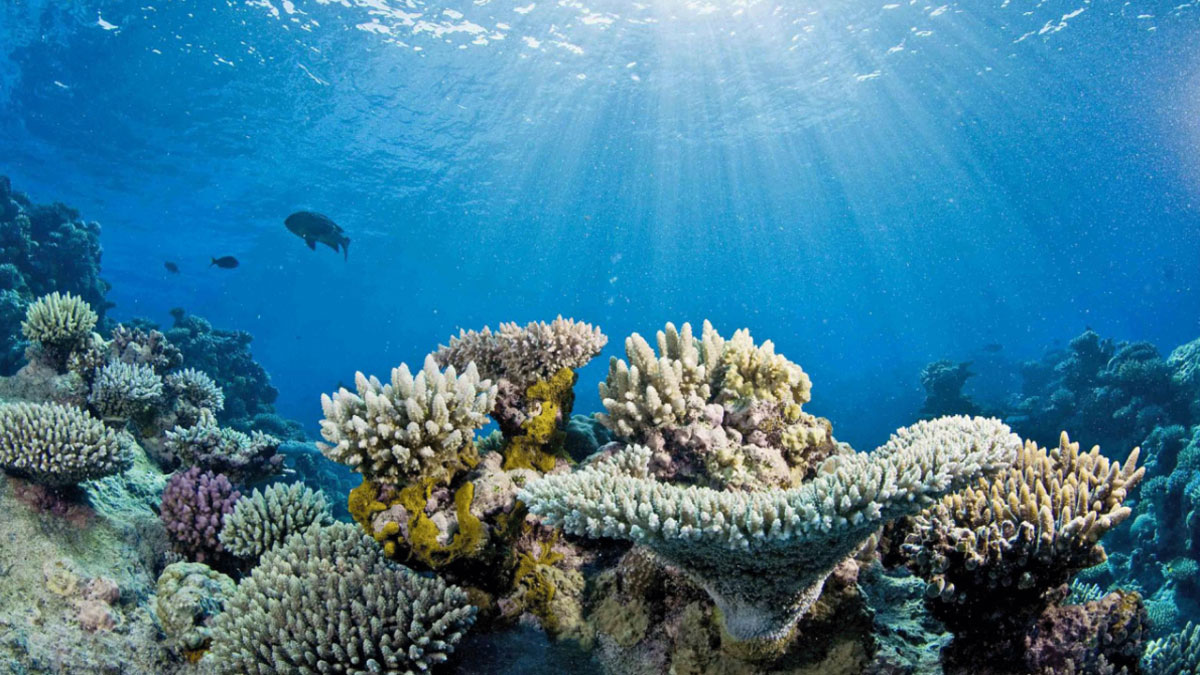
New research indicates a well-studied form of climate intervention might at least buy time for many at-risk reefs.
stratosphere
Some Summer Storms Spit Sooty Particles into the Stratosphere
Earth’s typically pristine stratosphere is filling with particles from wildfires and additional moisture due to strong convective storms.
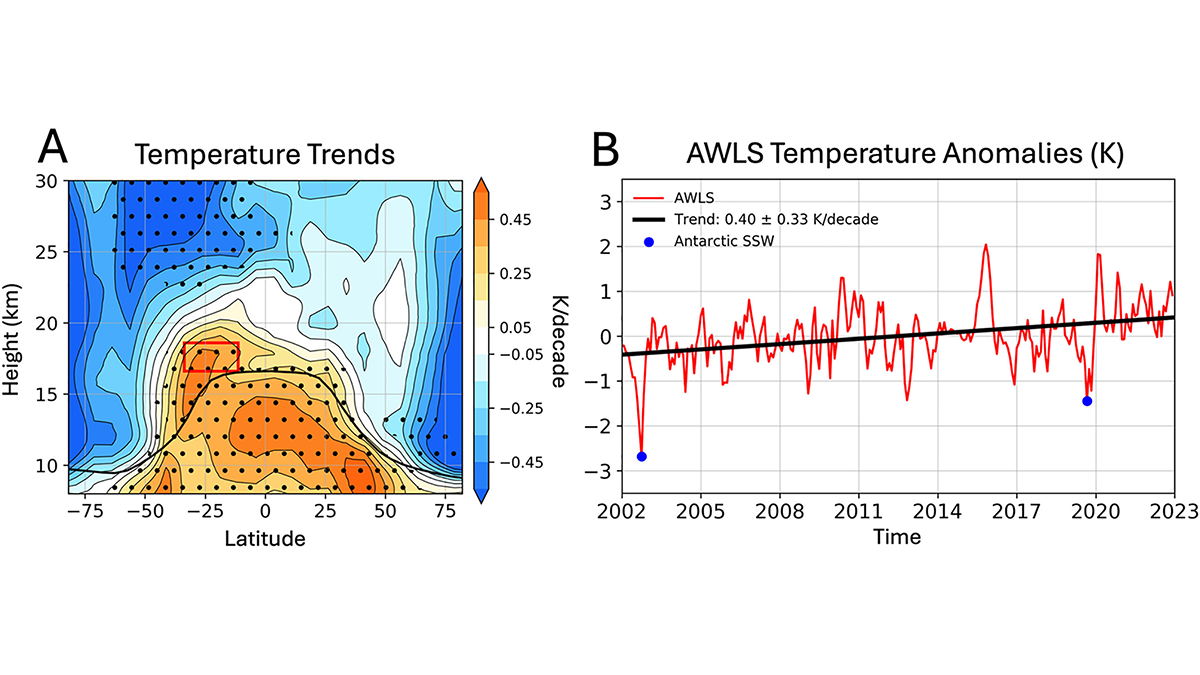
Southern Hemisphere Subtropical Lower Stratosphere is Warming
Warming of the Southern Hemisphere (SH) subtropical lower stratosphere is due to slowing of Brewer-Dobson Circulation, thus cooling the Antarctic lower stratosphere and masking anticipated ozone recovery.
An Air Parcel’s Journey Through the Stratosphere
The “age of stratospheric air” measures the speed of the global transport circulation in the stratosphere, which is crucial for understanding the distribution of important trace gases, like ozone.
Better Monitoring is Needed for Climate Change in the Upper Atmosphere
A new commentary calls for a better understanding of the impacts of climate change and anthropogenic emissions on long-term trends of the middle and upper atmosphere through enhanced observations and monitoring capabilities.
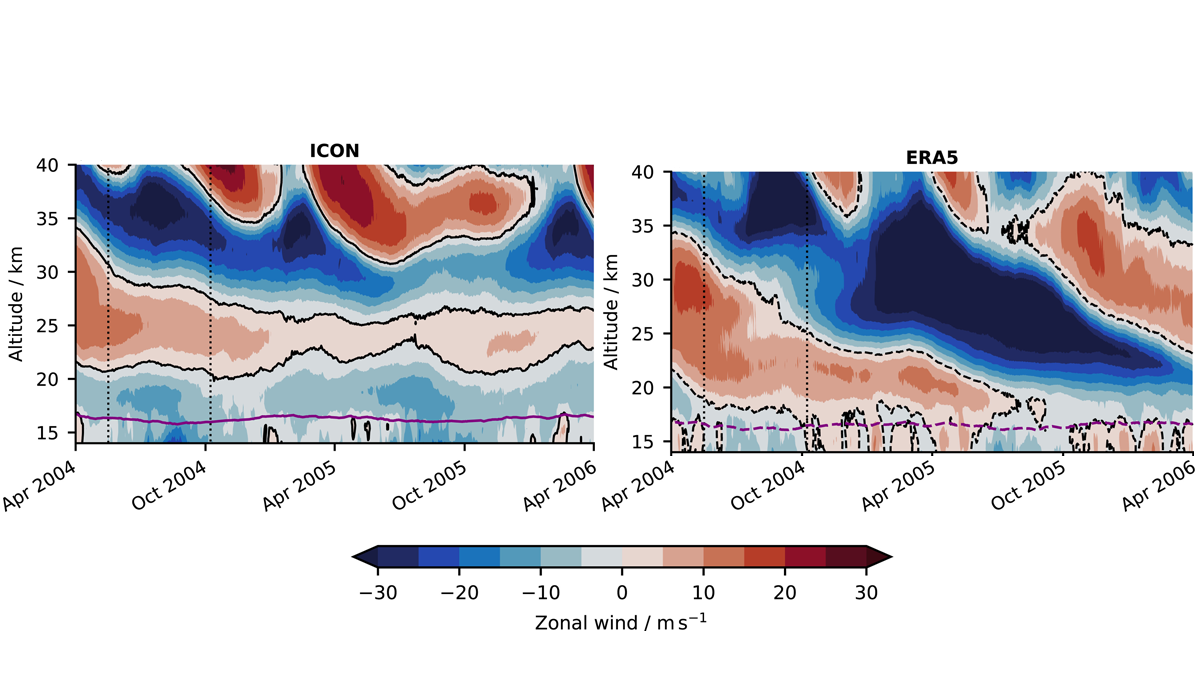
Simulating a Unique Wind System in a Kilometer-Scale Model
A new study shows that a kilometer-scale model can directly simulate aspects of the Quasi-Biennial Oscillation.
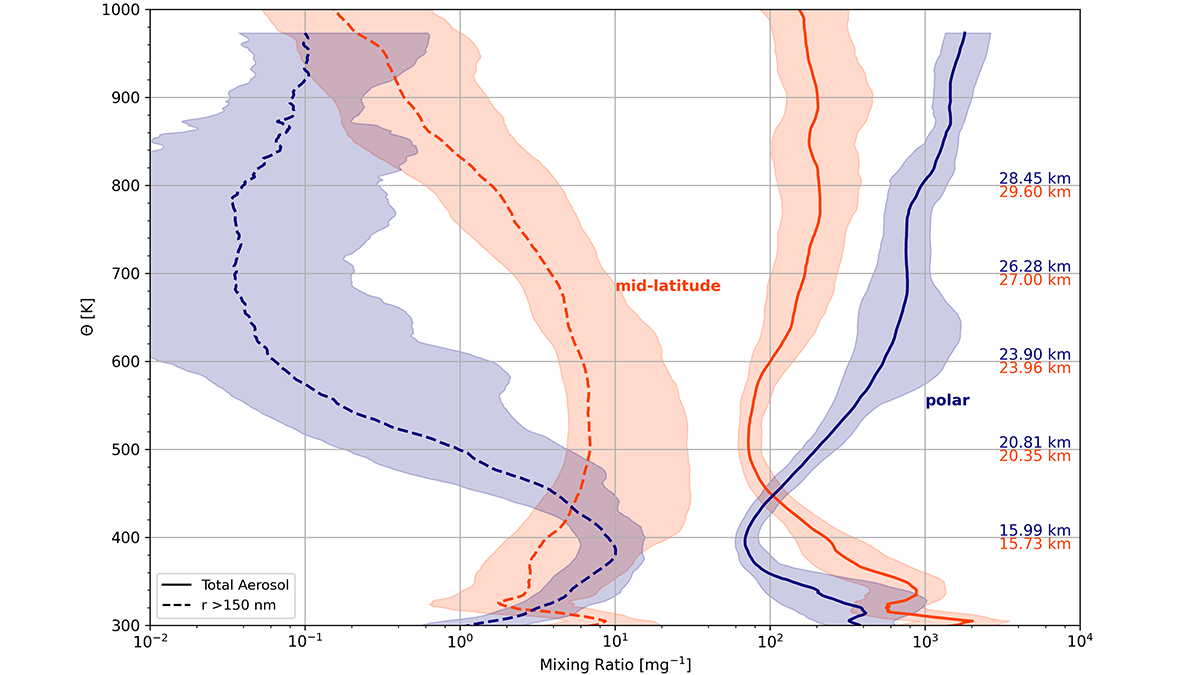
Five Decades of Stratospheric Aerosols from Balloon Measurements
Long-term global measurements of stratospheric aerosols reveal climatological structures and processes controlling new particle formation.
Atmospheric Effects of Hunga Tonga Eruption Lingered for Years
A new study builds on previous research of the underwater volcano’s effects on the climate.
What Happens in the Troposphere Doesn’t Stay in the Troposphere
A new study suggests that spillover of tropospheric ozone is affecting measurements of stratospheric ozone recovery more than previously realized.
Uncertainty Abounds in Seeding the Sky to Fight Climate Change
Some scientists have suggested injecting solid particles such as alumina, calcite, or even diamonds into the atmosphere to temporarily limit climate warming. But new research shows there are still big unknowns.