Satellite observations show how tropical forest carbon fluxes respond to changes in water from climate variability.
Reviews of Geophysics
Summer Monsoons: Regional Manifestations of a Global System
New insights from observations and theory suggest that the essential drivers of Earth’s summer monsoons are not as obvious as was previously thought.
Freshened Groundwater in the Sub-seafloor
Scientists are using a variety of geochemical, geophysical, and numerical methods to study offshore freshened groundwater and better understand its role in the global water cycle.
How is Modern Climate Change Affecting Landscape Processes?
Landscapes will respond to hydroclimatic changes associated with modern global warming, such as increasing extreme storms and wildfire, but to what extent is physical landscape change already evident?
Antarctica in a Changing Climate
The impacts of the Antarctic Ice Sheet response to climate change will have global consequences for millions living near the coast. It’s just a matter of when.
Halocarbons: What Are They and Why Are They Important?
CFCs and other halocarbons have long been known for causing an ozone hole over the Antarctic, but many of them are also powerful greenhouse gases.
Ice from Above: Toward a Better Understanding of Hailstorms
Globally relevant and locally devastating, hailstorms produce significant societal impacts; despite this, our understanding of hailstorms and our ability to predict them is still limited.
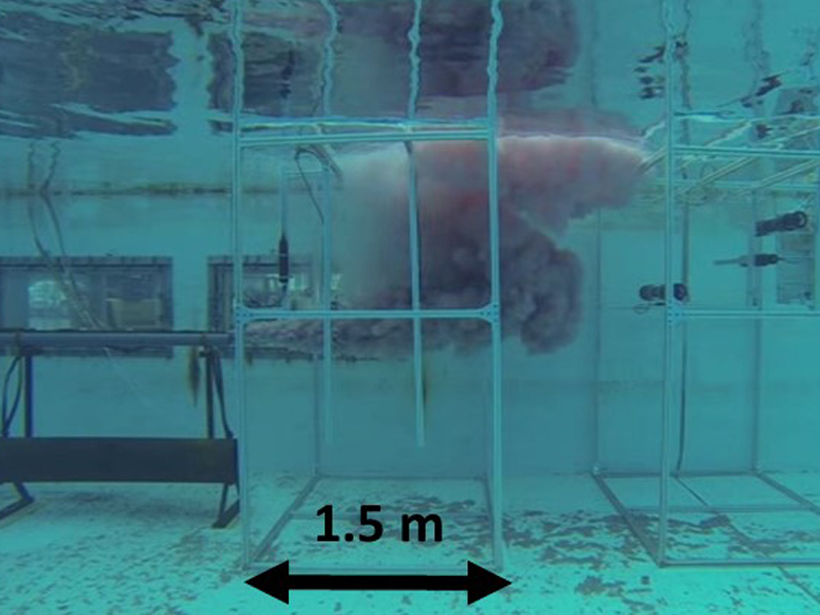
The Underwater Behavior of Oil and Gas Jets and Plumes
Exploring how the multiscale interaction between underwater oil and gas plumes and the environment impacts plume composition and trajectory.
The Ups and Downs of Tides
The size of tides has changed in the past and will continue to change in the future due to natural and anthropogenic influences on estuaries, coastlines, and near shore regions.
Understanding Earthquakes Caused by Hydraulic Fracturing
A better understanding of how earthquakes are caused by hydraulic fracturing is an important part of building better practices to manage and mitigate their risks.