Stars in the solar neighborhood could jostle planetary orbits, making it harder to turn back the clock and examine Earth’s orbital or climate history.
orbits & rotations
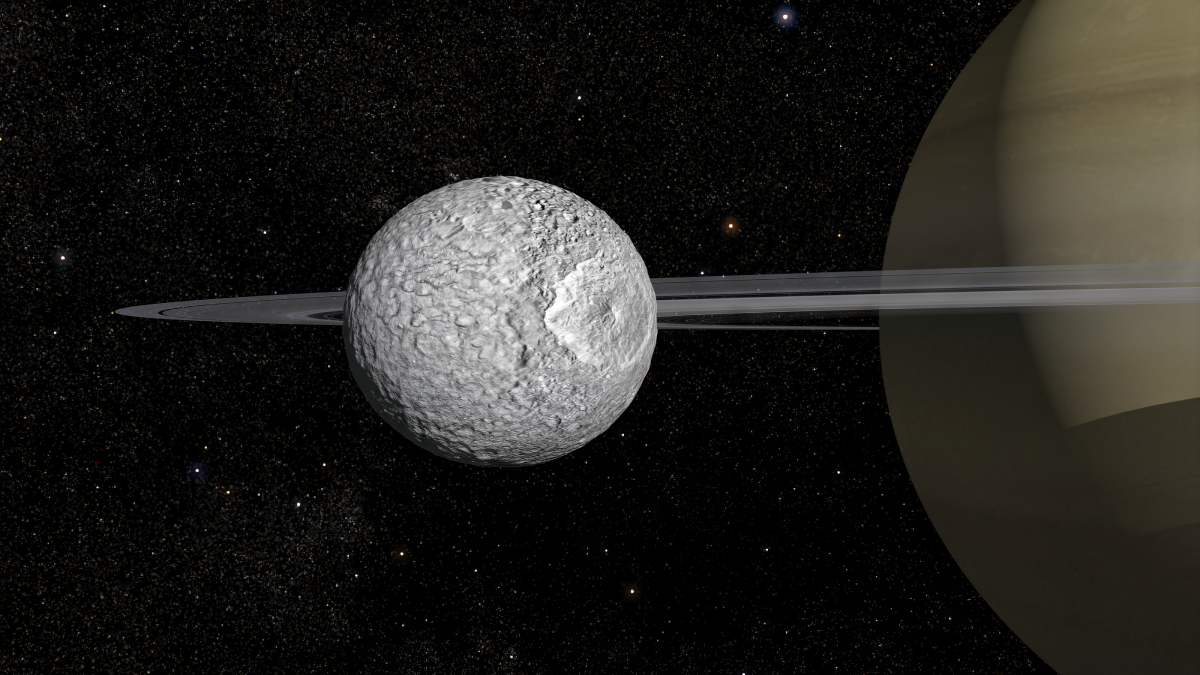
That’s No Moon; It’s an Ocean World
If Saturn’s cratered moon Mimas has liquid water beneath its surface, ocean worlds might be far more common in the solar system than we thought.
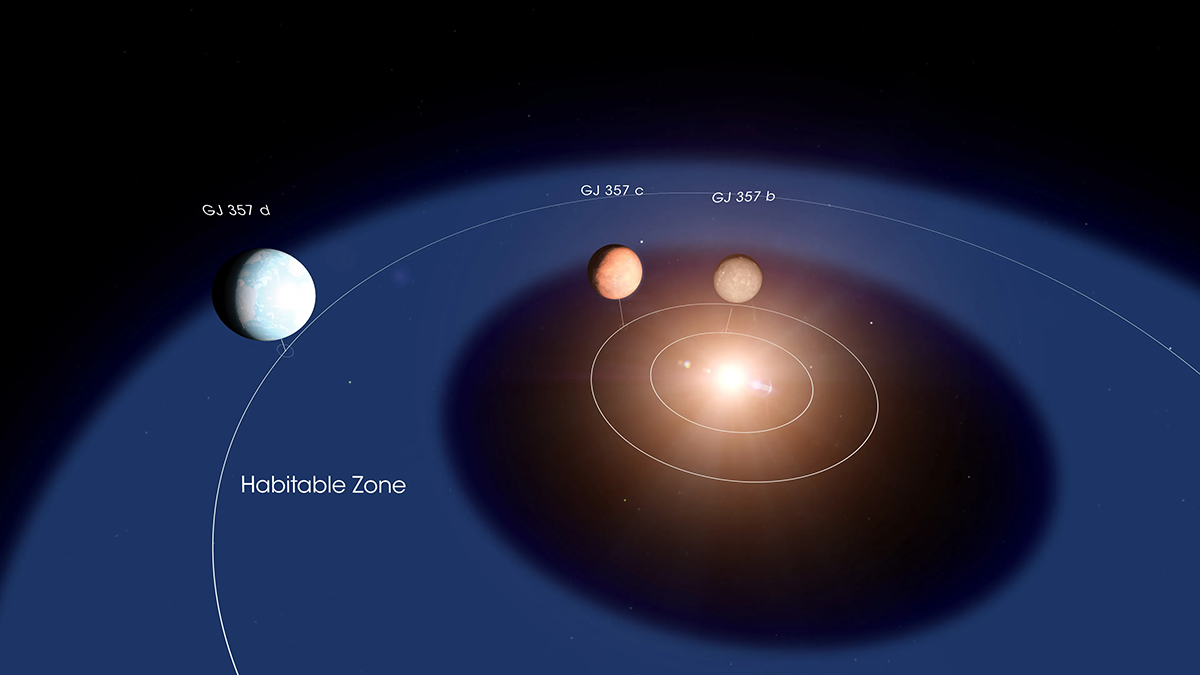
Giant Planets May Be “Agents of Chaos”
Two studies suggest that some giants could make it difficult or even impossible for terrestrial planets to remain in a star’s habitable zone.
Five Martian Mysteries That Have Scientists Scratching Their Heads
Despite centuries of study and many spacecraft visits, the Red Planet still holds secrets. Here are just a few.
A Planet Is Dramatically Losing Its Atmosphere
Helium that was once part of the atmosphere of the extrasolar planet HAT-P-32b is being ripped away and forming two giant streamers of gas several million kilometers long.
Exoplanets May Support Life in the Terminator Zone
A new study finds that the intersection between a searing dayside and a freezing nightside could be habitable.
Tides Ripple Across Earth’s Plasma “Donut”
Interactions between lunar gravity and the terrestrial magnetic field may cause a 90° offset from the Moon’s position in its orbit.
Ice Cores Record Long-Ago Seasons in Antarctica
Researchers used ice core data to reconstruct seasonal temperatures throughout the Holocene. The results link especially hot summers with patterns in Earth’s orbit.
Marauding Moons Spell Disaster for Some Planets
In solar systems beyond our own, some moons might eventually collide with their host planets, new simulations suggest.
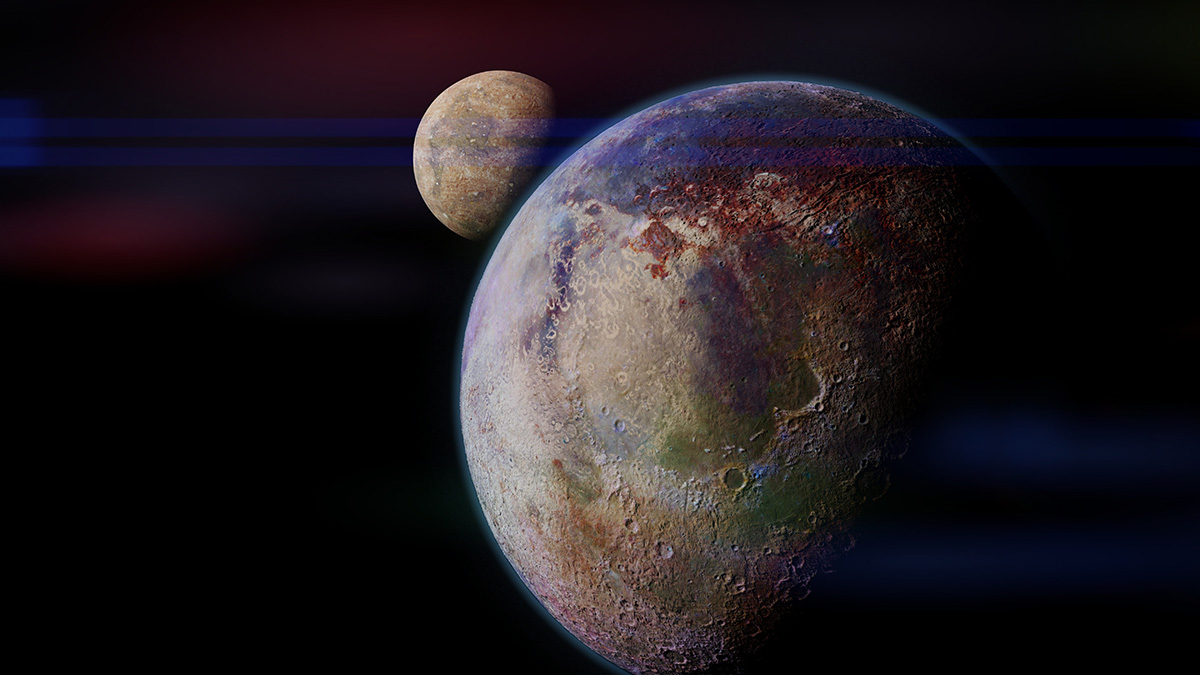
Quaoar’s Ring Defies Gravity
The dwarf planet’s ring makes astronomers question whether a long-held theory about ring and moon formation needs tweaking.