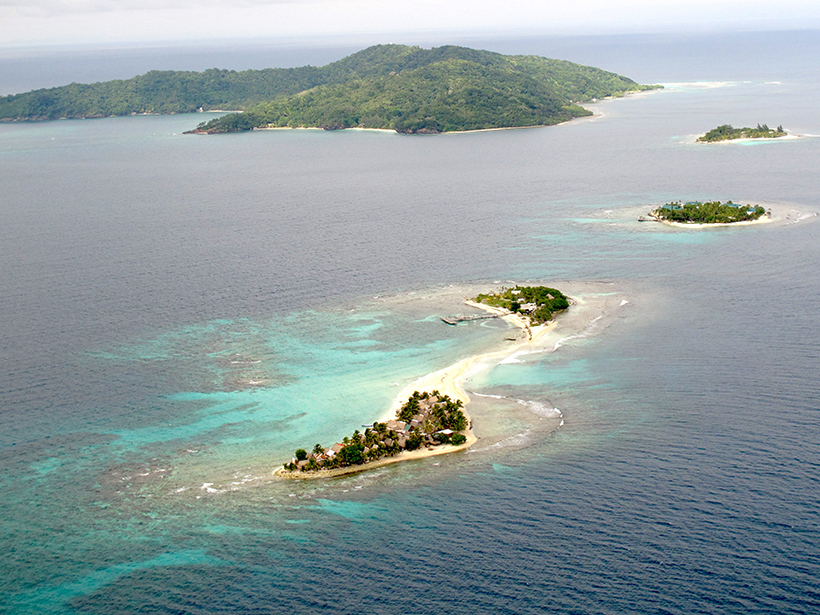
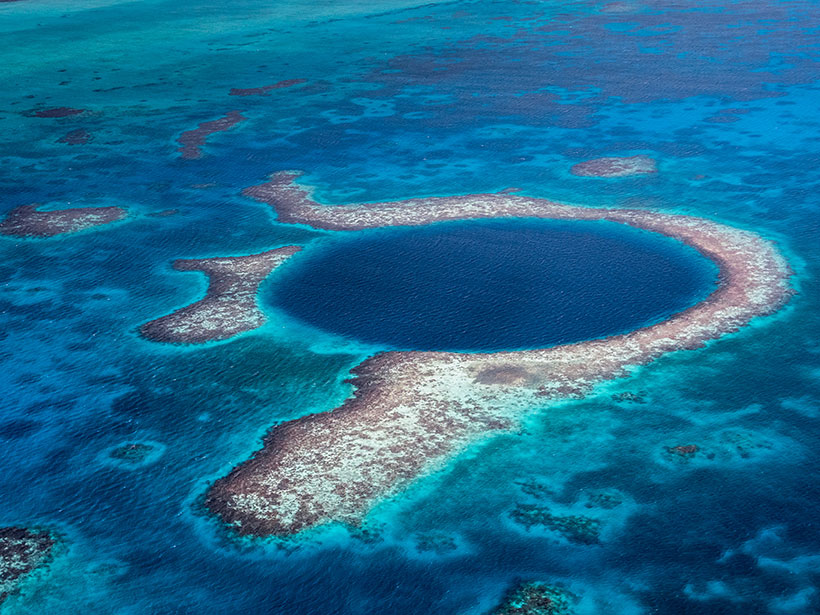
The reef’s report card analyzed 286 sites in Mexico, Belize, Guatemala, and Honduras. Communities, scientists, and governments are working to improve coral and ecosystem resilience.
Mexico
Severe Cyclones May Have Played a Role in the Maya Collapse
Sediment cores from the Great Blue Hole reveal that a series of extreme storms hit the region after 900. The storms may have irreparably damaged an already stressed Maya population.
Chicxulub Impact Crater Hosted a Long-Lived Hydrothermal System
Chemical and mineralogical evidence of fluid flow—potentially conducive to microscopic life—was revealed in rock cores extracted from the crater’s “peak ring.”
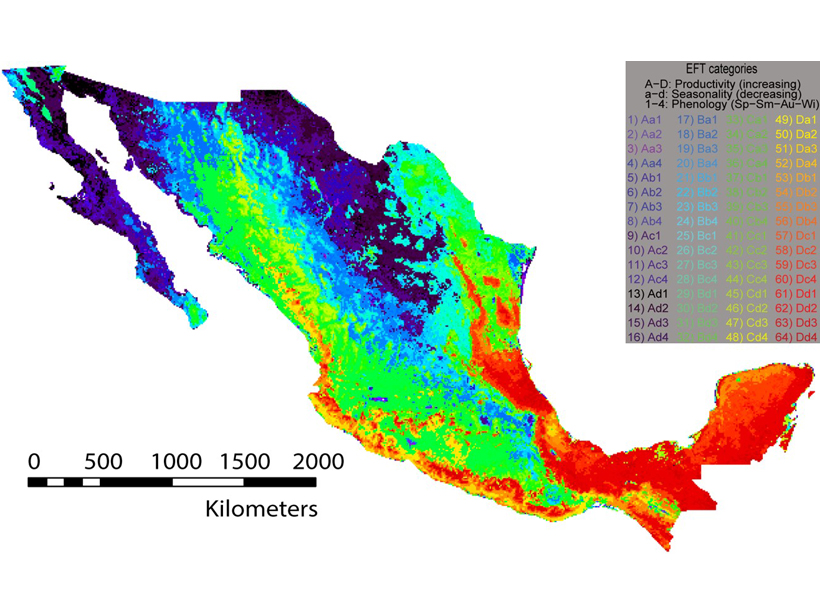
Stocking a Proper Buffet for a Megadiverse Smorgasbord
Mexico’s megadiverse biota challenge observation network design for efficient sampling, but novel methods can provide guidance and tests of representativeness.
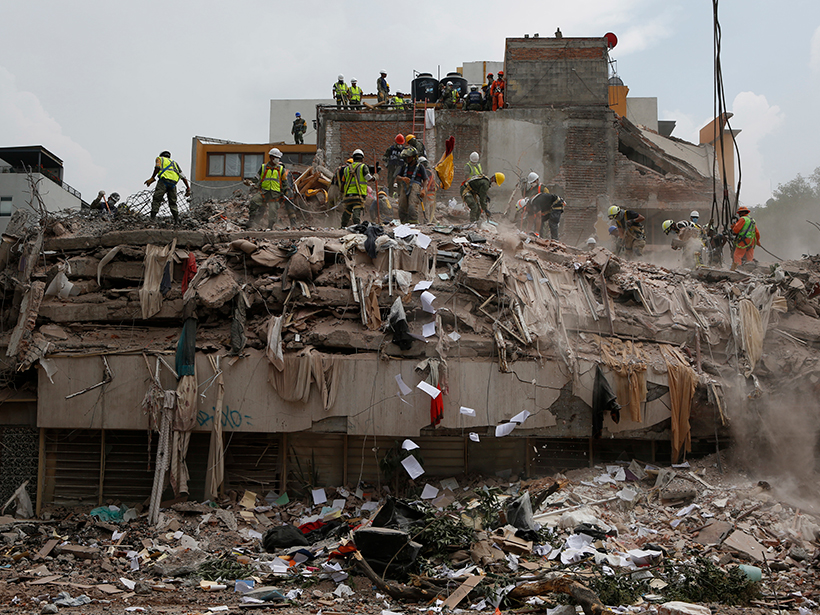
Lessons from Mexico’s Earthquake Early Warning System
The devastating 2017 Puebla quake provides an opportunity to assess how citizens perceive and use the Mexico City earthquake early warning system.
New Simulation Supports Chicxulub Impact Scenario
Mountains ringing the center of Earth’s most famous impact crater consist of porous rocks. Computer models of the impact can now predict those rocks’ microstructure.
Were Mexico’s September Quakes Chance or a Chain Reaction?
Last year, two major earthquakes—one 12 days after the first—shook Mexico. New analysis blames this very unlikely event on chance. But one of the pair may have triggered a third large nearby temblor.
How "Godzilla" El Niño Affected Tropical Fish in Low-Oxygen Zone
A warm period unexpectedly boosted some species of fish larvae off the coast of Mexico.
Cores from Crater Tied to Dinosaur Demise Validate Impact Theory
Drilling into the famous, deeply buried Chicxulub crater off Mexico, researchers found deformed and porous granite that opens new avenues of research.
Mexico City Hosts a Course on Remote Sensing for Latin Americans
Course on Remote Sensing Techniques Applied to Atmospheric Chemistry; Mexico City, Mexico, 7–11 December 2015