Odorant-binding proteins derived from pigs, bovines, and other animals are the next frontier in localized, climate-smart sensing of pesticide spills, greenhouse gas precursors, and more.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
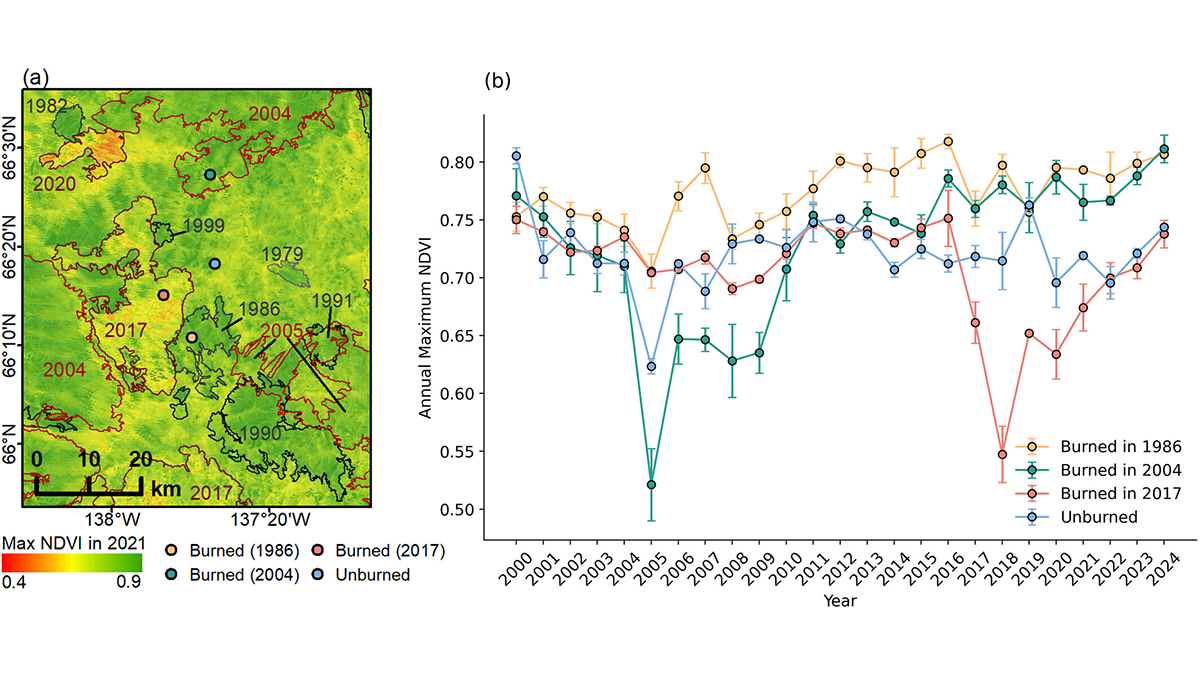
Radar Surveys Reveal Permafrost Recovery After Wildfires
Boreal-permafrost systems are still resilient against wildfires, but continuous and long-term monitoring is needed to control the impact of climate change.
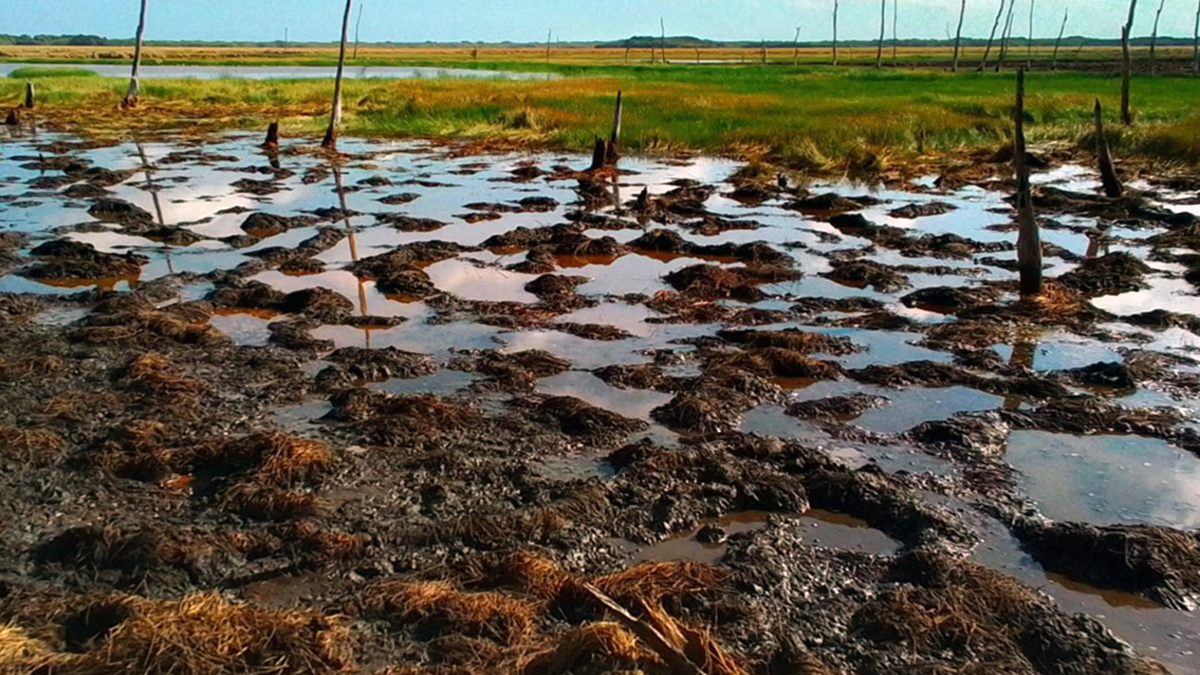
Where the Pigs and Buffalo Roam, the Wetlands They do Bemoan
A novel fenced enclosure study demonstrates the heavy toll that invasive ungulates have on greenhouse gas emissions from coastal wetlands on Indigenous lands in Australia.
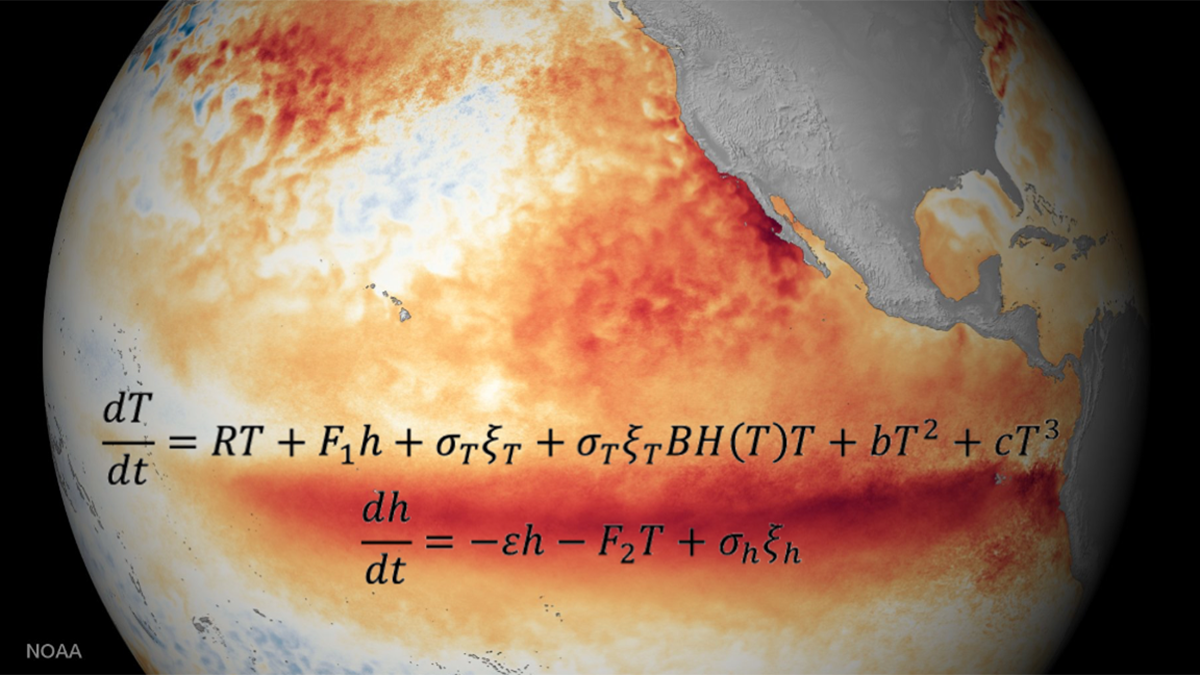
Two Equations that Unlock El Niño
Despite the El Niño–Southern Oscillation’s global reach and complex ocean–atmosphere interactions across timescales, two simple, elegant equations capture its key dynamics and defining properties.
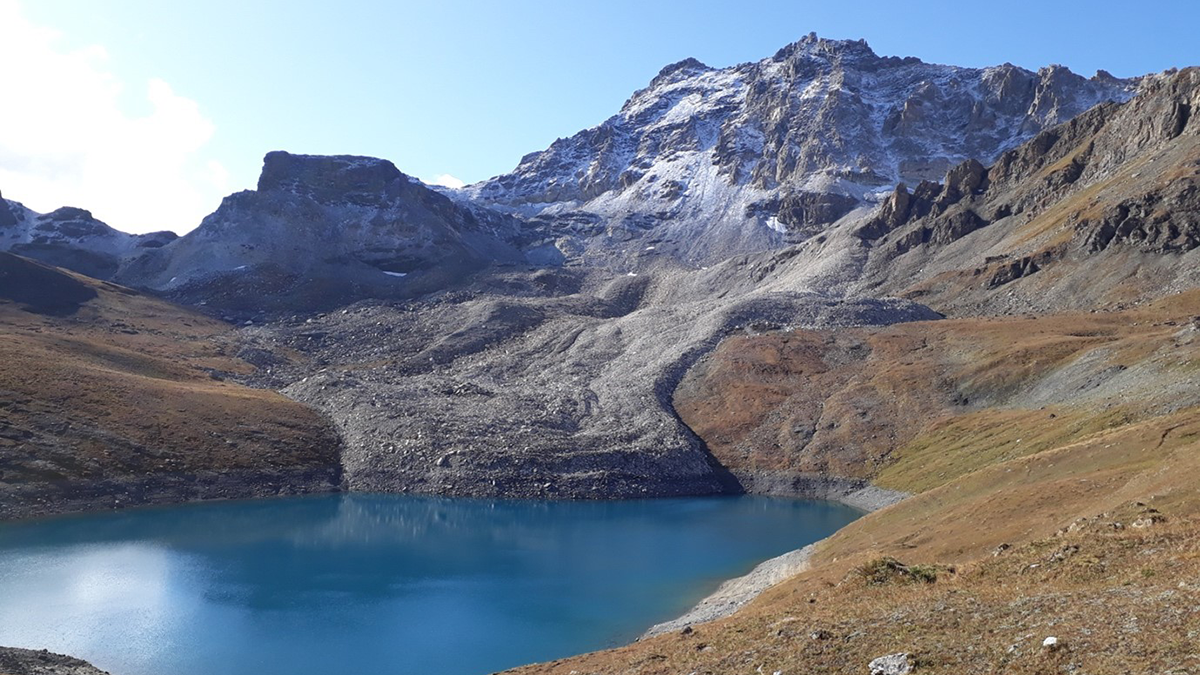
Rock Glacier Velocity: Monitoring Permafrost Amid Climate Change
The movement of unique landforms called “rock glaciers” give insight into how climate change is impacting permafrost in mountainous regions.
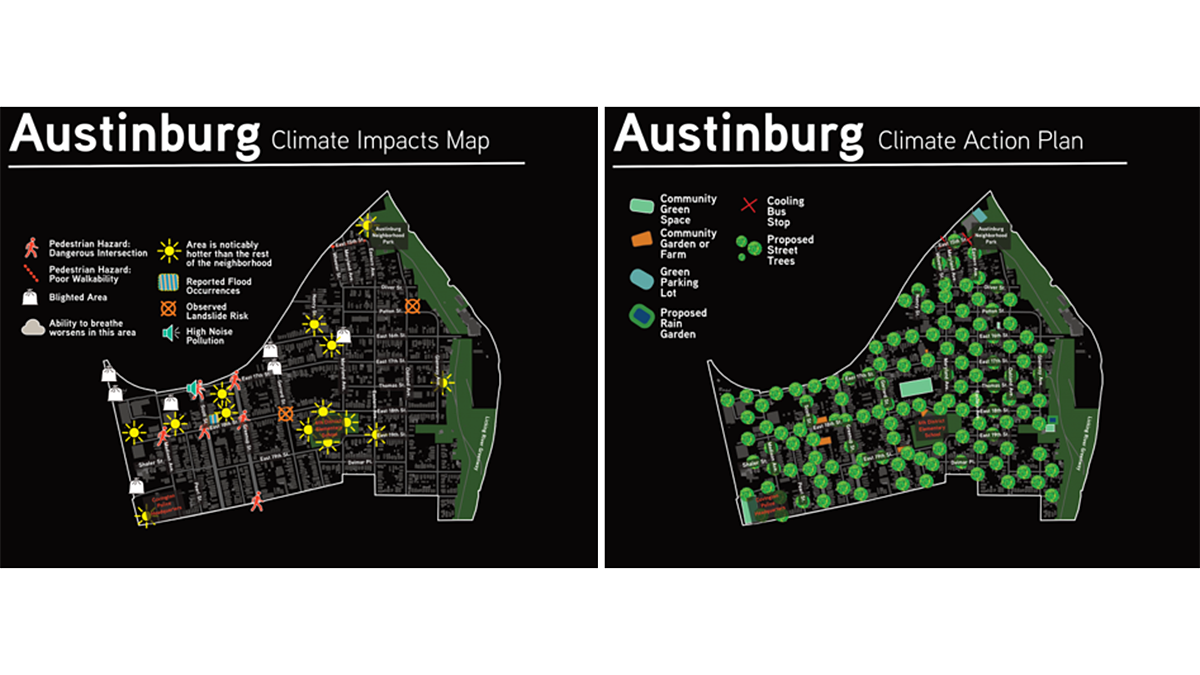
Resilient Solutions Involve Input and Data from the Community
Data dashboards assist in understanding a community’s vulnerability to climate impacts, but input from the communities themselves helps identify and support actionable solutions.
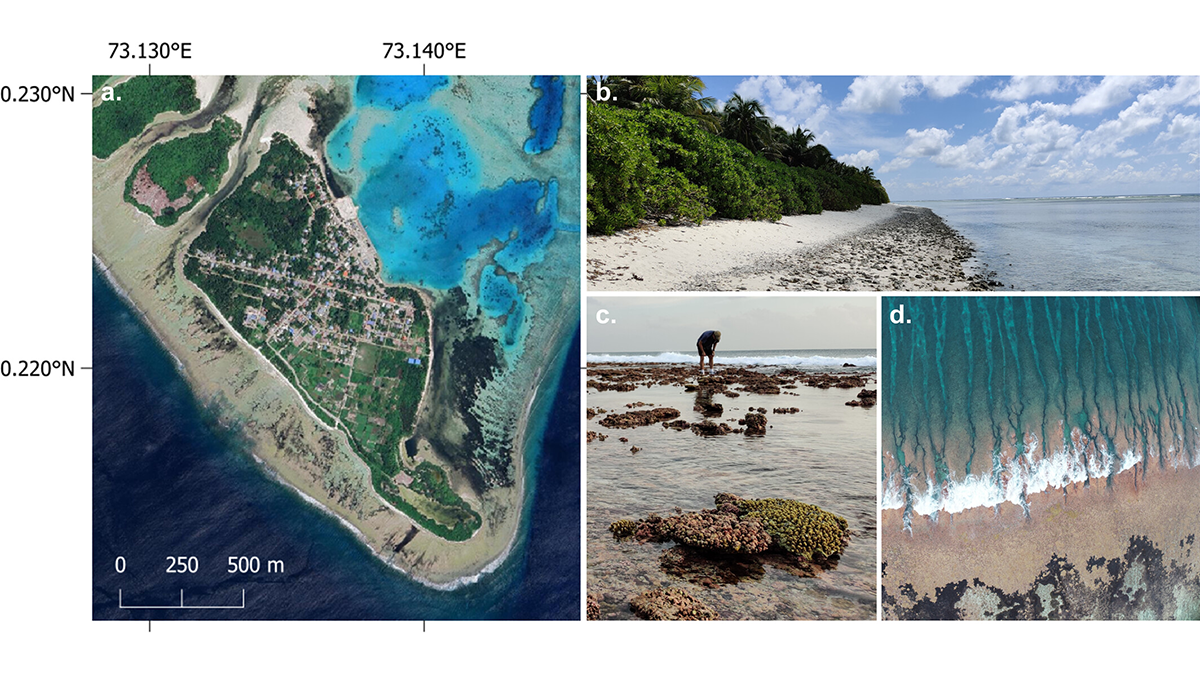
Coastal Models Quantify How Natural Islands Respond to Sea Level Rise
Coastal models enhance understanding of future flooding frequency on atoll islands, paving the way to explore the limits of adaptation in the face of rising sea levels and climate change.
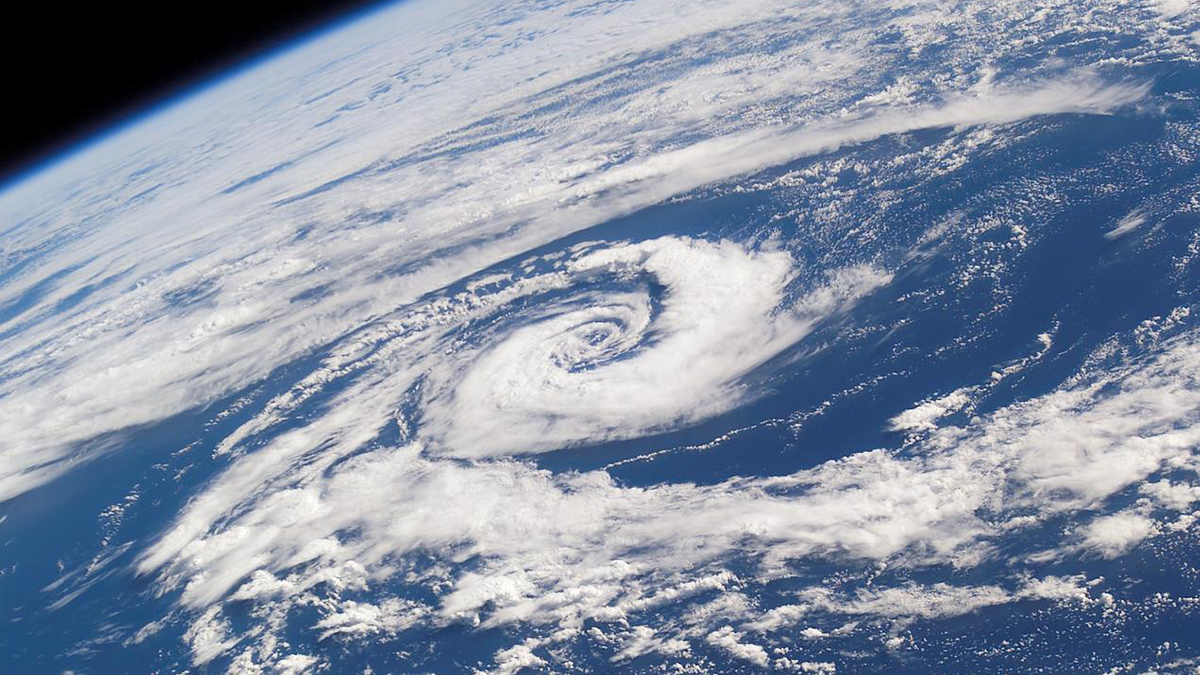
The All-In-One Cyclone Identification Framework
Researchers present a new framework for global detection and classification of all low-pressure systems.
Asian Megadeltas: Tackling Coastal Flooding Challenges
Integrating scientific insights into current actions is crucial for steering future research directions and underpinning informed management of coastal flooding in Asian deltas.
Using Satellite Data for More Effective Disaster Response
Satellite data play a crucial role in disaster assessment and response. Meeting expanding demand requires not only accelerated data processing but increased collaboration with responders.