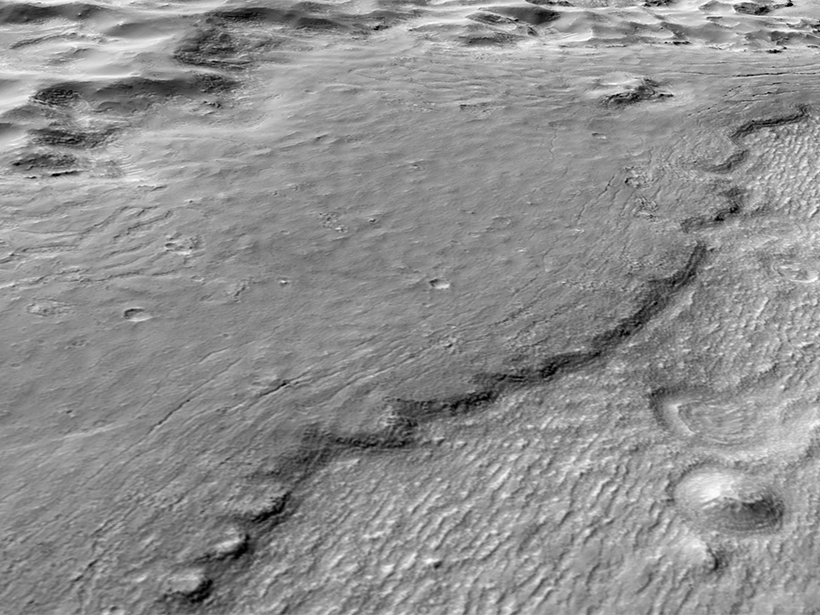
The impact crater is a dry lake bed that contains evidence of ancient water flows and perhaps signs of ancient microbial life.
Mars
Magnetic Mars Engages Lay Audiences in Science
A NASA team has developed resources to intrigue the public with the discoveries from its Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution (MAVEN) mission. Here are four tips for communicating that science.
Atacama Desert’s Unprecedented Rains Are Lethal to Microbes
Rainfall in the driest parts of Chile’s Atacama Desert in 2017 resulted in hypersaline lagoons that killed the majority of microbes adapted to millions of years of arid conditions.
Brine Pools Emerge as a New Place to Search for Life on Mars
Some pools of salty water on the Red Planet could contain enough dissolved oxygen for microorganisms and sponges to survive, new calculations suggest.
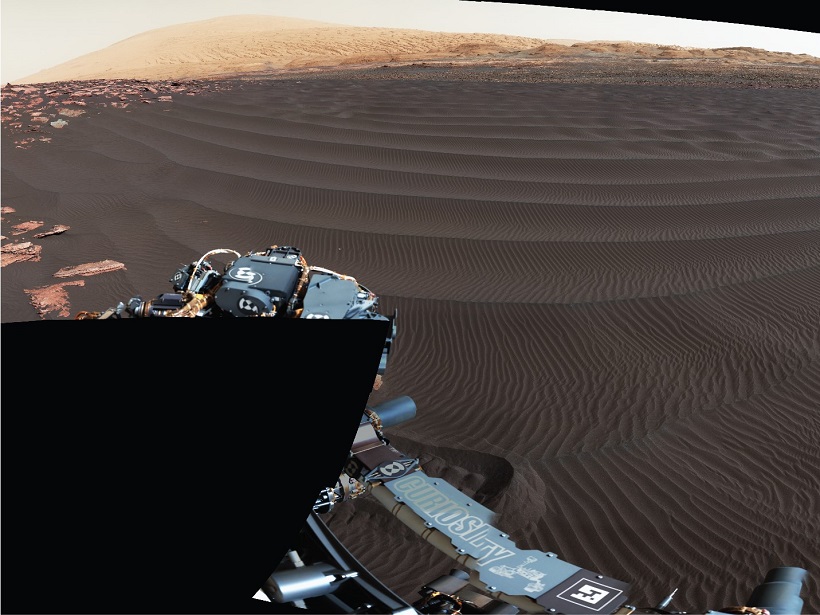
Seeing Mars in a Grain of Sand
The second phase of Curiosity’s campaign at the Bagnold Dunes brought new observations of windblown sands during Mars’s windy season.
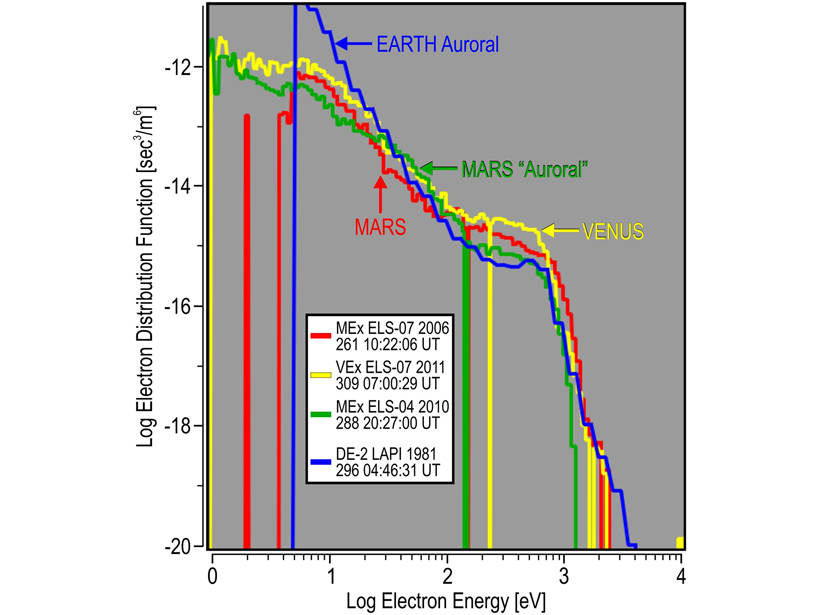
Extreme Space Conditions at Mars: The 10 Largest Electron Events
A solar cycle of data was scoured for the biggest electron energy fluxes seen in the Mars space environment.
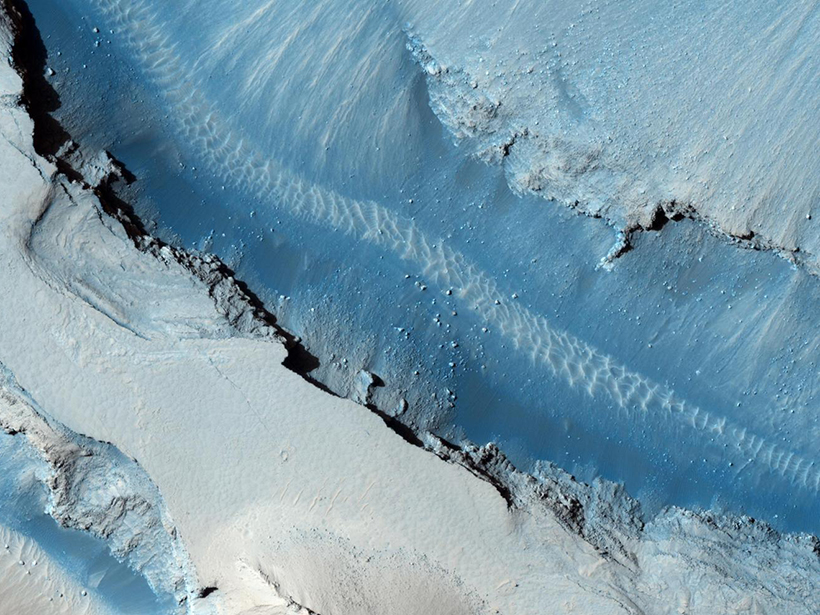
Searching for Signs of Marsquakes
Researchers use high-resolution images of Mars’s surface to look for signals of coseismic displacement.
Evidence of Regional Deposition in Mars’s South Polar Deposits
Shallow Radar correlation of discrete units in one of the Red Planet’s largest ice reservoirs suggests that its material was emplaced as a single, regional deposit.
Is Mars Not So Earthlike After All?
Light-colored Gale crater rocks could have formed from intraplate volcanoes, not continental crust, new study finds.
Tracing the Steps of Hydrothermal Activity in Hrad Vallis, Mars
Conditions that formed Amazonian age valleys may have been hospitable to microbial life.