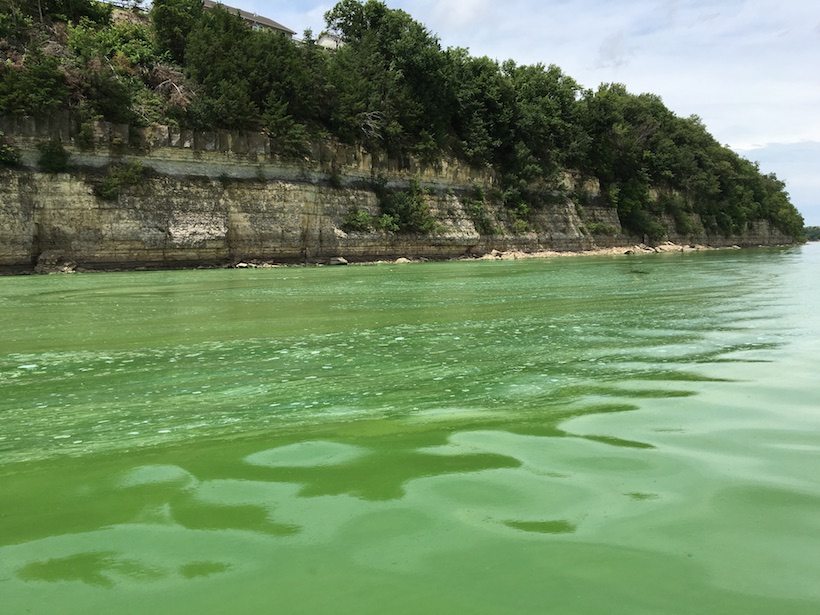
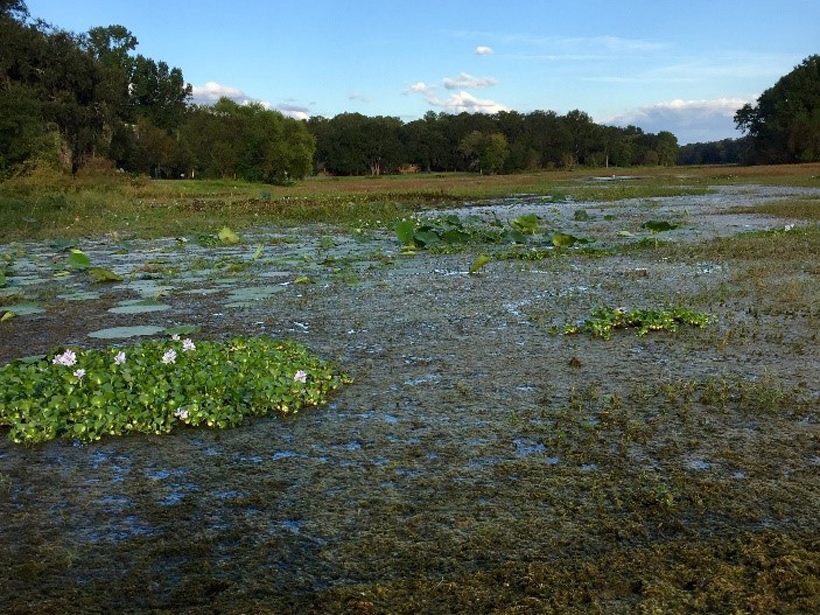
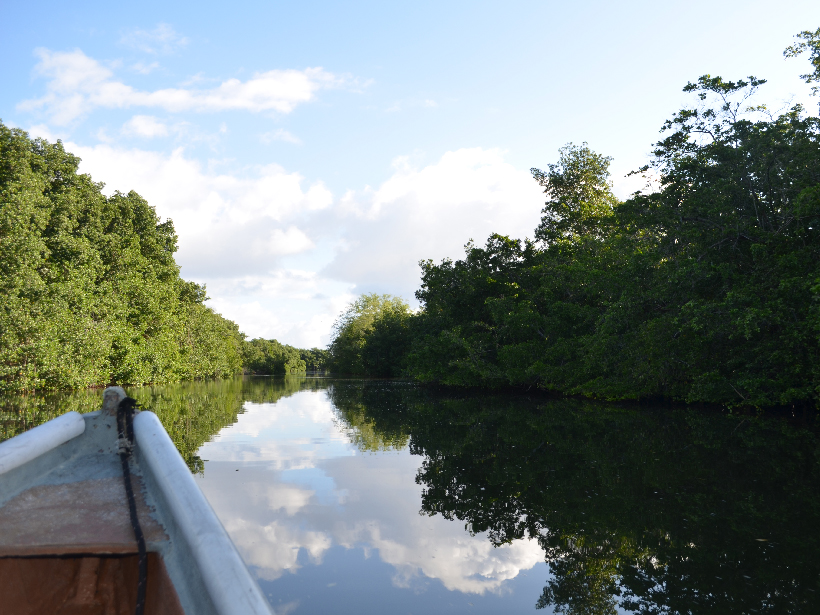
Excess of a single nutrient, such as nitrogen, may boost plant productivity, but the imbalance leads to less efficient water use as plants scramble for the nutrients they lack.
nitrogen
Tracking Excess Nitrogen with Freshwater Mussels
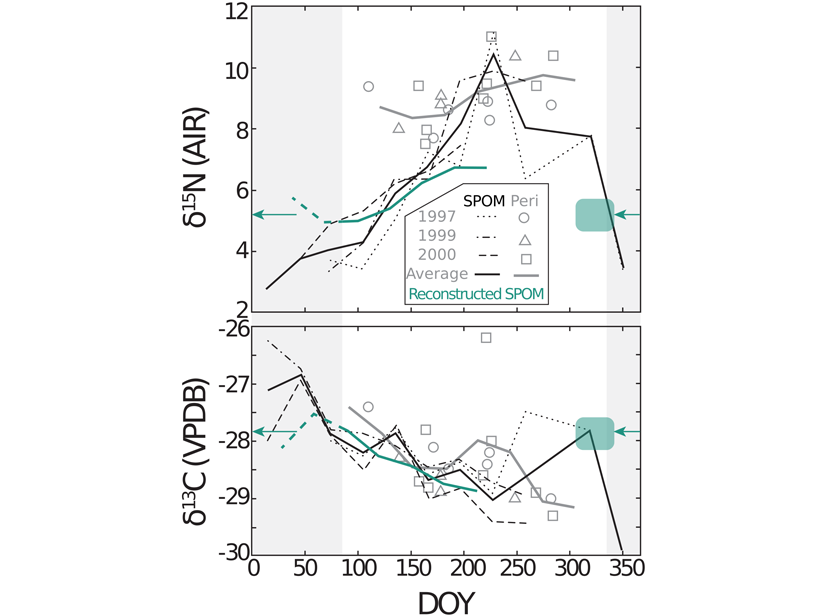
Mussel shell periostracum and carbonate bound organic matter document seasonal variability in the isotopic composition of riverine suspended particulate organic matter.
Turf’s Dirty Little Secret
Greenhouse gas emissions from sports fields may be scoring points for climate change.
Half of Earth’s Nitrogen May Be Homegrown
A new analysis of iron meteorites reveals a distinct isotopic signature that suggests nitrogen was present around early Earth.
Deciphering Reactive Nitrogen Emissions from Wildfire Smoke
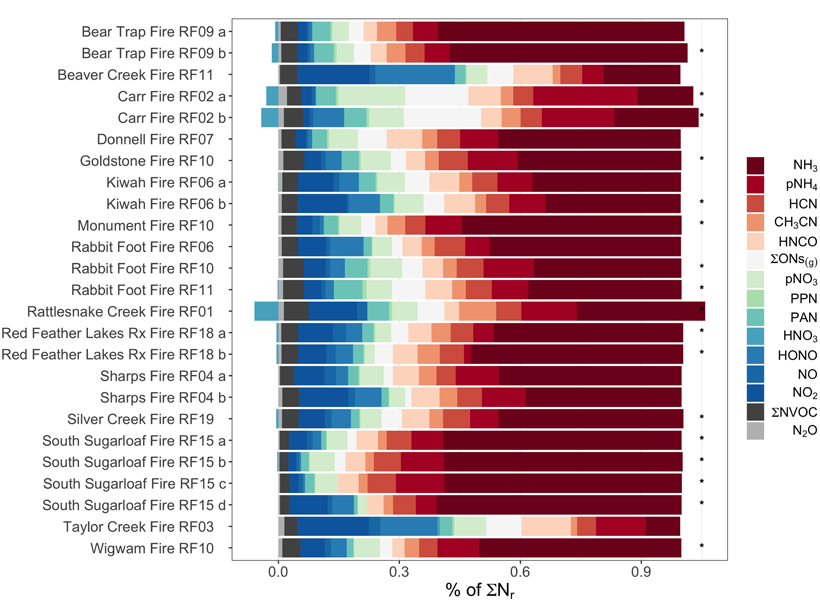
In-situ data gathered from an aircraft flying over 23 western US wildfires in 2018 reveal the importance of reduced nitrogen, shedding insights on ozone and aerosol formation from wildfires.
The Legacy of Nitrogen Pollution
Researchers track decades of nitrogen inputs and uptake across the United States, highlighting the need for policy to address the legacy effects of this essential nutrient and pollutant.
Exploring the Widespread Impacts of Ongoing Nitrogen Pollution
The release of reactive nitrogen into the environment is having severe and ongoing ecosystem, economic, and human health impacts. How can we reduce our nitrogen footprint?
Downhill from Here: Landscape Positions and Greenhouse Emissions
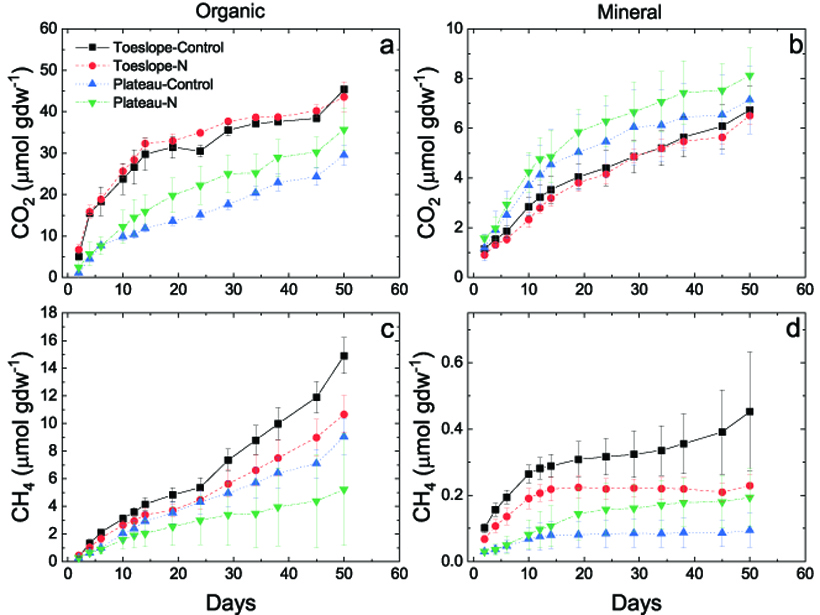
In comparing soils from two tundra wetland landscape positions, landscape position is found to matter, and toeslopes are associated with higher greenhouse gas production.
Shedding New Light on the Nitrogen Cycle in the Dark Ocean
Researchers find that the key players in nitrification may already be known.
Linking Hydrology and Biogeochemistry in a Tropical Urban Estuary
Low-lying coastal estuaries are intertwined with tropical cities around the world. Yet little is known about these water bodies, which affect millions of people globally.