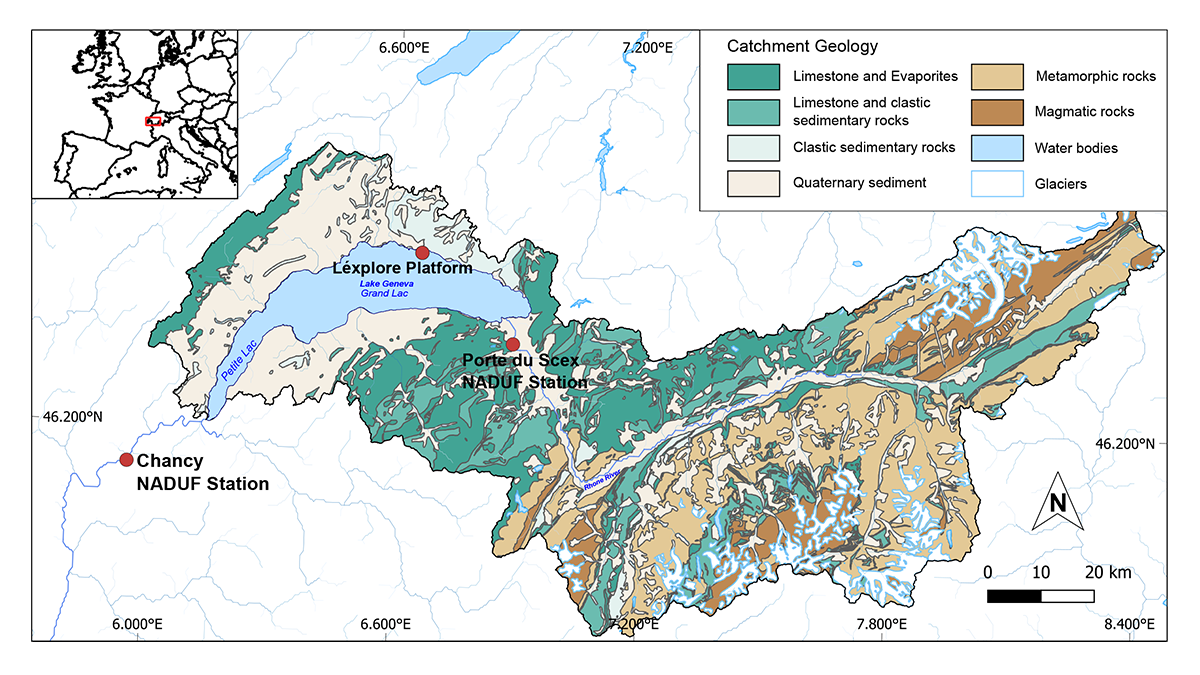
Organic and inorganic radiocarbon ages resolve the origin and dynamics of carbon in the largest natural lake of Western Europe.
nutrients
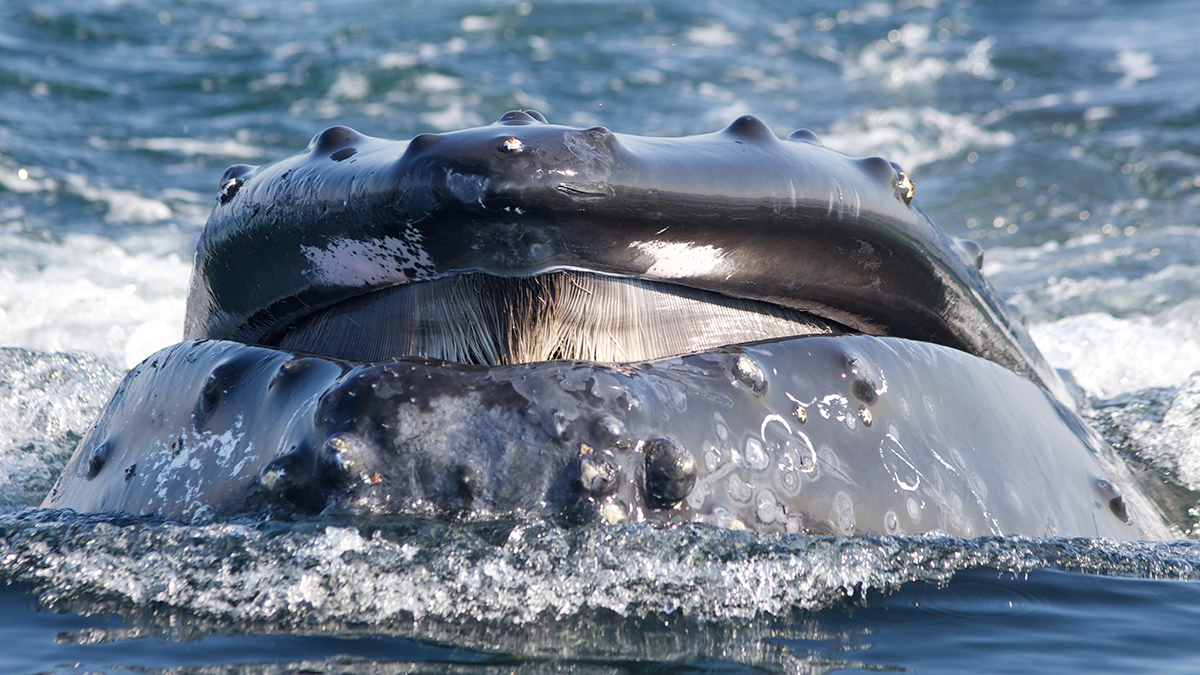
A Great Whale Conveyor Belt Transports Nutrients Across Oceans
Baleen whales shift huge amounts of nutrients, including nitrogen, from high-latitude feeding waters to tropical breeding areas.
Could Bubbling Oxygen Revitalize Dying Coastal Seas?
Reoxygenation approaches have shown some success in lakes, but their potential risks must be examined carefully before they’re implemented as solutions to improve the health of coastal waters.
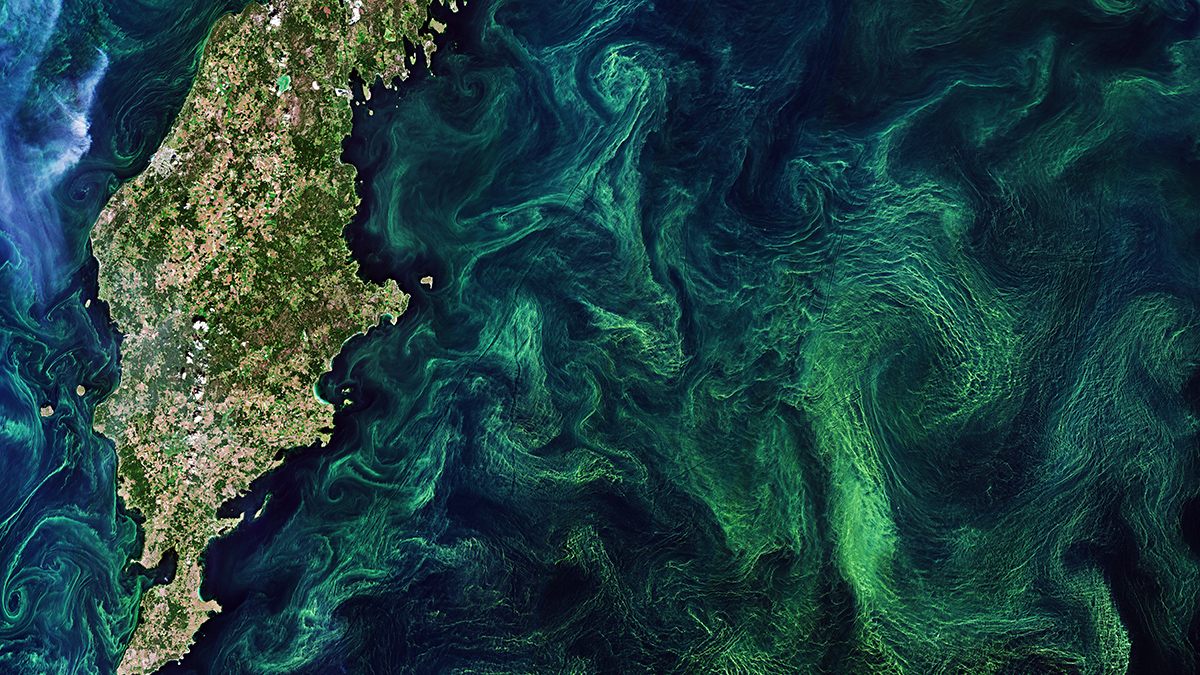
Upwelling Near Fronts Initiate Offshore Phytoplankton Blooms
A new study finds that phytoplankton blooms, often seen near the separation point of western boundary currents, are supported by nutrient supply upwelling and cross-shelf transport.
Carbon-Nutrient Ratios Drive Nitrate Removal in Mediterranean Streams
The type of organic matter, and ratio of nutrients to carbon, impact the ability of heterotrophic bacteria to effectively remove certain forms of nitrogen pollution (nitrate) from streams.
Physics and Biology as Likely Stream Bedfellows
Streambeds are key sites for removal of nutrients and other contaminants through microbial processes, but are limited by diffusion, which can now be modeled from streambed physical properties.
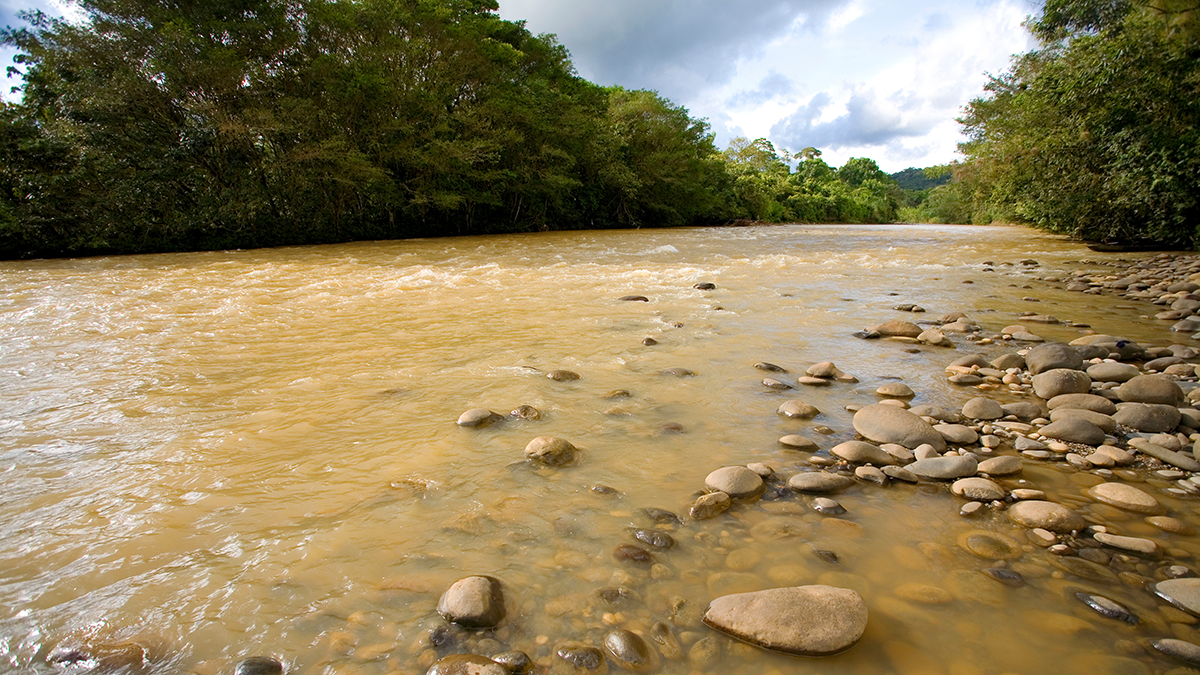
Insights Biogeoquímicos de um Importante Rio Amazônico
Sub-representados nos orçamentos globais de carbono, rios tropicais como o Tocantins, no Brasil, necessitam de estudos para estabelecer suas características de base face às crescentes mudanças globais.
An All-Community Push to “Close the Loops” on Southern Ocean Dynamics
A new study highlights the connected nature of the Southern Ocean dynamic system, the research priorities needed to understand its influence on climate change, the importance of cross-disciplinary collaborations.
Reactive Barriers Could Keep Nitrate out of the Atlantic
Microbes in mulch scrub nitrate from groundwater before it flows to the sea.
The Open Ocean, Aerosols, and Every Other Breath You Take
Phytoplankton and other marine plants produce half of Earth’s atmospheric oxygen and have big effects on food webs and climate. To do so, they rely on nutrients from the sky that are hard to quantify.