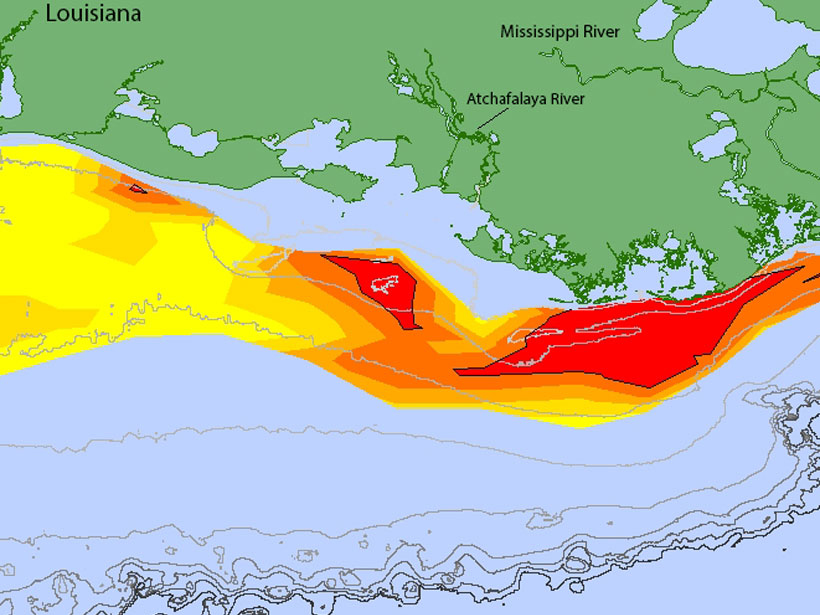
A new forecast predicts widespread hypoxia after a wet Midwest spring.
Mississippi River
Posted inNews
Secrets from the New Madrid Seismic Zone’s Quaking Past
High-resolution lidar topography reveals a long history of ancient earthquakes.
Posted inFeatures
Rethinking the River
The Mississippi River and its delta and plume provide insights into research-informed approaches to managing river-dominated coastal zones.
Posted inResearch Spotlights
Reimagining a Fatal Flood
Researchers use high-resolution simulations to reexamine the rainfall events that led to one of the most destructive floods in U.S. history.