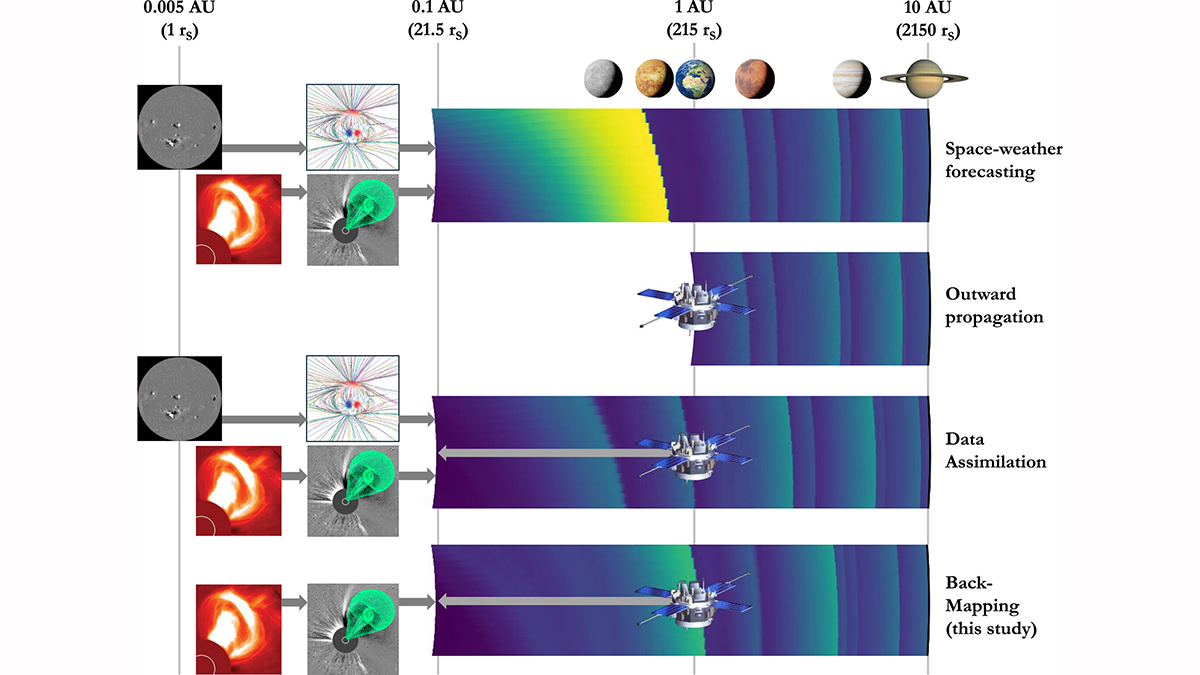
A new method shows how solar wind measurements at Earth can be used to define initial conditions for solar wind models to reduce their need for solar magnetic maps and decrease their uncertainty.
solar wind
Magnetic “Switchback” Detected near Earth for First Time
Until recently, this type of zigzag shape—formed by energetic rearrangement of magnetic field lines—had been seen only near the Sun.
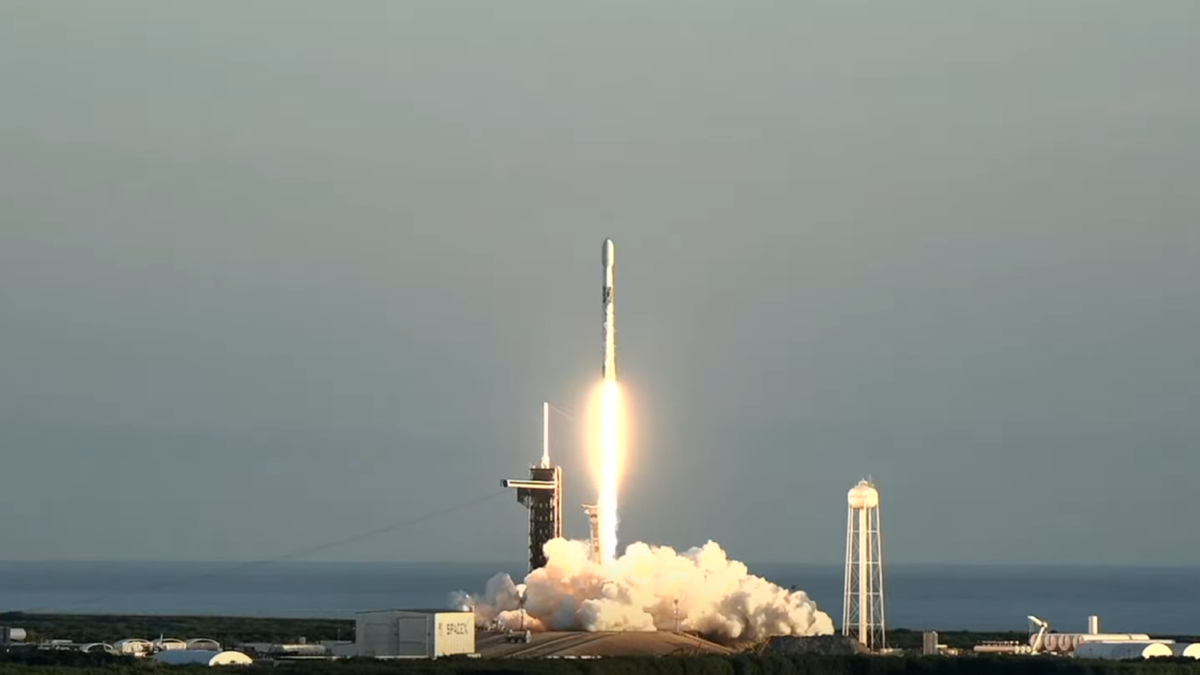
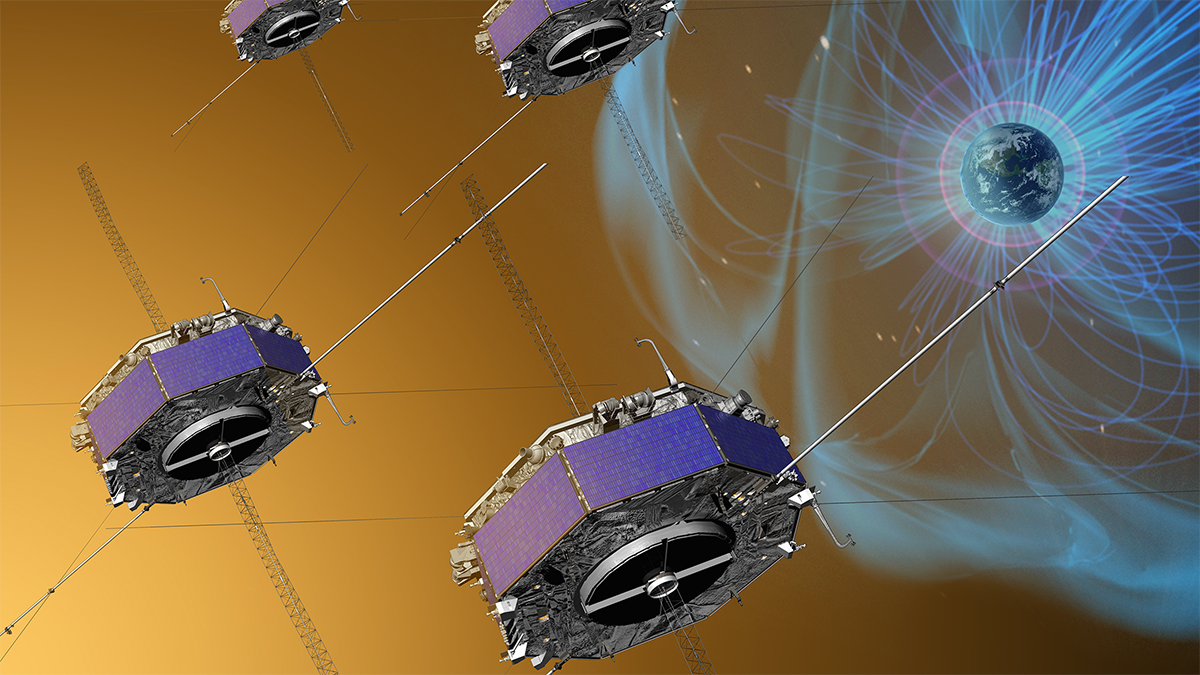
Trio of Space Weather Satellites Take Flight
These three satellites will that study the solar wind and its impacts.
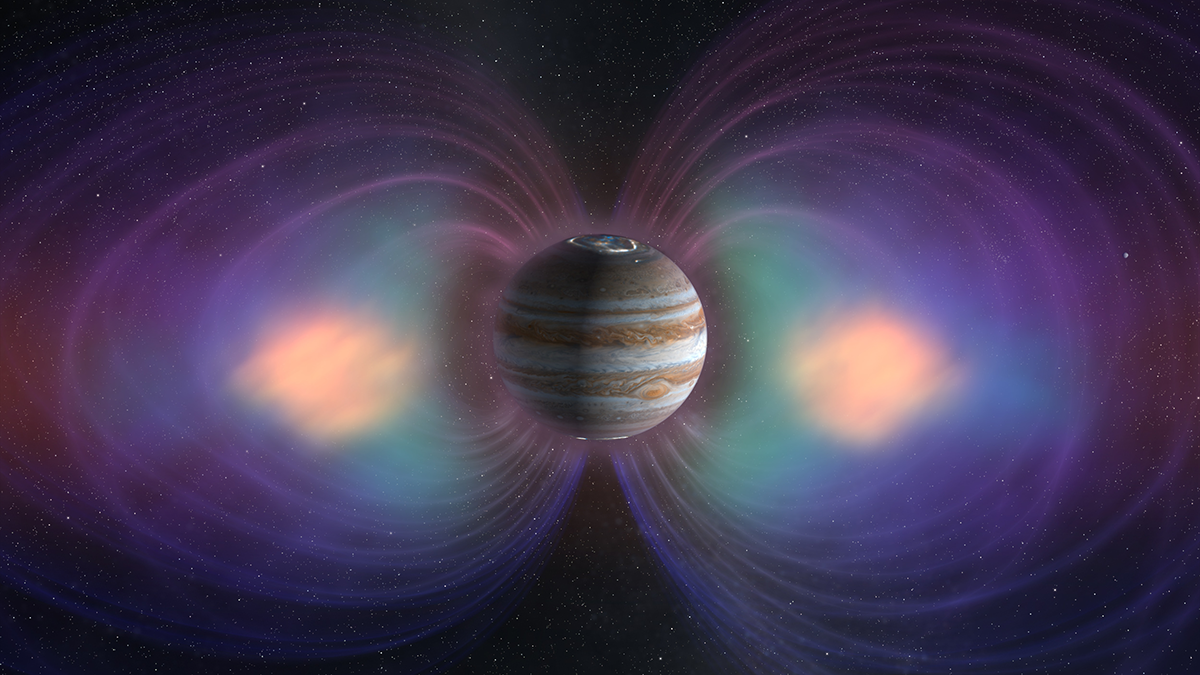
A Solar Wind Squeeze May Have Strengthened Jovian Aurorae
Juno spacecraft data suggest an extreme compression of the planet’s magnetosphere in December 2022, caused by the solar wind, briefly brightened the ultraviolet light displays.
Why Subsequent ICMEs are More Geoeffective
A new study demonstrates how an interplanetary coronal mass ejection (ICME) clears the path for following transients and explains why subsequent ICMEs are more geoeffective.
U.K. Space Weather Prediction System Goes Operational
Officials now have access to a suite of models they can use to head off damage to critical infrastructure.
Heating Mechanism at Earth’s Bow Shock Depends on Shock Speed
A new technique shows that the dominance of gradual versus chaotic electron heating processes at Earth’s bow shock is controlled by how fast the shock is moving.
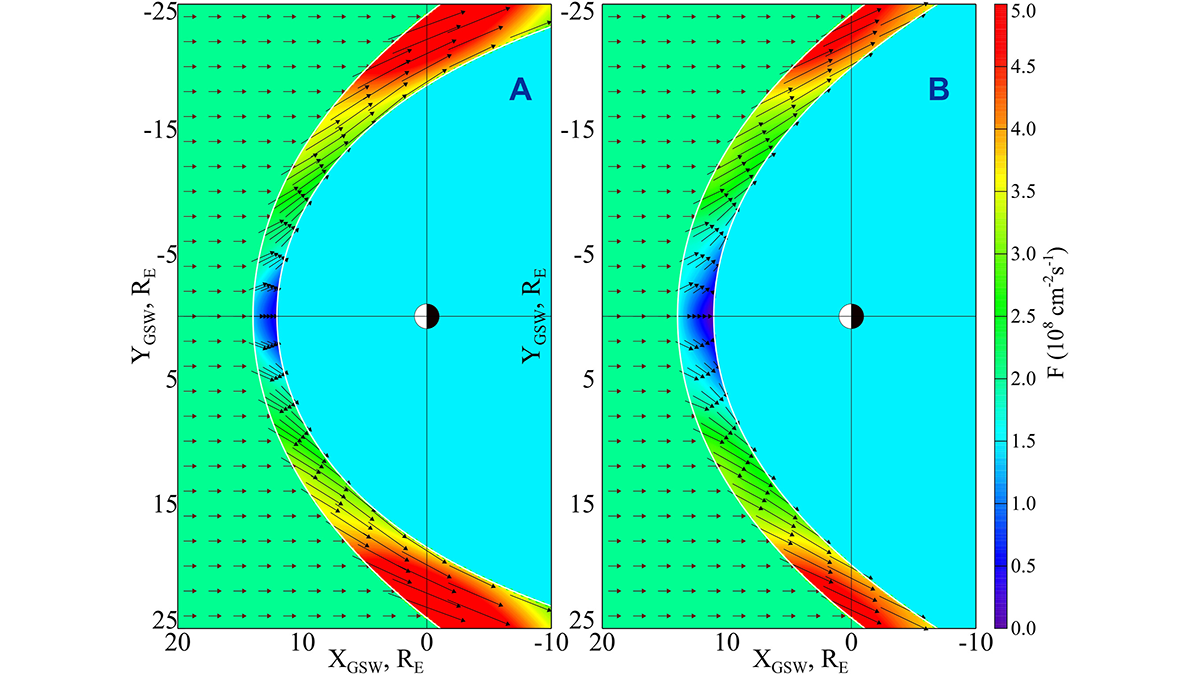
New Empirical Model of the Flux in the Magnetosheath
A new study presents a model that reconstructs the plasma flux in the Earth’s magnetosheath.
Unusual Occurrence of STEVE: An Aurora-Like Glow
STEVE is a mysterious purple-white arc near the aurora, typically seen after space disturbances called substorms. A new study reveals a rare STEVE event without a substorm, prompting questions about its origin.
Blasts from the Past: New Insights from Old Space Storms
Reassessment and comparison of past space weather events highlight the potential for Earth to experience destructive geomagnetic disturbances.