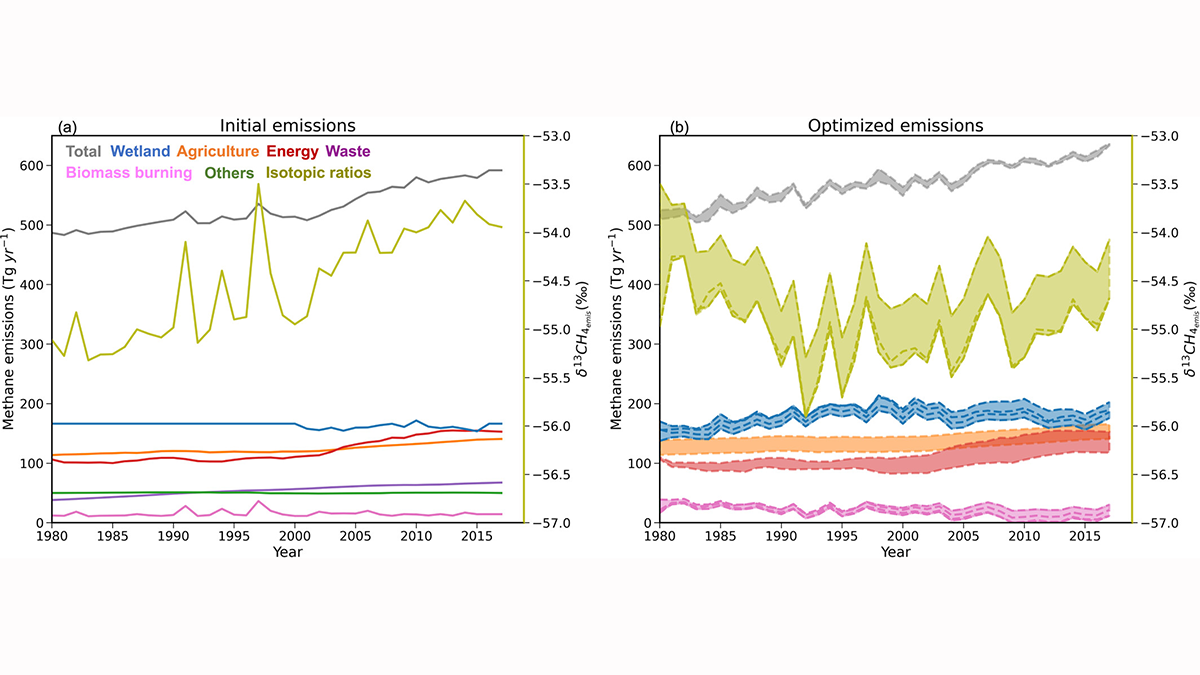
Recent increases in atmospheric methane are a result of changing natural and manmade sources, climate, and other less-understood factors linked to its role in the atmosphere’s self-cleaning mechanisms.
methane
Global Methane Emissions Projected to Fall, According to United Nations Report
The world has made significant progress on methane mitigation since 2020, though meeting the goals of a major international pledge will require additional action, according to a United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) report.
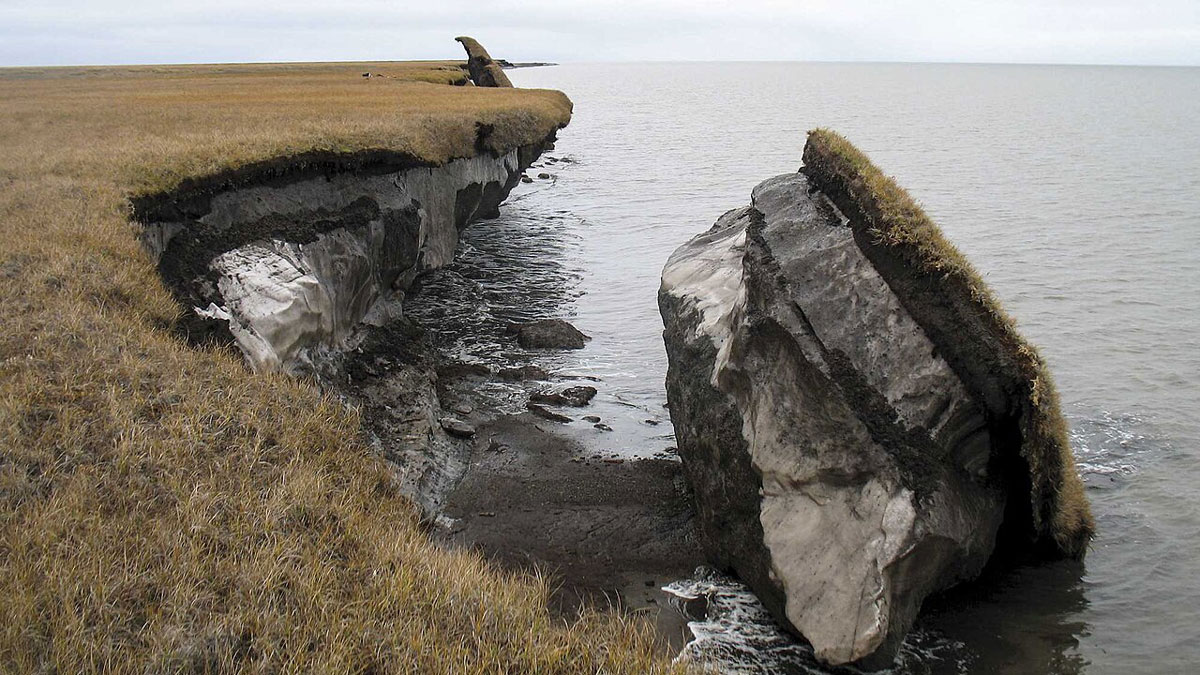
In Arctic Soils, Methane-Eating Microbes Just Might Win Out over Methane Makers
Methanotrophs, including those that capture methane from the air, seem to outcompete methanogens in dry environments, a new study shows.
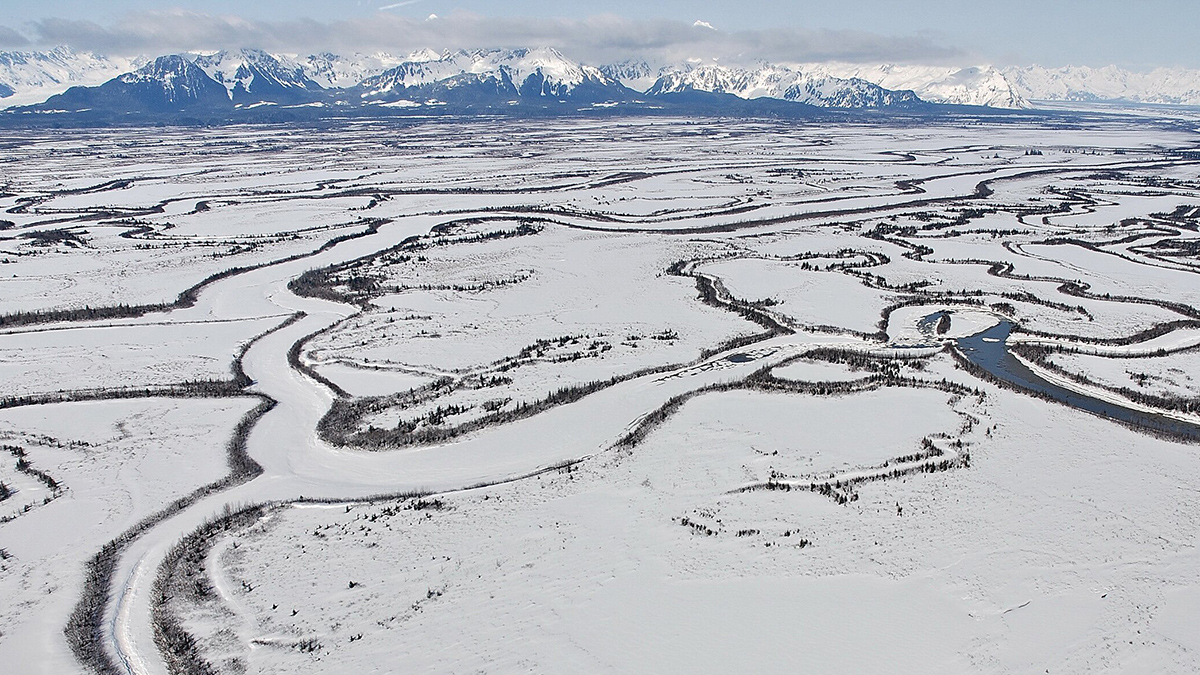
Tectonics and Climate Are Shaping an Alaskan Ecosystem
Biogeochemical research reveals the web of forces acting on a high-latitude microbe community in the Copper River Delta.
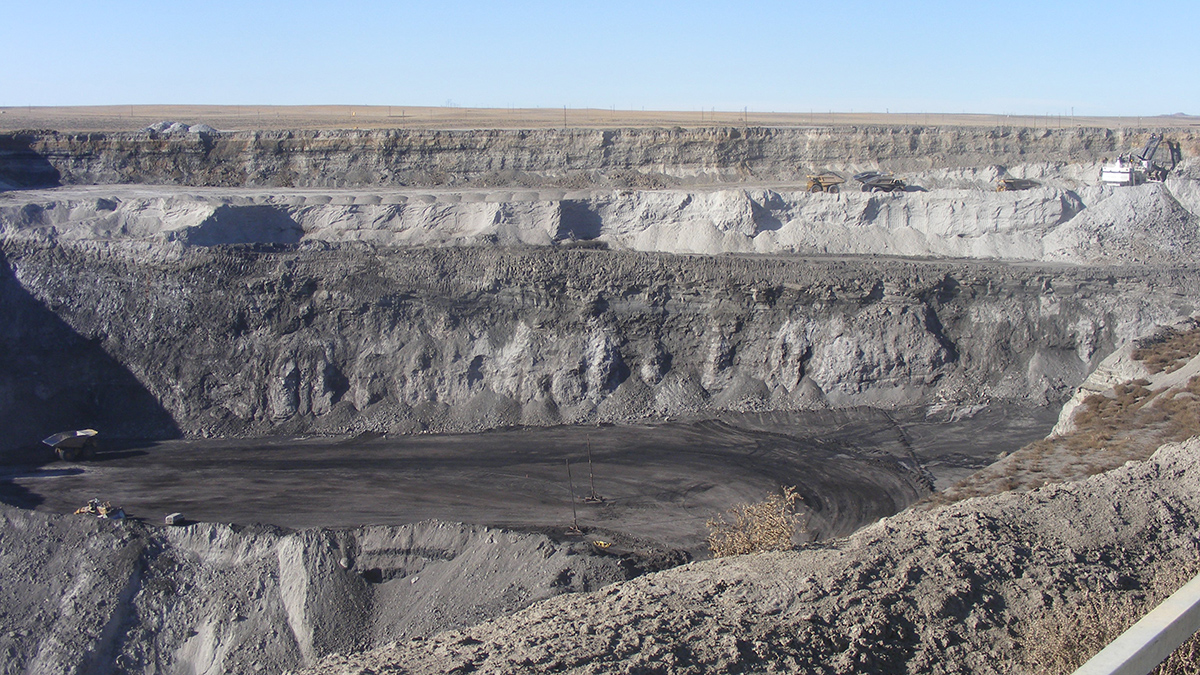
By 2051, Emissions from Coal Mining on Federal Lands Could Drop by 86%
Researchers predict that if early 2024 policies hold, emissions related to coal’s extraction, transportation, and combustion will drop over the next 25 years.
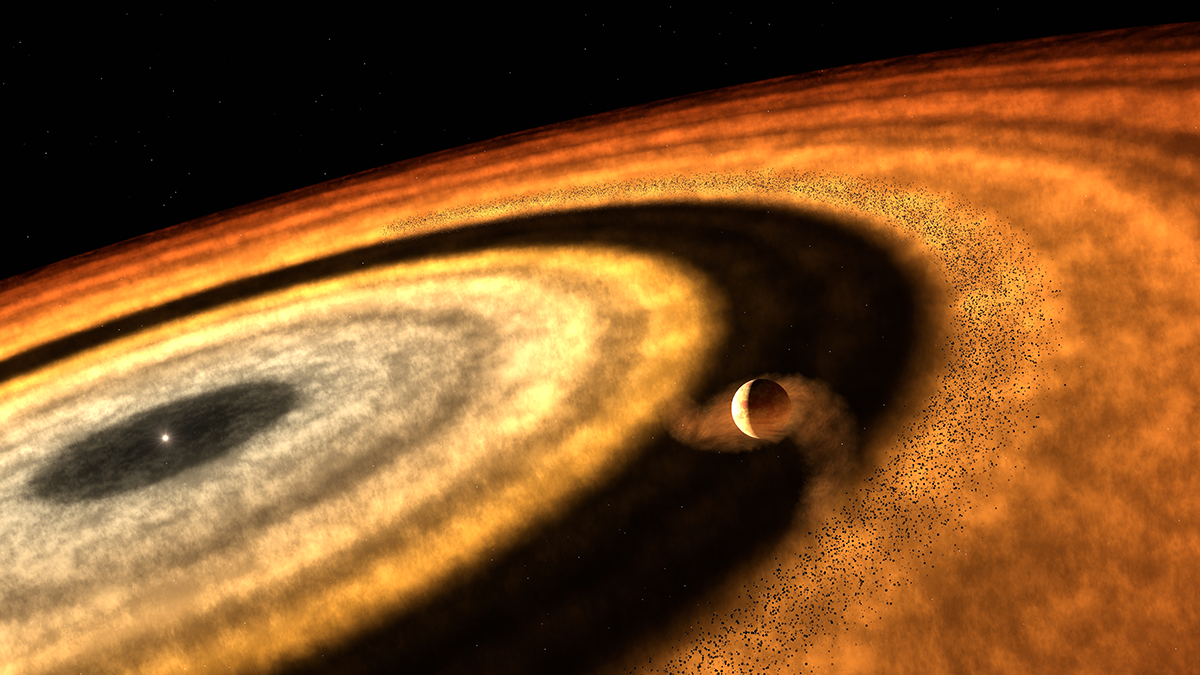
This Exoplanet May Have Grown Stranger as It Journeyed Starward
WASP-121b, an already unusual planet, might have a remote origin that explains some of its peculiar properties—from iron rain to the unexpected presence of methane.
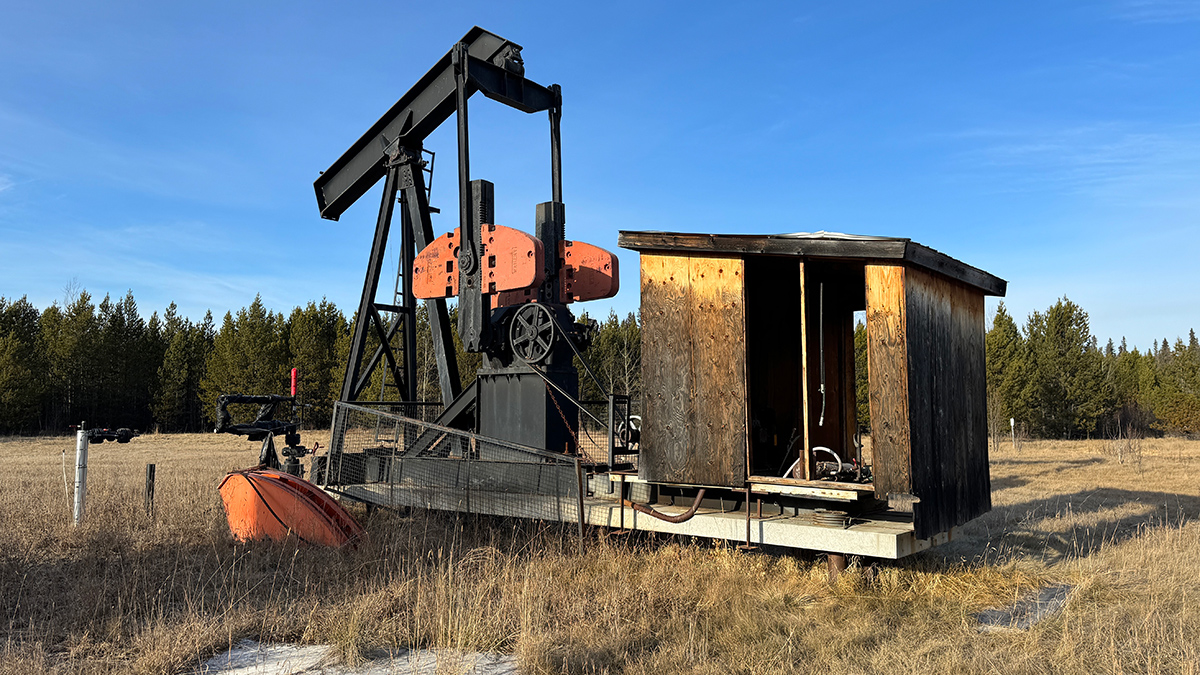
Nonproducing Oil Wells May Be Emitting 7 Times More Methane Than We Thought
A study measured methane flow from more than 450 nonproducing wells across Canada, but thousands more remain unevaluated.
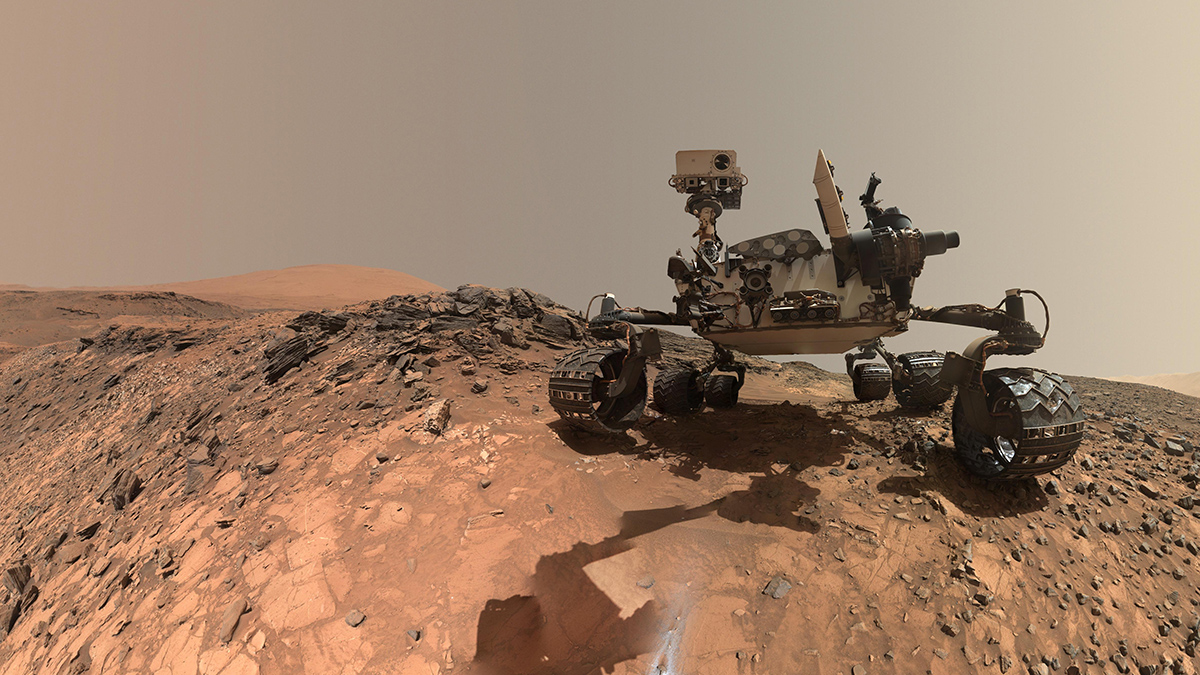
Proposed Experiment Could Clarify Origin of Martian Methane
Curiosity’s detection of the gas, if atmospheric, could be an indicator of life on the Red Planet. But skeptics say further work is needed to rule out the rover itself as the source of the methane.
Peatland Plantations in Southeast Asia are Carbon Hotspots
A new study reports a rare set of data on greenhouse gas production and transport for a tropical peatland plantation showing exceptionally high concentrations of dissolved organic carbon.
Rice Paddies, Like Cows, Spew Methane. A New Variety Makes Them a Lot Less Gassy.
Rice plants are a big source of methane, an extremely potent greenhouse gas. Scientists just developed a strain that cuts those emissions by 70 percent.