New simulations suggest that subsurface oceans on icy moons with small natural Rossby numbers may be dominated by rotational effects.
orbits & rotations
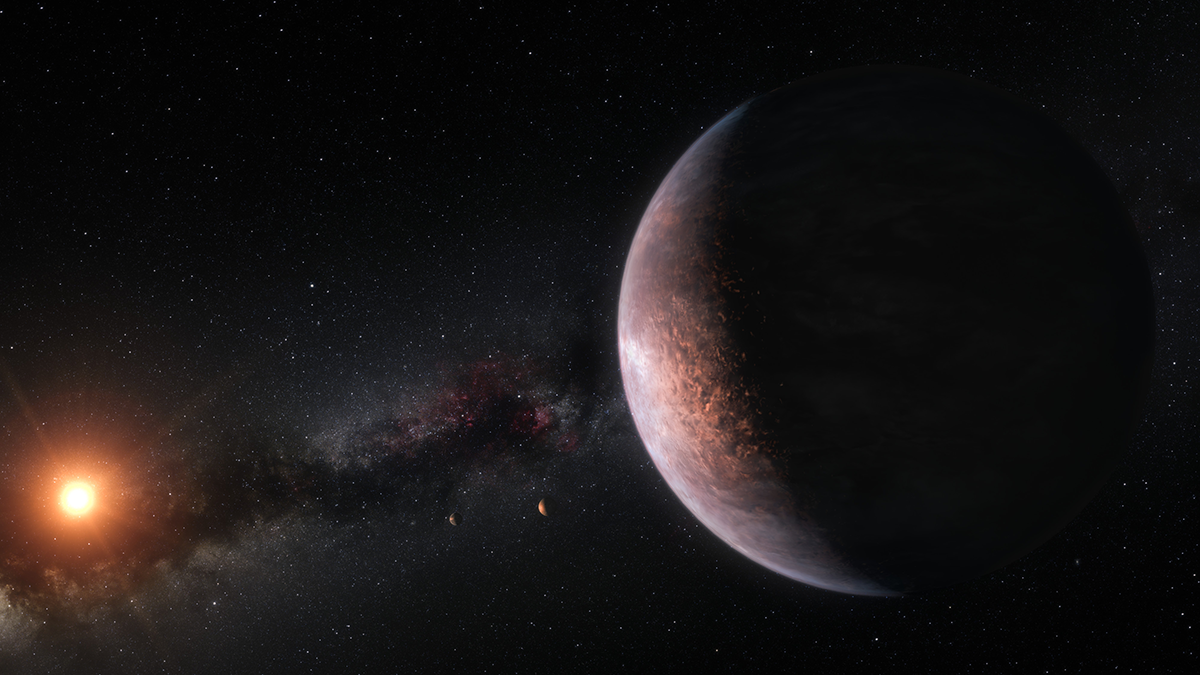
Tidally Locked and Loaded with Questions
Tidally locked planets always present the same face to their host stars. What does this mean for their potential to support life?
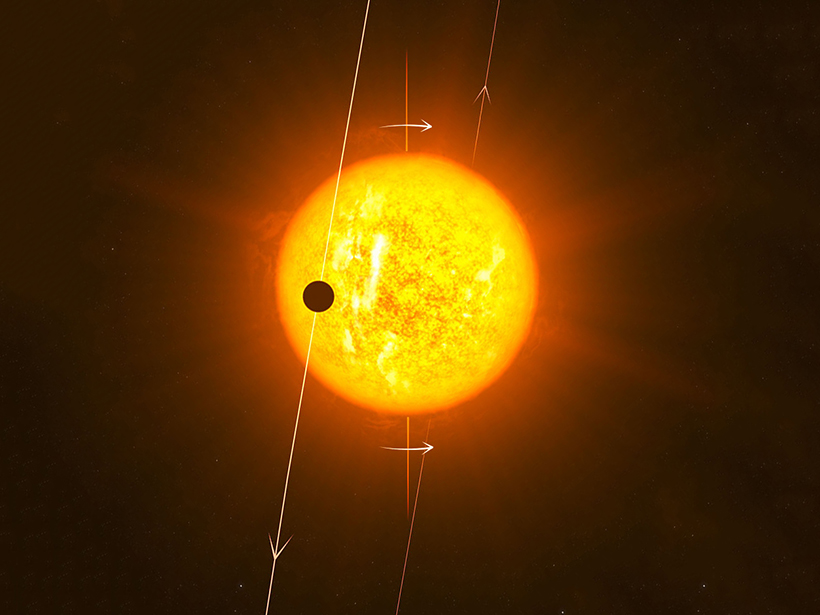
Peculiar Planets Prefer Perpendicular Paths
Some exoplanets orbit their stars from pole to pole instead of across the equator. Why do they do that?
Fifteen Years of Radar Reveal Venus’s Most Basic Facts
Venus’s heavy atmosphere tugs the planet’s surface enough to change the length of its day by up to 21 minutes.
Martian Meteorites Shed Light on Solar System’s Early Dynamics
Chemical compositions of rocks from Mars indicate that the earliest orbits of Jupiter and Saturn were more circular than they are today.
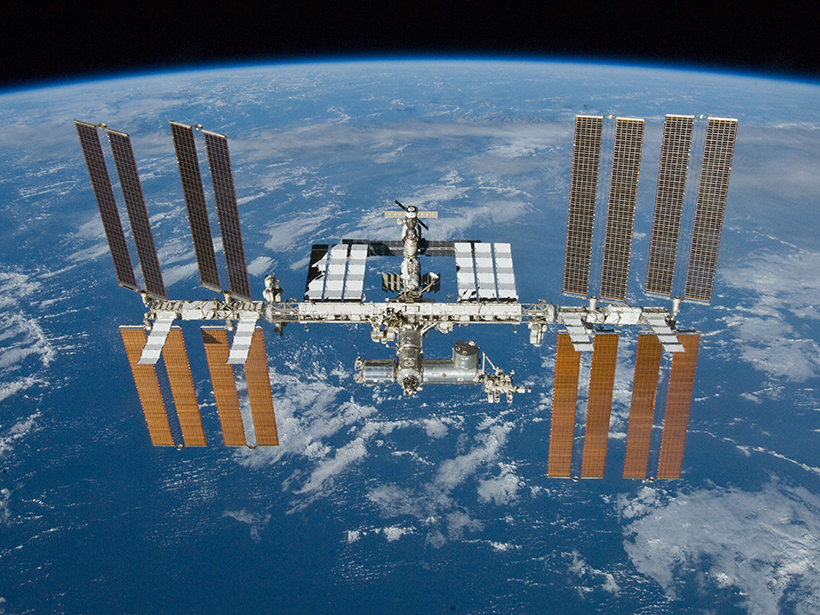
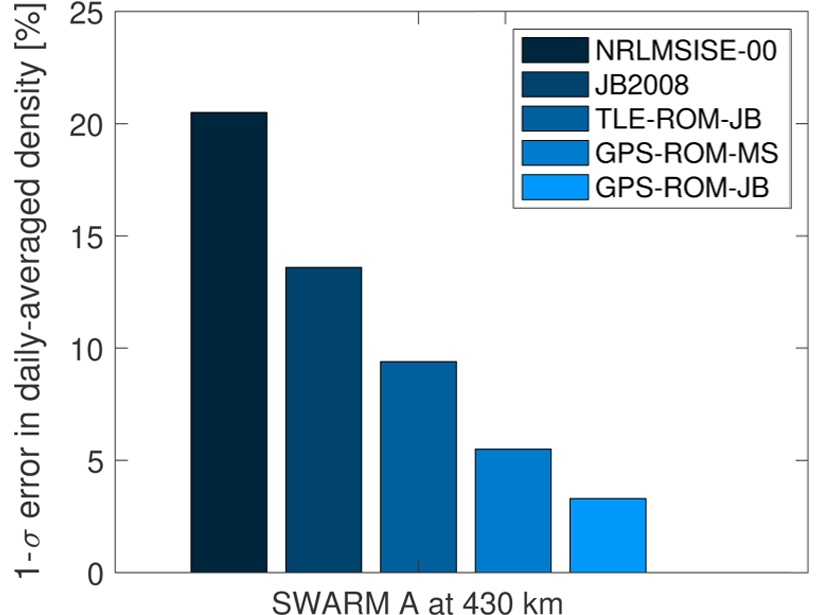
Better Thermospheric Monitoring is Vital to Space Safety
Better real-time estimates of thermospheric density are vital to the safe management of satellite traffic in Low Earth orbit, ensuring those satellites continue to deliver critical services.
Electron Density near Enceladus Shows Orbital Variation
The electron density peaks well after the activity of the moon’s distinctive south polar ice plume reaches its maximum, but the cause of the lag remains puzzling.
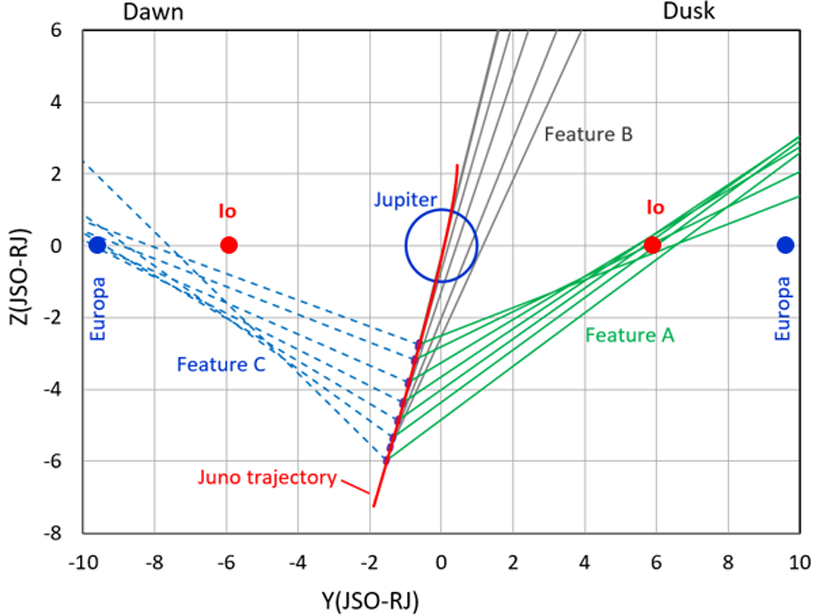
New Energetic Neutral Atom Emissions from Jupiter, Io, and Europa
The first Jovian off-equator Energetic Neutral Atom viewings reveal distinct emissions from Jupiter and the orbits of Io and Europa: Energetic particle injections surprisingly occur inside Io’s orbit.
Sunburned Surface Reveals Asteroid Formation and Orbital Secrets
Thanks to spectacular high-resolution images from Hayabusa2, scientists can now better estimate how and when the asteroid Ryugu formed, how its orbit has changed over time, and what its surface looks like.
Atmospheric Drag Alters Satellite Orbits
A new modeling study shows how the density of the thermosphere influences the paths of satellites in low Earth orbit.