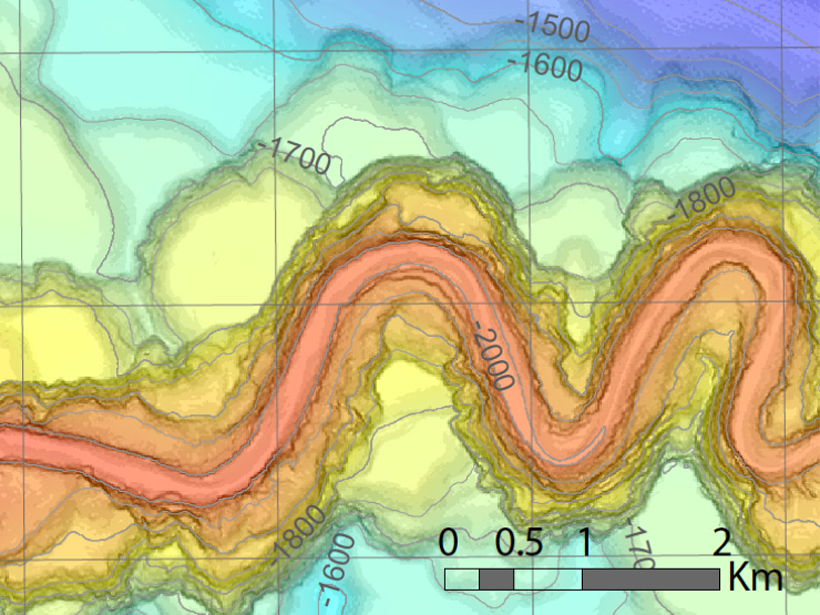
The first field measurements of turbidity currents flowing around submarine channel bends indicate spiral flow plays a key role in keeping sediment suspended for hundreds of kilometers.
sediments
Tracking Deep-Earth Processes from Rapid Topographic Changes
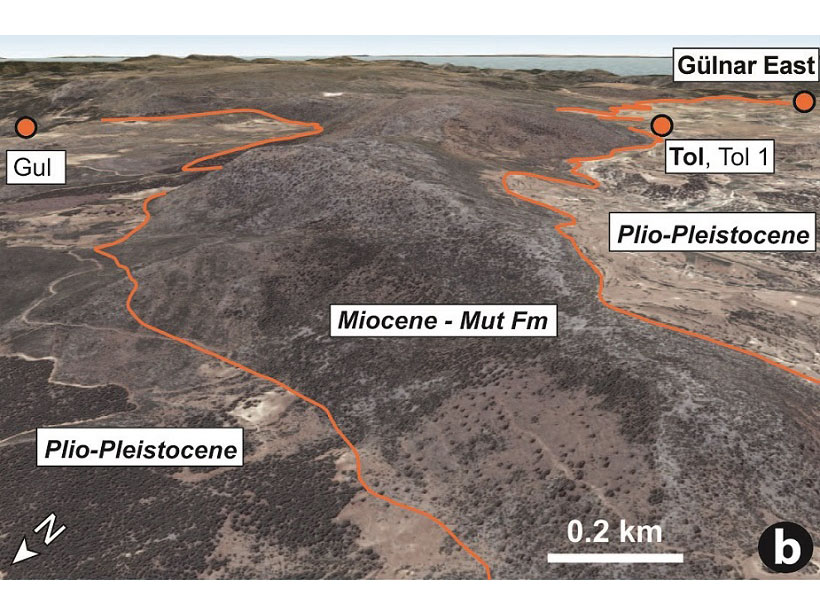
Rapid elevation-rise in Turkey, tracked by marine sediments that now sit at 1.5 km in elevation, is linked to deep-Earth processes that can explain short-lived, extreme rates of topographic change.
Untangling Sediment Transport Through River Networks
A stochastic sediment routing model for river networks is inverted to determine sediment source areas based on point observations of grain size and sediment flux at the basin outlet.
Accounting for the Missing Silica in the Marine Sediment Cycle
Cosmogenic silicon-based estimates of the amount of biogenic silica stored in clays along continental margins could explain the large discrepancy in the nutrient’s global marine budget.
Nonflood Flow May Be Major Driver of Delta Growth
Plants and fluctuating river flow work together to balance vertical sediment buildup with sediment delivery to the delta’s edge.
Church Receives 2017 G. K. Gilbert Award
Michael Church will receive the 2017 G. K. Gilbert Award in Surface Processes at the 2017 American Geophysical Union Fall Meeting, to be held 11–15 December in New Orleans, La. The award recognizes a scientist who has made “a single significant advance or sustained significant contributions to the field of Earth and planetary surface processes” and “also promoted an environment of unselfish cooperation in research and the inclusion of young scientists into the field.”
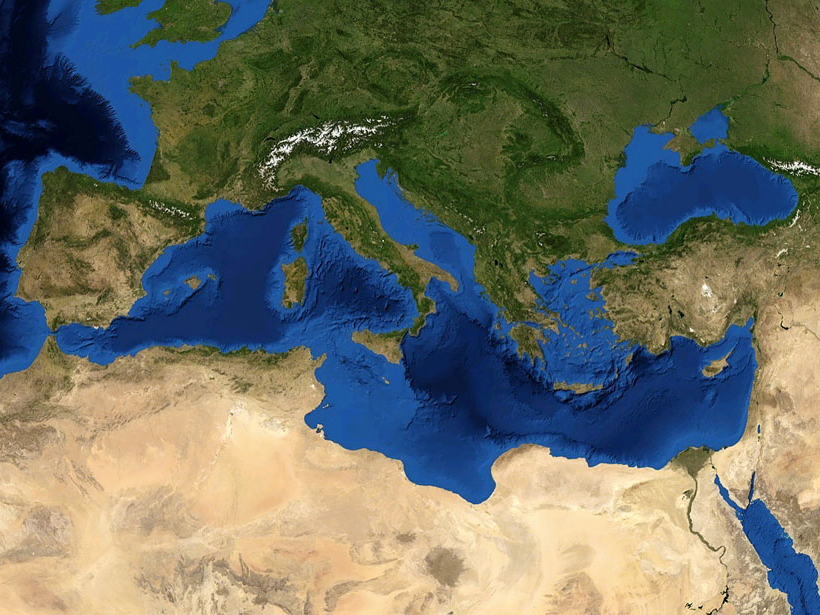
Storms May Have Produced Most Mediterranean “Tsunami” Deposits
A new analysis reveals that nearly all of the region’s sedimentary evidence ascribed to tsunamis, which dates back 4,500 years, corresponds to periods of heightened storminess.
Caribbean Sediment Traced to 1755 Portuguese Quake and Tsunami
Archaeologists digging in Martinique chanced upon the first tsunami deposit from the earthquake found in the New World. The tsunami left a strong trace, it seems, because the wave went up a river.
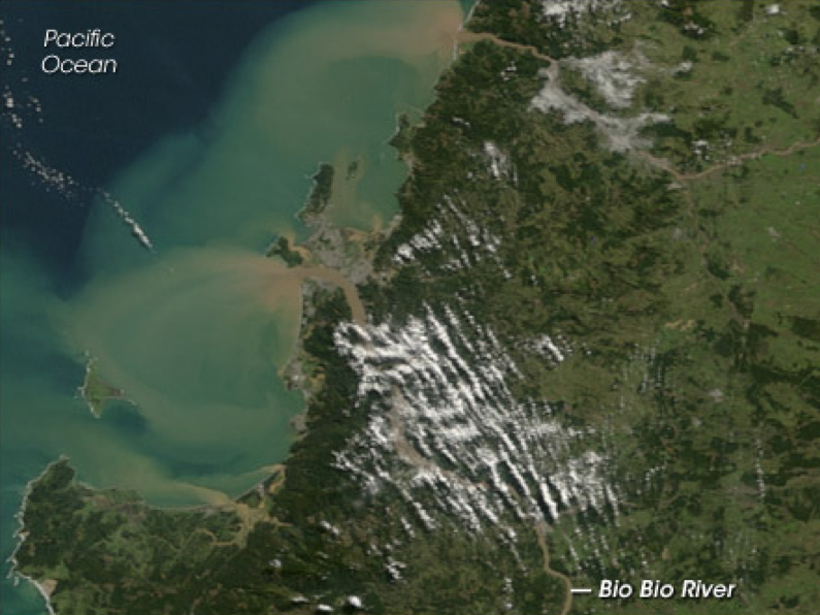
Tracing Land to Ocean River Transport with Cosmogenic Isotopes
Beryllium stored in marine sediments can help scientists study erosion and other environmental changes.
New Baseline for Understanding Arctic Oxygen and Nutrient Fluxes
Significant spatial and temporal patterns emerge from the first pan-Arctic comparison of oxygen demand in marine sediments.