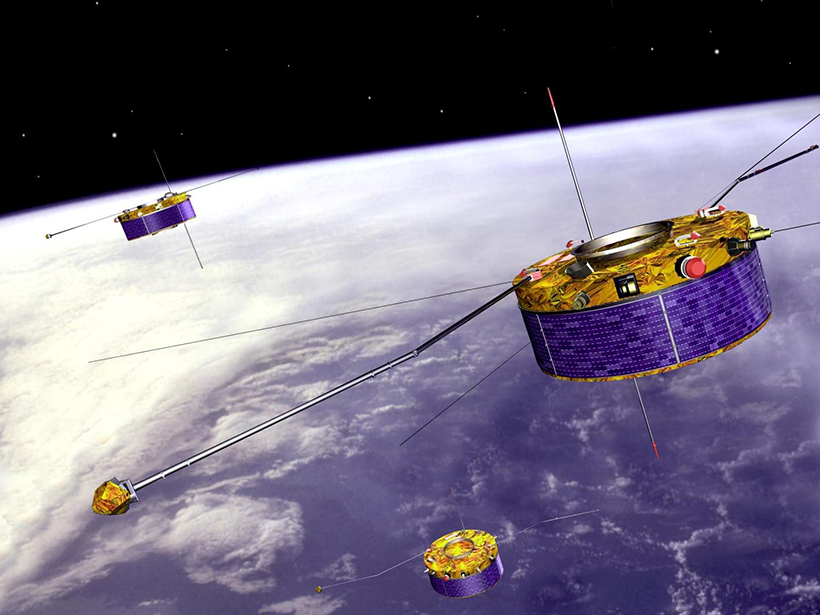
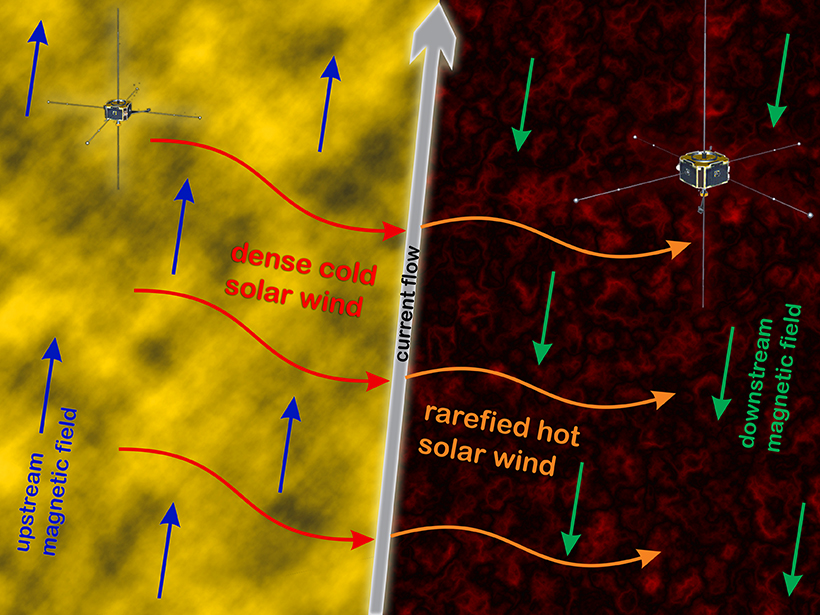
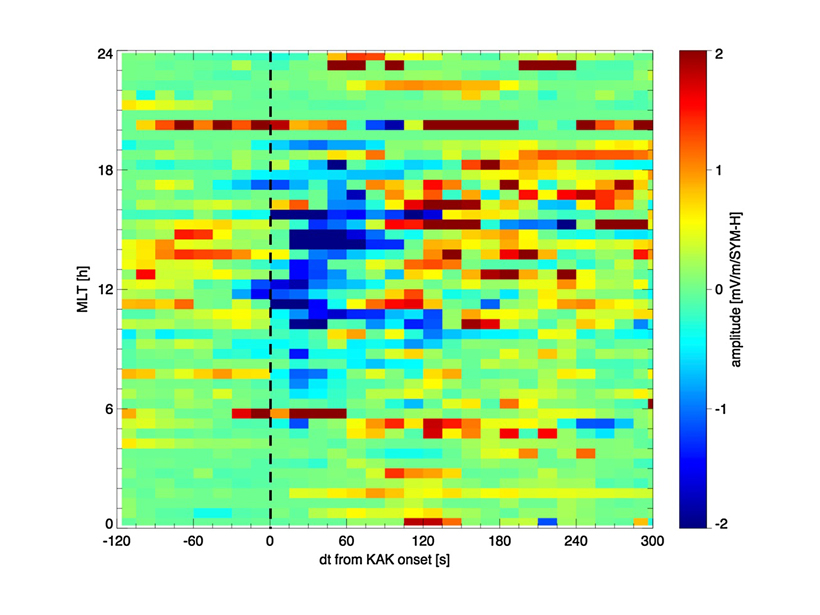
Sometimes the conditions in the solar wind can change dramatically over short distances. Satellite observations of these features show that they’re more complex than previously thought.
solar wind
John T. “Jack” Gosling (1938–2018)
This prolific researcher helped us understand the interactions of the solar wind and coronal mass ejections with Earth’s magnetic field.
How Space Storms Affect the Satellite Superhighway
A powerful numerical model reveals how space weather disturbs magnetic field at geosynchronous orbit.
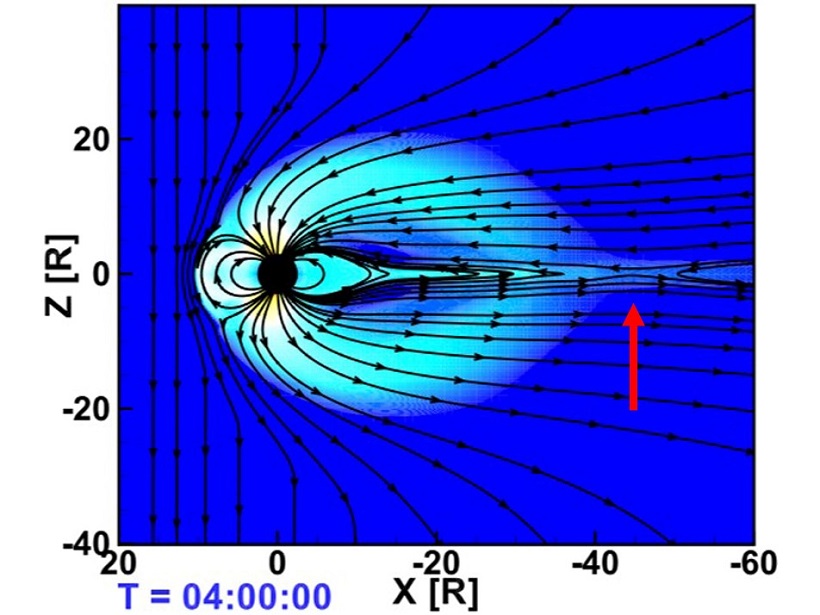
Evidence That Earth’s Forehead Controls the Wagging of its Tail
Yes, Earth has a tail, a magnetotail, and there is debate about how much Earth’s upper atmosphere plays a role in the controlling the dynamics of this region of space.
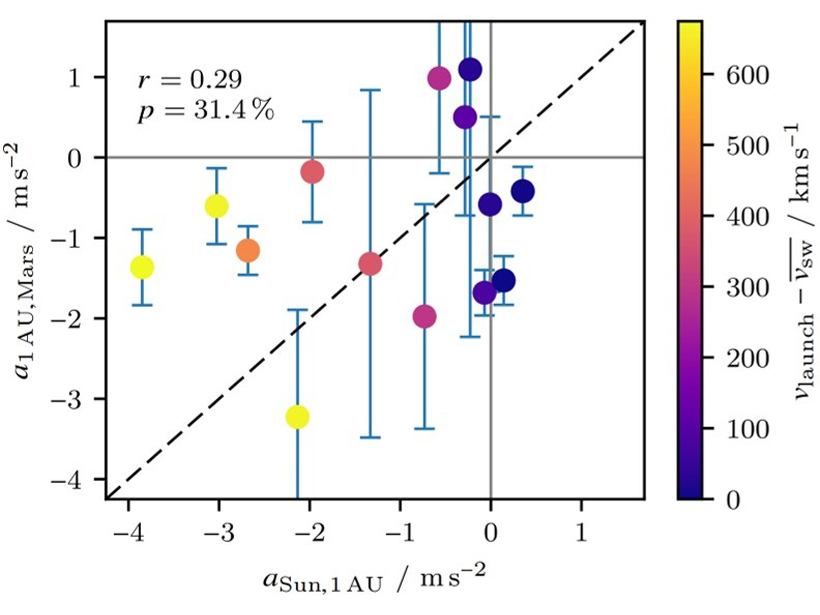
Fast CMEs Continue to Decelerate in the Outer Heliosphere
Most fast coronal mass ejections will be decelerated into ambient solar wind quickly in the inner heliosphere, but some of them continue the deceleration with an even larger amplitude beyond 1 AU.
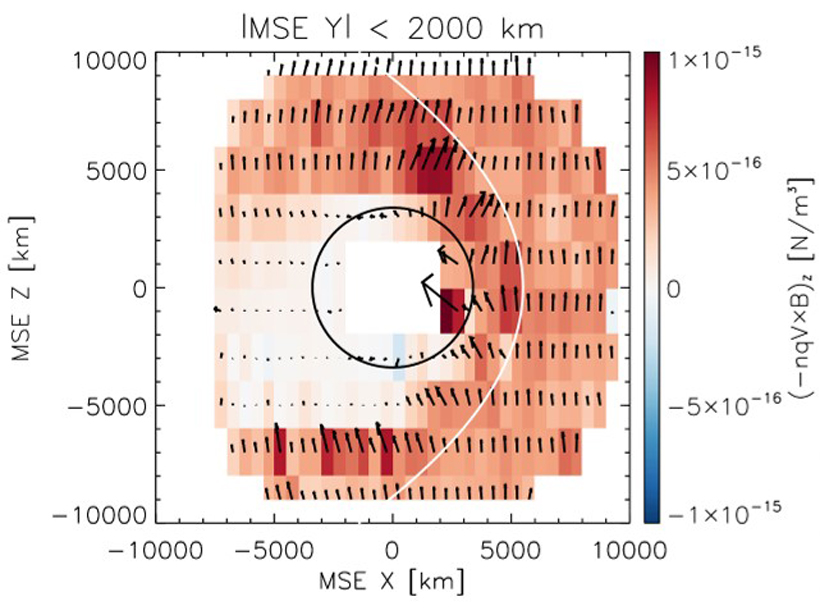
Where the Solar Wind Meets Mars
A comprehensive look at how the solar wind is diverted around Mars, including the relative strength of the three biggest forces at work in this region.
A Better Way to Predict Space Storms
A new model of solar winds could reduce false alarms.
Solar Wind Sets the Magnetosphere Ringing
A combination of data from satellites and ground-based instruments gives new insight into solar wind-magnetosphere-ionosphere interactions.
Jets of Ionospheric Cold Plasma Discovered at the Magnetopause
The lower-energy particles may play a larger role in magnetic reconnection than previously believed, influencing space weather near Earth.
How Earth’s Outer Radiation Belts Lose Their Electrons
A new analysis of three space storms reveals the mechanisms of particle loss from the Van Allen belts.