Solar winds are not the main culprit in stripping the planet’s atmosphere, a new study suggests.
planetary evolution
Rover and Lasers Unlock Clues to Early Martian Atmosphere
Sediments from the Curiosity rover and experiments using tanks of gas and laser beams helped reveal how water continued to flow on Mars after the planet lost its atmospheric carbon dioxide.
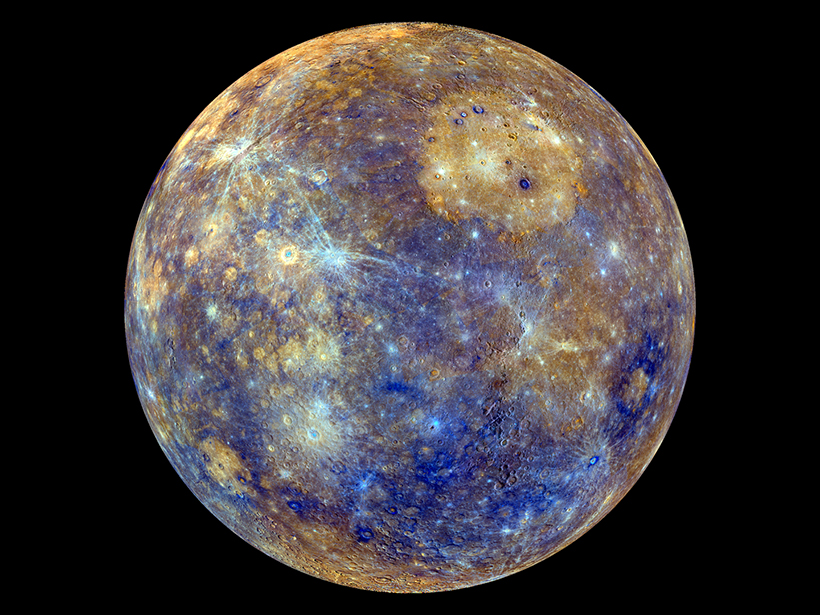
Mercury Mission Will Map Morphology and Measure Magnetics
BepiColombo may launch as early as this weekend. It seeks to unravel the mysteries of Mercury’s geologic and magnetic past and map the small planet’s cratered surface.
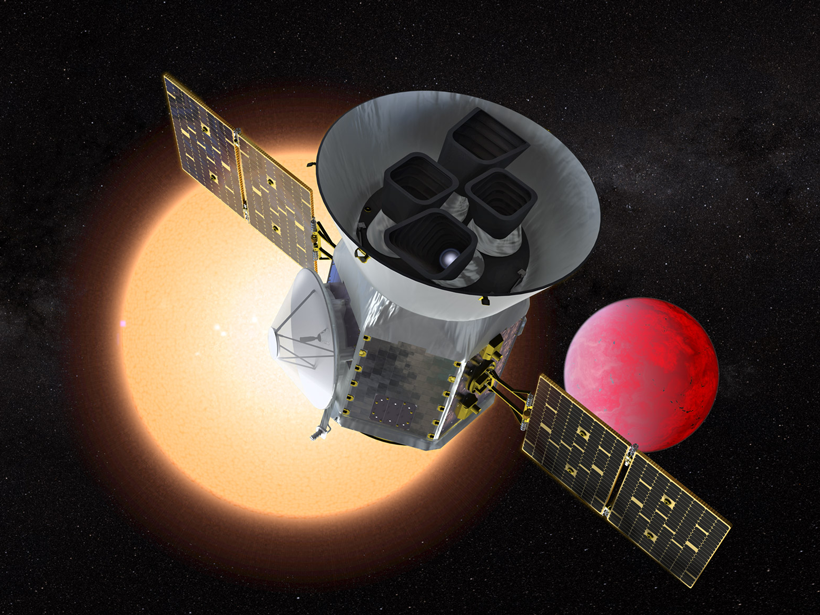
New Exoplanet Telescope Detects Its First Two Planets
The two possible planets, each larger than Earth and too hot to be habitable, are the first of hundreds of Earth-sized exoplanets expected to be discovered by a recently launched telescope.
The Kepler Revolution
The Kepler Space Telescope will soon run out of fuel and end its mission. Here are nine fundamental discoveries about planets aided by Kepler in the 9 years since its launch.
New Lander en Route to Probe the Red Planet’s Interior
The Mars InSight mission aims to answer key planetary science questions about seismicity, meteorite impacts, and the formation of rocky planets.
Exoplanet-Hunting Telescope Launches
Scanning for traces of faraway worlds, TESS will make observations over an area hundreds of times larger than that observed by its predecessor, the Kepler Space Telescope.
Signs of Water in a Moon Rock
NASA Solar System Exploration Research Virtual Institute (SSERVI) Lunar Volatiles Workshop; Laurel, Maryland, 15–17 November 2016
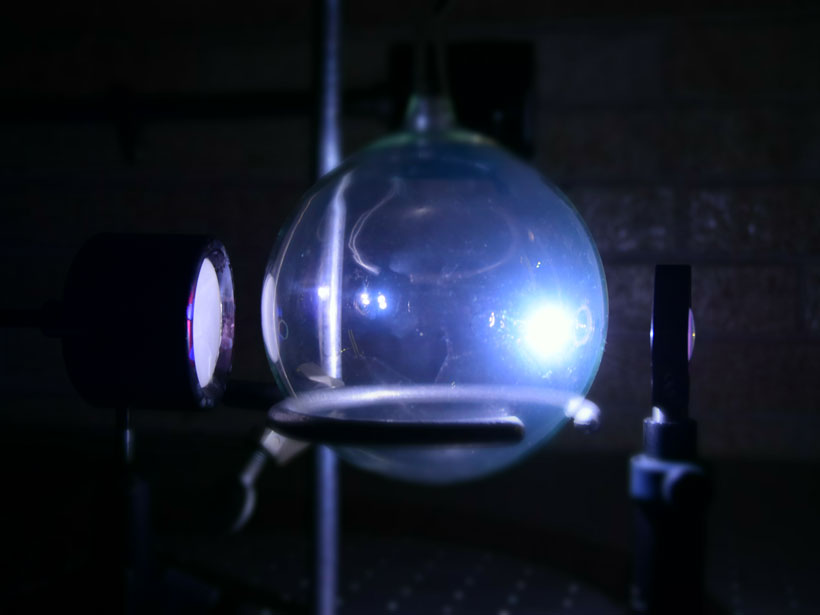
Meet KELT-9b, the Hottest Exoplanet Ever Discovered
The exoplanet’s host star blasts it with so much radiation that it will someday evaporate.
A Volcanic Trigger for Earth’s First Mass Extinction?
Abnormally high levels of mercury in Ordovician rocks may imply that a huge surge of volcanism took place at a time when much of the planet’s ocean life vanished.