic reconnection
Spotting the Source of Slow Solar Wind
A new study suggests that magnetic reconnection may fuel slow solar winds, which top out at speeds below 500 kilometers per second.
First Results from NASA’s Magnetospheric Multiscale Mission
Understanding magnetic reconnection is important in the context of Sun-Earth Connection, because of the resulting exchange of mass and energy, and the large amount of energy involved.
Solar Wind Disconnects Venus’s Magnetotail
Polarity reversals in the solar wind magnetic field disconnect the magnetic field trailing behind Venus, allowing ions from the atmosphere to escape.
Chasing Down the Slow Solar Wind
The Sun's plasma blasts Earth’s magnetosphere at more than a million miles per hour. The fastest pours from holes in the corona, but until recently the source of the "slow" solar wind was a mystery.
Electrons Thrown Off Course in Near-Earth Magnetic Reconnection
NASA Magnetospheric Multiscale (MMS) mission detects energy differences in electrons scattered by magnetic reconnection.
Exploring New Knowledge on Magnetospheric Interactions
AGU Chapman Conference on Magnetospheric Dynamics; Fairbanks, Alaska, 27 September to 2 October 2015
Great Mysteries of the Earth's Magnetotail
Workshop on Magnetotail Reconnection Onset and Dipolarization Fronts; Laurel, Maryland, 16–18 September 2015
Satellites Test Theory of Magnetic Reconnection
A quartet of satellites flying through Earth's magnetic field measures its interaction with the Sun's and puts a theory about their reconnection to the test.
X Marks the Spot of Magnetic Islands in Space
At the edge of Earth's magnetic field, satellites have found X-shaped fields and fast-moving "islands" of magnetism that could shed light on the physics of solar storms.