A novel antenna design promises to improve bandwidth and allow for better communication between Earth stations and satellites.
Radio Science
New Analysis Provides a Fresh View of the Atmosphere on Venus
Researchers apply a radio holographic method to standard Venusian atmospheric data, resulting in outputs with finer vertical resolution and revealing small-scale atmospheric structures.
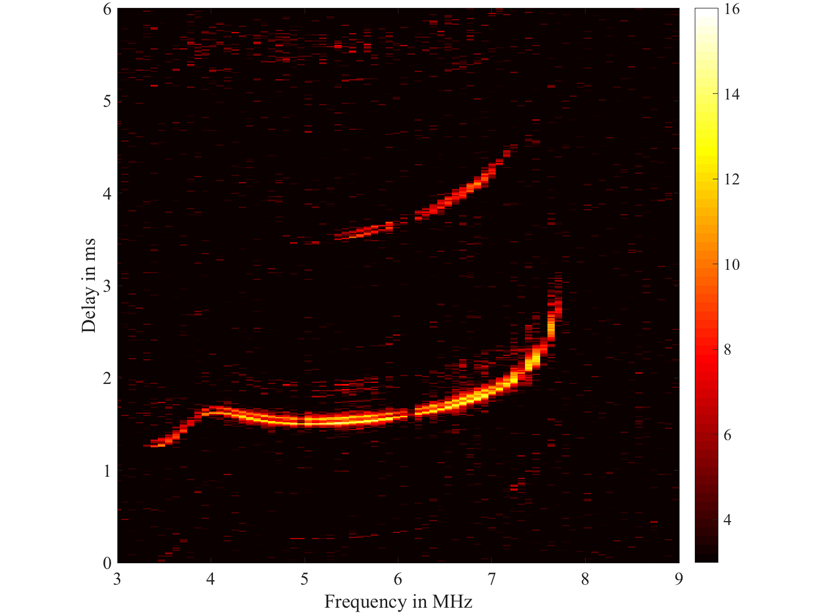
High Resolution Imaging of Ionosphere by Lightning
The three-dimensional distribution of electron density in the Earth’s ionosphere could be obtained using the broadband radiation of naturally occurring lightning discharges.
Polarization Measurements Probe the Physics of Lightning
A new measurement capability can detect the polarization of the radio frequency wave of lightning sources, which reveals different forms of lightning breakdown processes.
Equatorial Ionospheric Scintillation During Daytime
Scintillation—flickers and distortions in radio waves passing through the ionosphere—can happen during daytime and at much lower dip latitudes than previously thought.
Meteors Can be Used to Calibrate a Radar System
Every day meteors burn up in the atmosphere with highly predictable results, reflecting radio waves that could be used to calibrate antennas.
How to Build a Better Light Trap
Nanosized chambers capture bits of light for infinite amounts of time.
Managing Radio Traffic Jams with the Cloud
Sensor networks and data mining allow for fully automated, real-time monitoring of radio waves.
Mystery of the Ionosphere’s “Gyro Line” Solved
A new study provides an updated hypothesis to describe a unique radar signature from plasma waves high above Earth, correcting errors that had stood for decades.
Tracking Meteor Trails to Study the Mesosphere
Twelve years of radar data reveal new phenomena in Earth’s upper atmosphere.