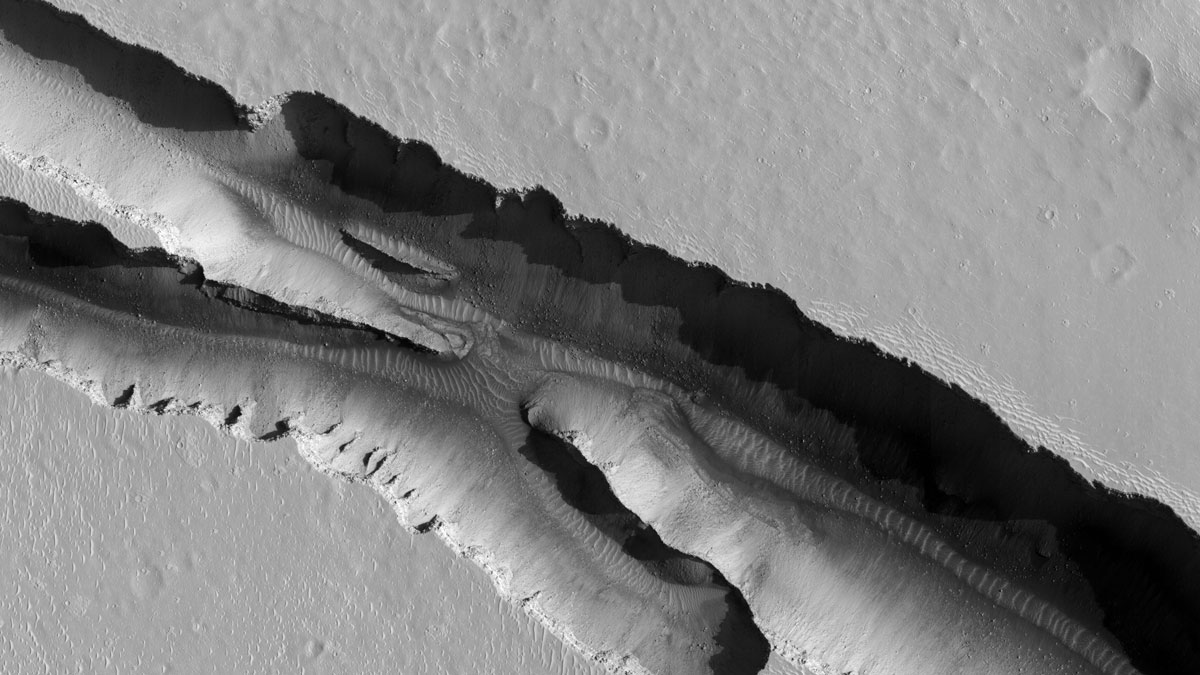
InSight data hint that shifting carbon dioxide ice loads, illumination changes, or solar tides could drive an uptick in marsquakes during northern summer—a “marsquake season.”
unsolved mysteries
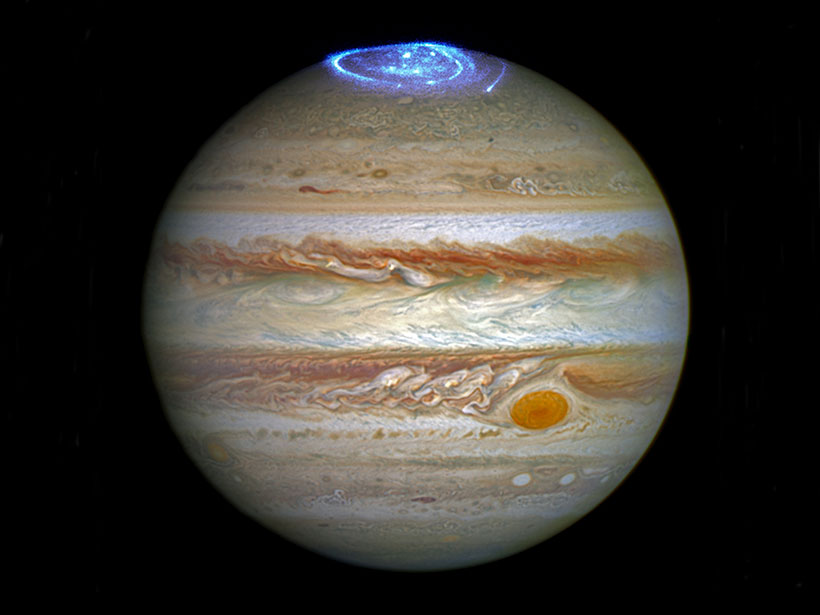
Could Low-Altitude Reconnection Power Jupiter’s Polar Aurorae?
Magnetic reconnection events less than 2 Jovian radii above the planet’s cloud tops could explain why Juno has yet to observe a source for Jupiter’s polar aurore.
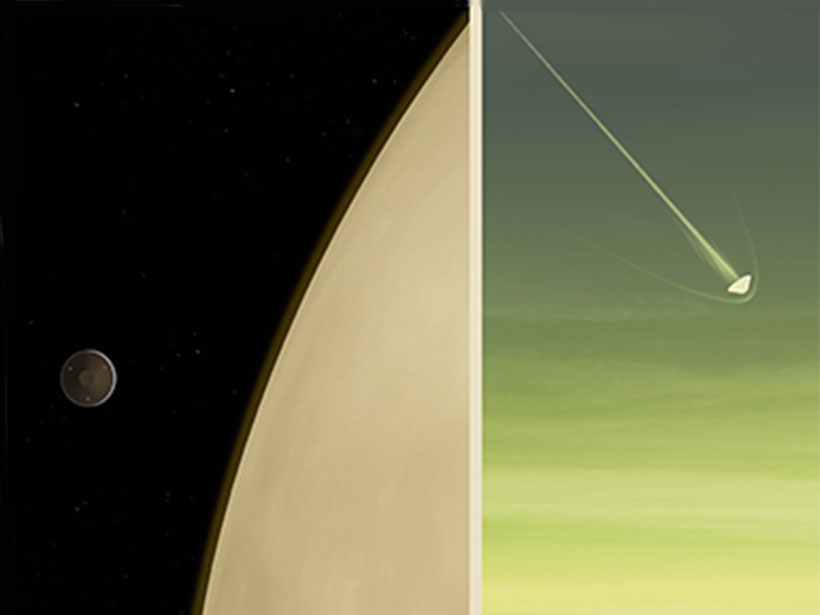
Mission to Venus Could Help Solve an Atmospheric Mystery
NASA’s recently announced DAVINCI+ mission to Venus will probe the planet’s atmosphere, hoping to shed light on the unknown dark patches that surround the planet.
Satellites Allow Scientists to Dive into Milky Seas
Satellites may finally be able to report the fleeting phenomena of milky seas in near-real time, allowing researchers to potentially study an ocean mystery that has survived more than 2 centuries.
Earth’s Continents Share an Ancient Crustal Ancestor
How did today’s continents come to be? Geological sleuths found clues in grains of sand.
Predictive Forensics Helps Determine Where Soil Samples Came From
Researchers deploy geochemical analyses to narrow down the search area for a soil sample’s site of origin—an approach that could prove useful to law enforcement.
Exploring the Dramatic Shift in Ice Age Duration
Scientists are still seeking an explanation for the Mid-Pleistocene Transition when ice ages became longer in duration and exploring what it may mean for future climate change.
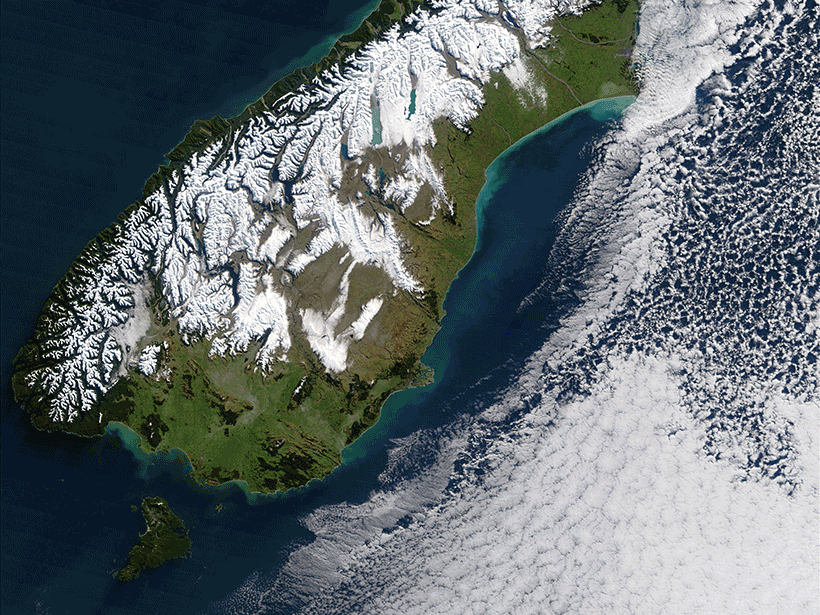
Subduction Initiation May Depend on a Tectonic Plate’s History
New seismic imaging study of the Puysegur Trench aims to solve one of the last major questions in plate tectonics.
Convective Transport Explains “Missing” Ice near the Tropical Tropopause
Spaceborne lidar shows that more ice than expected is leaving the tropical tropopause layer in the atmosphere.