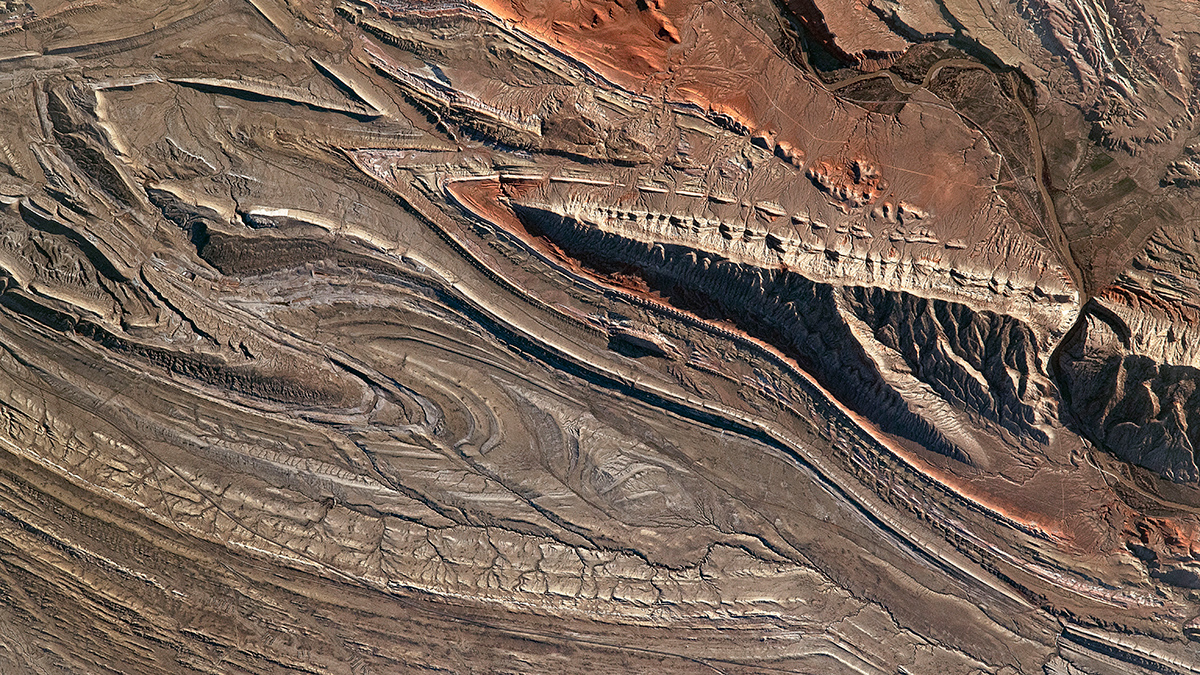
A new study evaluates the performance of kilometer-scale models in predicting large tropical storms, which are key drivers of extreme rainfall and severe weather.
Modeling
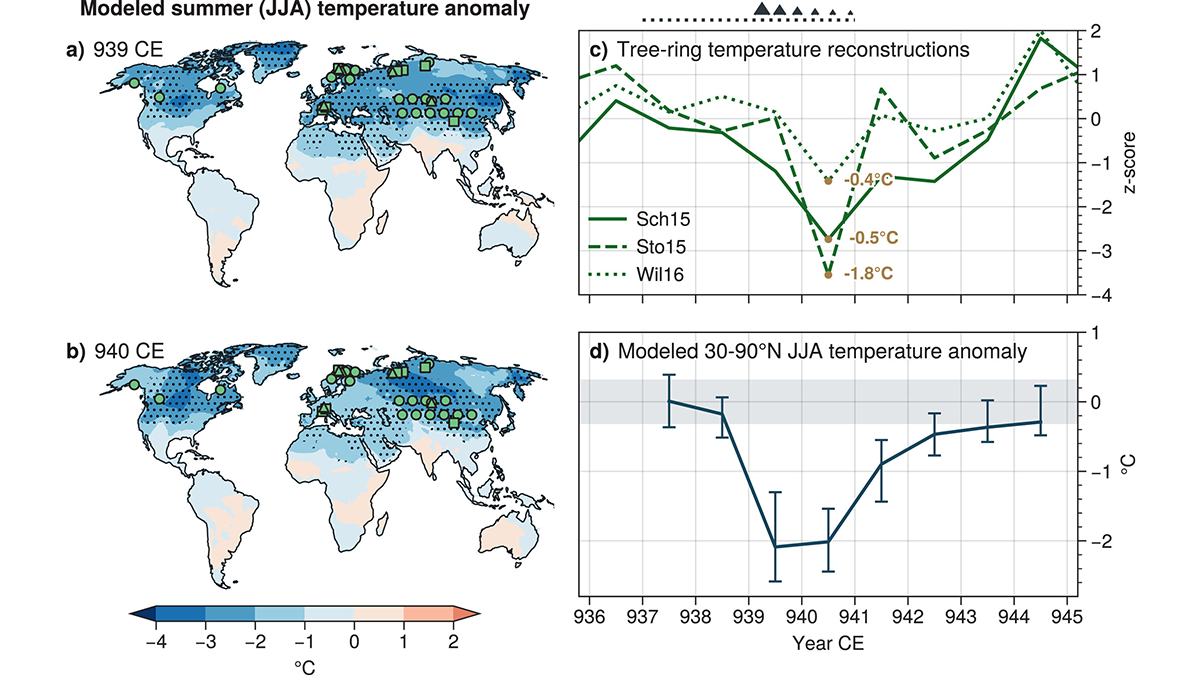
Revised Emissions Show Higher Cooling in 10th Century Eruption
The associated cooling from the Eldgjá eruption is larger than previously predicted and better matches tree-ring temperature reconstructions based on updated estimated emissions.
An Ancient Warming Event May Have Lasted Longer Than We Thought
New research on the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum used probabilistic analysis to learn more about its duration and how long modern warming could affect the carbon cycle.
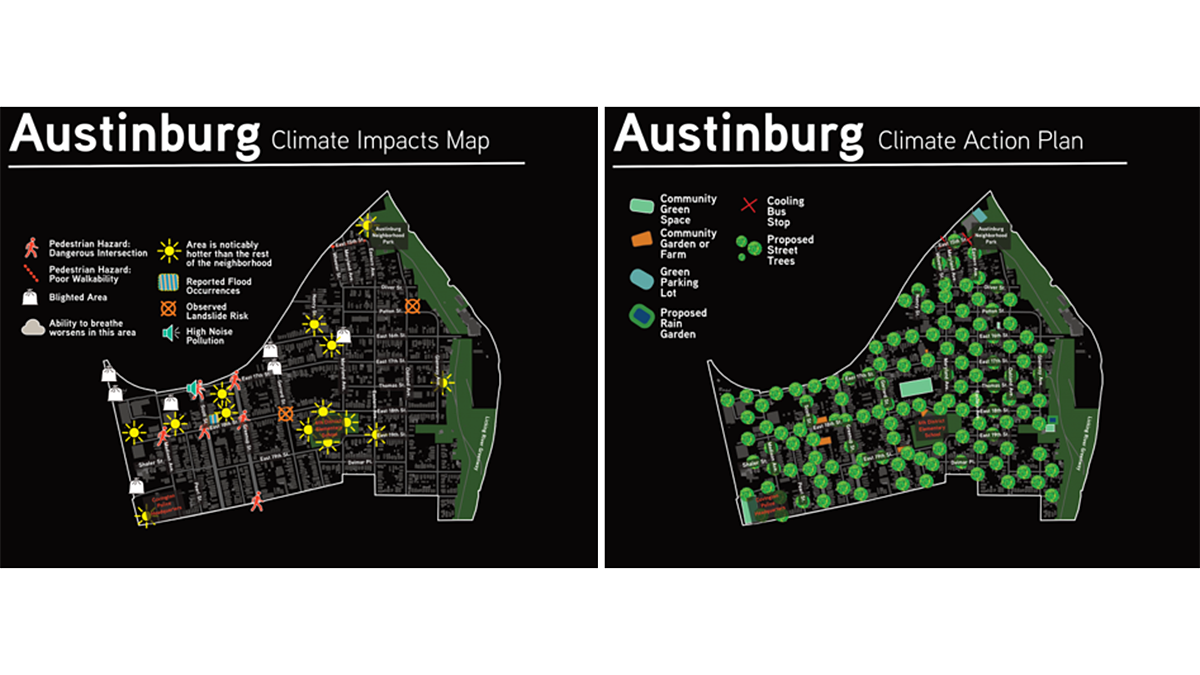
Resilient Solutions Involve Input and Data from the Community
Data dashboards assist in understanding a community’s vulnerability to climate impacts, but input from the communities themselves helps identify and support actionable solutions.
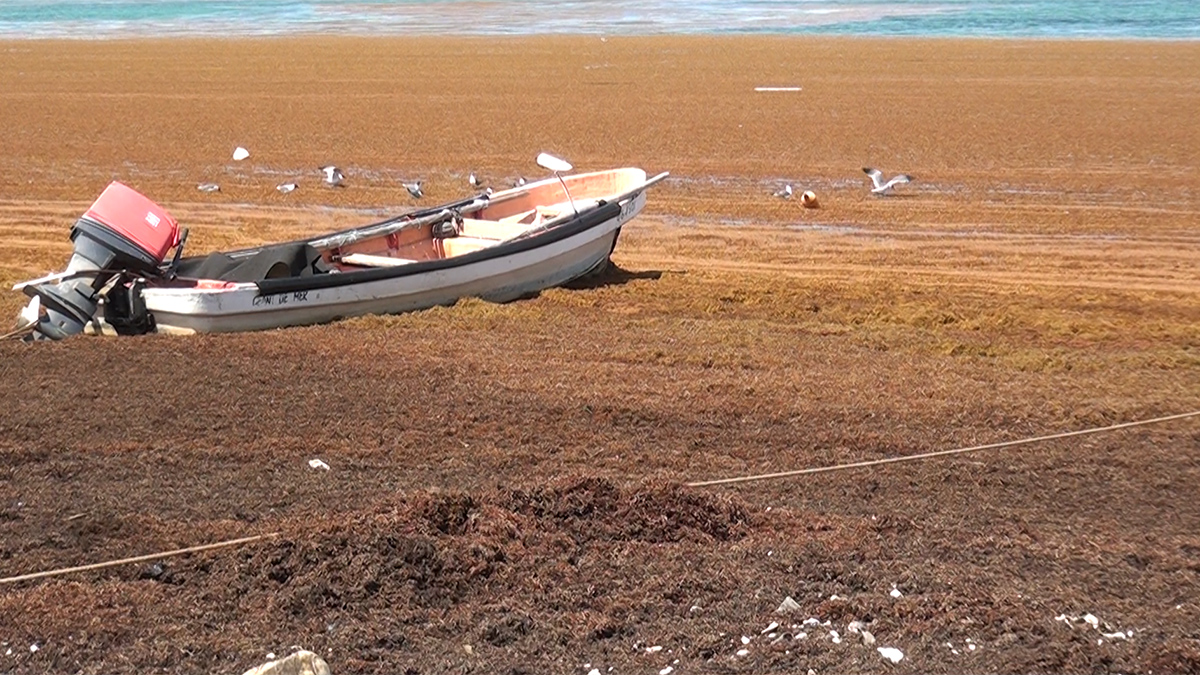
Have We Finally Found the Source of the “Sargassum Surge”?
The complexity of modeling the tropical Atlantic makes identifying the source of the ongoing seaweed blooms difficult.
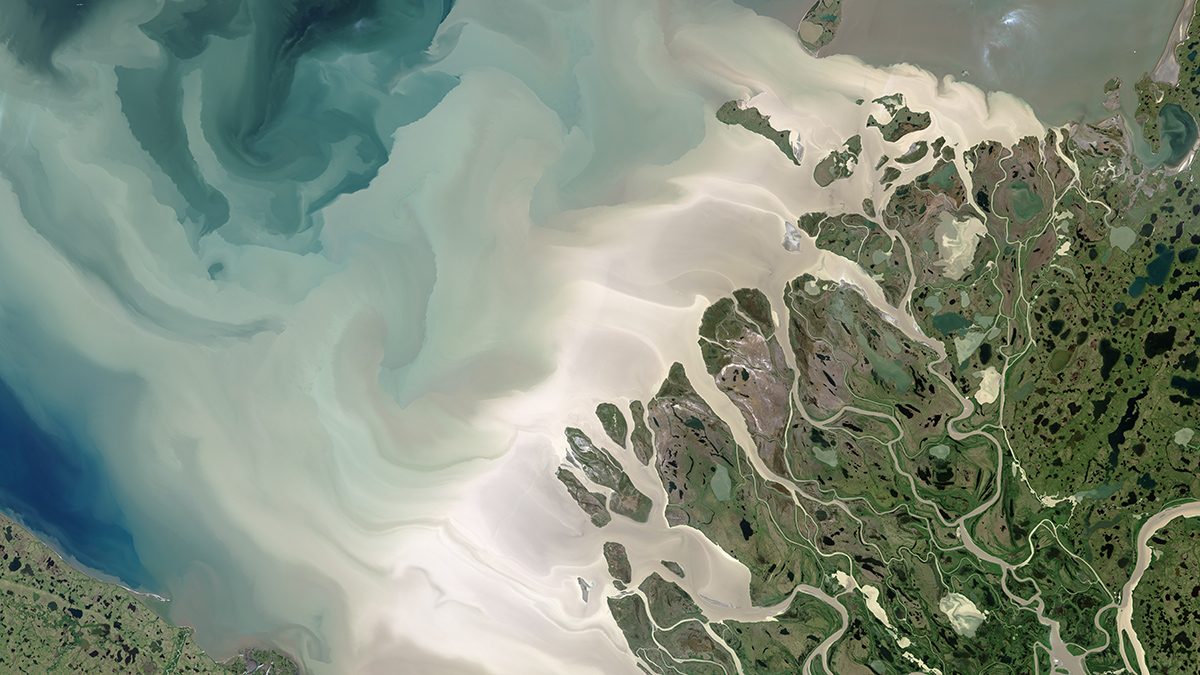
The Uncertain Fate of the Beaufort Gyre
Climate models produce widely varying predictions for what will happen to this influential ocean current, but most models predict it will weaken or stop.
Beyond Up and Down: How Arctic Ponds Stir Sideways
Contrary to common assumptions, Arctic ponds mix in more than one direction. A new study finds that nighttime sideways flows, not vertical mixing, renew bottom waters.
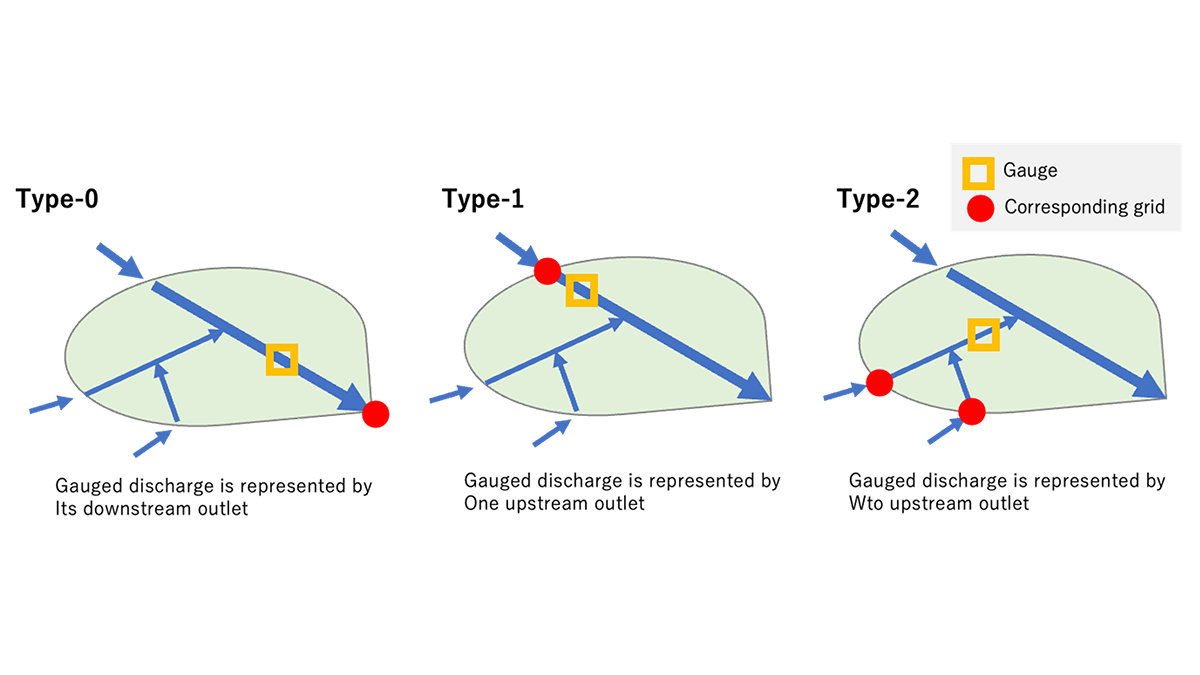
First Benchmarking System of Global Hydrological Models
A benchmarking framework for global hydrological models, essential for Earth System Model evaluations, has finally been proposed.
Decoding Crop Evapotranspiration
The intricate factors influencing cropland evapotranspiration is uncovered in a new article, from stressors to diverse management practices, and reveals critical insights into changing climates.
Mapping the Ocean Floor with Ancient Tides
A new study uses a paleotidal model to trace the formation of carbon-rich mud deposits over thousands of years.