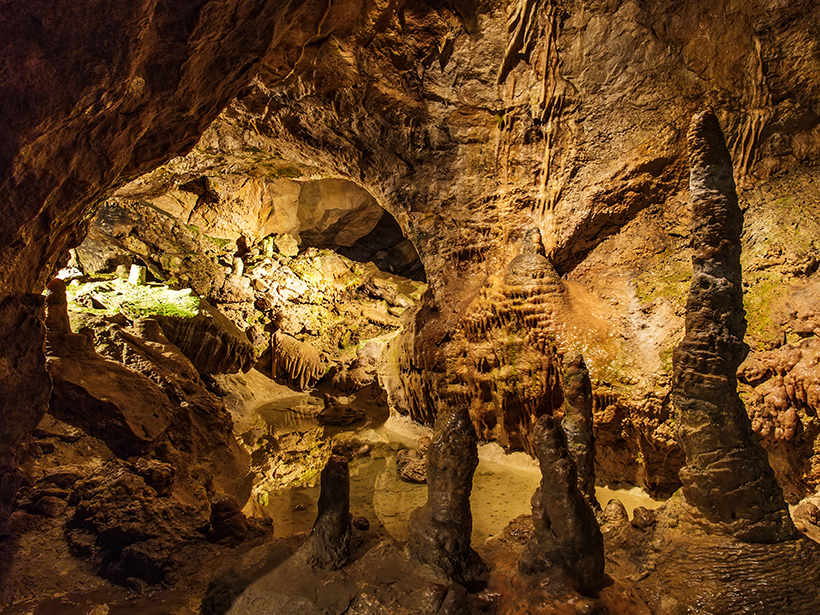
Chemical measurements of a stalagmite from a cave in Iran reveal a large uptick in dust activity in northern Mesopotamia roughly 4,200 years ago, coincident with the decline of the Akkadian Empire.
unsolved mysteries
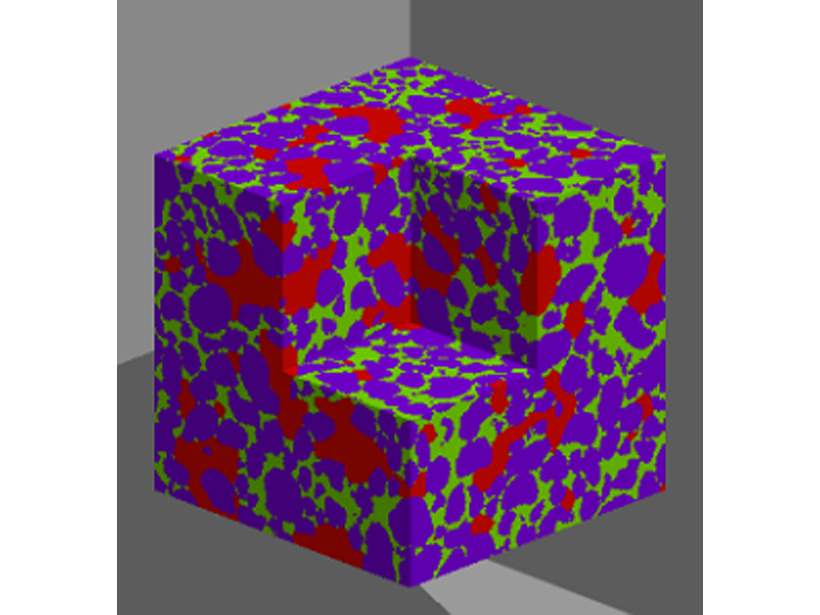
Peering into Pores: What Happens When Water Meets Soil?
New research sheds light on the long-standing puzzle of how and why soil water density differs from free water density.
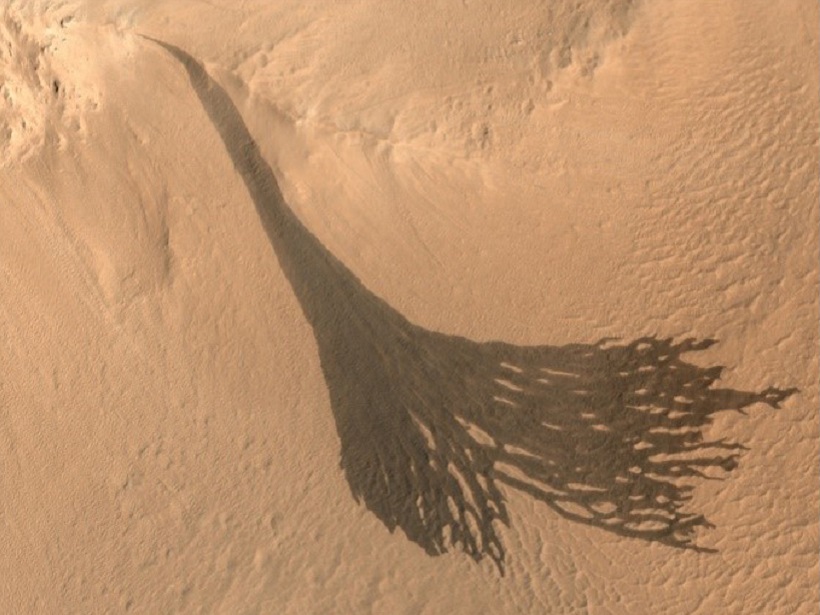
Revisiting Enigmatic Martian Slope Streaks
Slope streaks of different sizes and shapes are a common feature on the surface of Mars, but scientists disagree about the mechanisms for their formation and development.
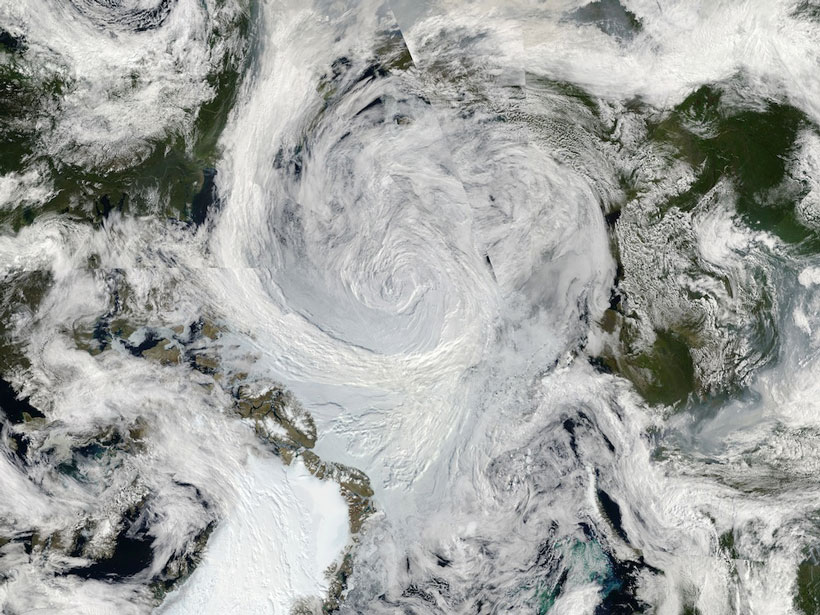
How Arctic Cyclones Change the Sea Ice
Whirlwinds disrupt the sea ice in the Arctic Ocean. Scientists are now beginning to understand how.
Microbes Rain Down from Above, to the Tune of the Seasons
Every time snow or rain falls, it brings with it microbes from high in the atmosphere. Could those microbes have a seasonal signal, just like the plants on the land below?
Investigating the Northern Indian Ocean’s Puzzling Geodynamics
International Ocean Discovery Program (IODP) Proposal Nurturing Workshop on Indian Ocean; Goa, India, 17–18 September 2018
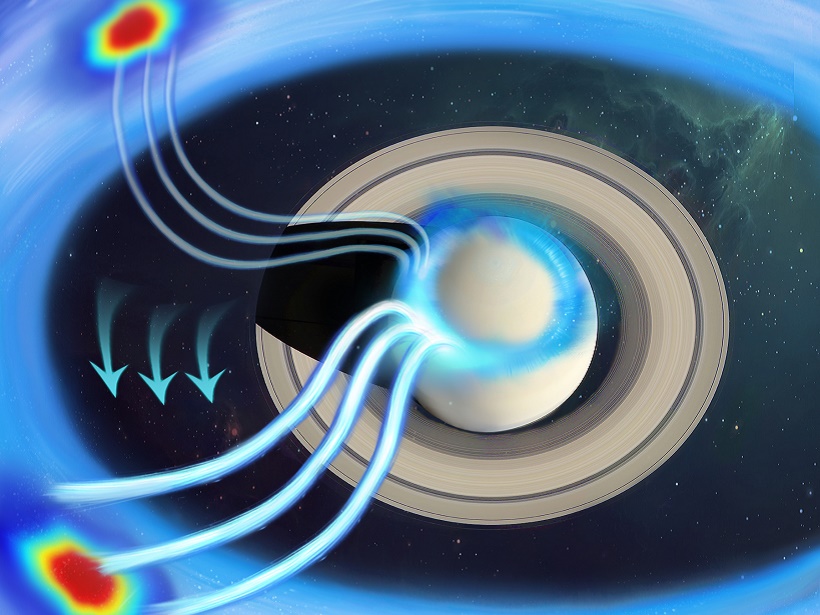
Cassini Reveals a Missing Link on Saturn’s Rotating Aurora
The bright aurorae dancing in the sky are produced by charged particles traveling along the magnetic field lines from tens of planetary radii. By why do aurorae rotate at Saturn but not at Earth?
What Makes a Terrestrial Gamma-Ray Flash in Thunderclouds?
Two lightning flashes were observed in the same location: One produced a bright gamma-ray flash with about 1000 counts per millisecond, but the other did not.
Exploring the Unknown of the Ross Sea in Sea Ice–Free Conditions
A team of polar scientists aboard the OGS Explora, cruising in rare ice-free conditions, discovered new evidence of ancient and modern-day ice sheet sensitivity to climatic fluctuations.
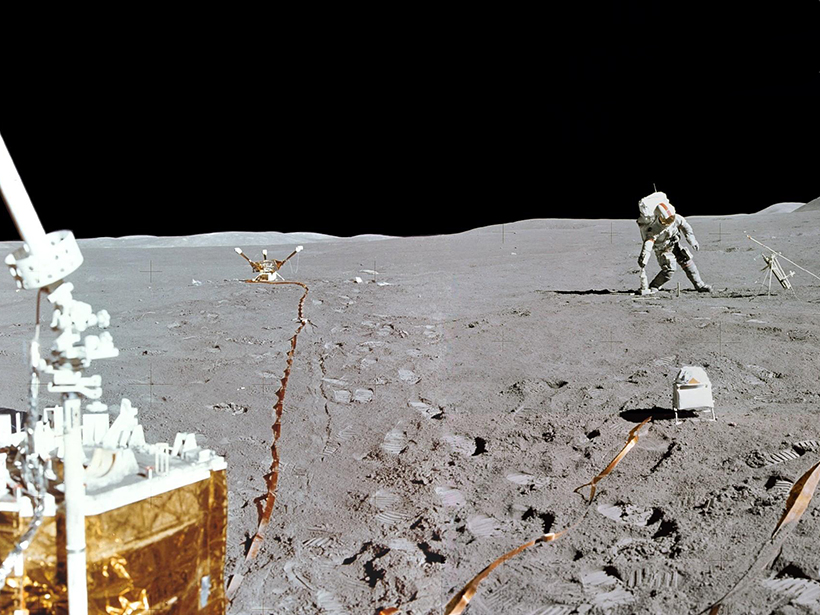
The Case of the Missing Lunar Heat Flow Data Is Finally Solved
Decades-old data analyzed for the first time suggest that astronauts’ disturbance of the Moon surface increased solar heat intake, warming the ground below.